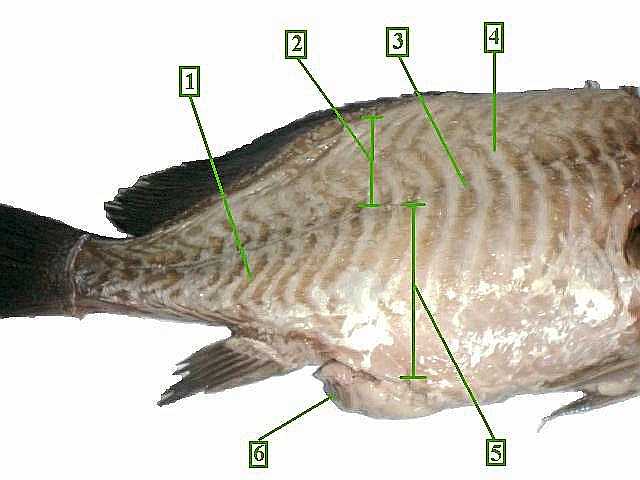
There are three distinct types of myomeres: amphioxine, cyclostomine and piscine. All have in common the function of bending their possessors' bodies from side to side to provide locomotor force. In all cases pull is applied obliquely to the long axis of the body.
What are myomeres and how do they work?
Since myomeres are composed of multinucleated myofibers (contractile cells), force can be generated via muscle contraction that gets transmitted by the intricate connective tissue (myosepta) network. The folded shape of each myomere as “V” or “W” shaped extends over various axial segments, allowing fibers control over a large amount of the body.
What is the function of myomeres in chordates?
Specifically, three types of myomeres in fish-like chordates include amphioexine (lancelet), cyclostomine (eel), and piscine (fish). A common function shared by all of these is that they function to flex the body laterally into concavity to provide force for locomotion.
What is the shape of myomere?
The folded shape of each myomere as “V” or “W” shaped extends over various axial segments, allowing fibers control over a large amount of the body. Specifically, myomeres are overlapping cones bound by connective tissue.
What is a mymyomere count?
Myomere counts are sometimes used for identifying specimens, since their number corresponds to the number of vertebrae in the adults. Location varies, with some species containing these only near the tails, while some have them located near the scapular or pelvic girdles.
What is the advantage of myomeres?
Each myomere covers several vertebral segments and succeeding myomeres overlap. This allows the bending to progress smoothly along the body as each myomere affects not only its own section of the body but also those of its neighbours.
What are myomeres and Myosepta?
bundles of muscle fibres called myomeres. The myomeres are separated by thin horizontal (myosepta) and vertical (myocommata) layers of connective tissue. The unique structure and thin connective tissue sheaths of fish muscle give the meat its characteristic soft, flaky texture.
What is Myocomata?
my·o·com·ma·ta (mī'ō-kom'ă, -kom'ă-tă), The connective tissue septum separating adjacent myotomes. Synonym(s): myoseptum. [myo- + G. komma, a coin or the stamp of a coin]
What is myotome in fish?
The study focused on the myotome (a group of muscles served by a spinal nerve root) that makes up most of the fish body. These fish muscles power the fish's side-to-side swimming motion and the chevron pattern is thought to increase swimming efficiency.
What is Myofibrillar?
Myofibrils are bundles of protein filaments that contain the contractile elements of the cardiomyocyte, that is, the machinery or motor that drives contraction and relaxation.
What is the function of the adductor Mandibulae muscle?
The adductor mandibulae, a large muscle below the spiracle, closes the jaw. The intermandibularius is on the ventral surface, posterior to the jaw. It originates on the Mechel's cartilage (lower jaw) and inserts on the central raphe. Its function is to elevate the floor of the mouth for swallowing.
What are myomeres for vertebrates?
Myomeres compose most of the lateral musculature and provide propulsive force to travel along the line of travel. In this sense, they cause flexion to either side in order to produce locomotor force. Myomeres attach to centra of vertebrae, and neural and haemal spines.
Where is a dorsal fin?
The dorsal fin is located on the top of a fish (as well as some marine mammals). Predominately, the fin is used to stabilize fish in the water and help direct the fish through turns and stops.
What is the horizontal septum?
The well-known 'W'-shaped myosepta of fishes are divided into an epaxial and hypaxial part by a horizontal sheet of connective tissue, the horizontal septum (HS) which is generally regarded as standard part of their segmented musculature (e.g. Liem et al., 2001).
Which animals show myotomes?
Myotome is a muscle which shows in the fishes.Myotome muscles can be seen in the both sides of the vertebral column of the body of the fishes.The contraction and relaxation of the V-shaped muscle help in the horizontal undulation and propulsion of the body of the fishes.More items...•
What is the function of the muscle in a fish?
Fish have a system of muscles for movement. Muscle contractions ripple through the body in waves from head to tail. The contractions whip the tail fin against the water to propel the fish through the water.
What myotome is knee flexion?
L1/L2: Hip Flexion. L3: Knee extension. L4: Ankle dorsi-flexion.
How are myomeres separated?
The myomeres are separated from adjacent myomere by connective tissues and most easily seen in larval fishes or in the olm. Myomere counts are sometimes used for identifying specimens, since their number corresponds to the number of vertebrae in the adults.
What is the block of skeletal muscle tissue found commonly in chordates?
Myomere. Myomere are the blocks of skeletal muscle tissue found commonly in chordates. They are commonly zig-zag, "W" or "V"-shaped muscle fibers. The myomeres are separated from adjacent myomere by connective tissues and most easily seen in larval fishes or in the olm.
What is the shape of a fillet?
The fillet is made up of segmentally arranged structures called myotomes or myomeres, the shape of which varies along the length of the body. In three dimensions, the myomeres constitute a series of overlapping cones that are bounded by connective tissue sheets or myocommata called myosepta.
What is the muscular system of a fish?
The muscular system of “pacu” is characterized by W-shaped, piscine myomeres. As a rule, fish muscles are grouped according to their location and biochemical characteristics (Fig. 2.27 ). The epaxial and hypaxial myomeres practically form the entire musculature of a fish’s body.
What are the hypaxial muscles of a mudpuppy?
Hypaxial muscles of the mudpuppy: (a) flank muscles in lateral view, with deeper layers exposed in successive cut-outs of body wall; and (b) subvertebralis muscle, with body cavity opened. Other subdivisions of the hypaxial musculature are the subvertebralis and the rectus abdominis.
Why are the stomach and pyloric ceca not visible?
However, the stomach and the pyloric ceca are not very visible because the circumvolutions of the intestine overlap these structures ( Figs. 2.32 and 2.33 ). The topography of internal organs of hybrid Colossoma macropomum × P. mesopotamicus is very similar to that of parental species ( Ferreira et al., 2013 ).
What is the absence of a sternocleidomastoid muscle?
Unilateral absence of a sternocleidomastoid muscle is one cause of congenital torticollis. Absence of one pectoralis major muscle is part of the Poland anomaly. When innervation does not develop, as in the lower limbs in severe cases of myelomeningocele, muscles can fail to develop.
What is the extracellular matrix?
The extracellular matrix (ECM) in muscle has a complex organisation and is composed of collagen, non-collagenous glycoproteins and proteoglycans. Most of the collagen is located in the myocommata separating the individual myotomes.
What is white muscle?
White muscle is composed of fast contracting fibres that primarily rely on anaerobic metabolic pathways and are recruited during burst swimming ( Johnston et al., 1977 ). White or fast muscle fibres comprise the bulk of the edible portion of the fillet, 80–95% depending on species.
Locomotion
The myomeres described above usually make up the great bulk of the lateral musculature, and provide almost all the propulsive force. Other muscle systems or modifications in the trunk will be described briefly.
Muscle Development and Growth
The myomeres are composed of a series of overlapping cones and therefore a transverse section of the trunk will section several myotomes at different levels. The number and diameter of muscle fibers varies along the length of the body and in different regions of the cross-section (Fig. 1 ).
The biological basis of variability in the texture of fish flesh
The fillet is made up of segmentally arranged structures called myotomes or myomeres, the shape of which varies along the length of the body. In three dimensions, the myomeres constitute a series of overlapping cones that are bounded by connective tissue sheets or myocommata called myosepta.
Caecilians
Laurie J. Vitt, Janalee P. Caldwell, in Herpetology (Fourth Edition), 2014
A review of the fisheries, life history and stock structure of tropical tuna (skipjack Katsuwonus pelamis, yellowfin Thunnus albacares and bigeye Thunnus obesus) in the Indian Ocean
Iraide Artetxe-Arrate, ... Hilario Murua, in Advances in Marine Biology, 2021
The Mudpuppy
Gerardo De Iuliis PhD, Dino Pulerà MScBMC, CMI, in The Dissection of Vertebrates (Second Edition), 2011
Muscle Biopsy for Diagnosis of Neuromuscular and Metabolic Diseases
Harvey B. Sarnat, Stirling Carpenter, in Neuromuscular Disorders of Infancy, Childhood, and Adolescence (Second Edition), 2015