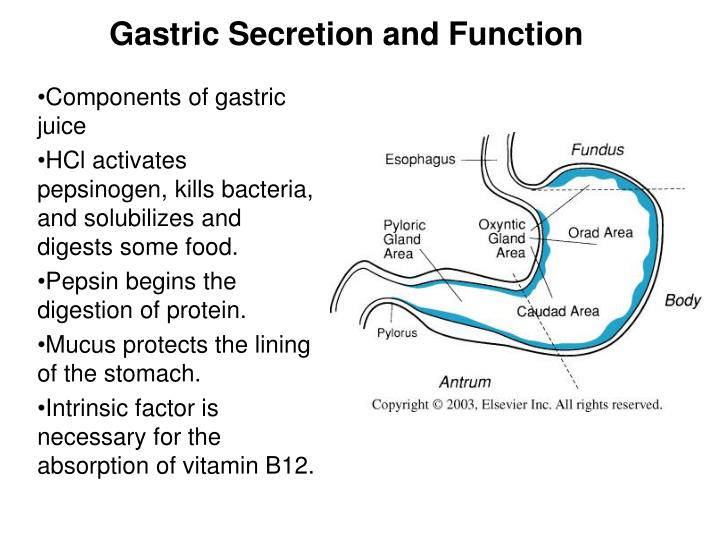
What does the fundus of the human stomach do?
- Enterochromaffin like cell (ECL cell) - they release serotonin and histamine. These cells store and release histamine when the pH of the stomach becomes too high. ...
- G cells- They secrete gastrin hormone. Gastrin stimulates the gastric glands to release gastric juice. ...
- D-cells - D cells secrete somatostatin. ...
What is the major function of the stomach?
- The innermost layer is the mucosa. This is where stomach acid and digestive enzymes are made. ...
- Next is a supporting layer called the submucosa.
- Outside of this is the muscularis propria, a thick layer of muscle that moves and mixes the stomach contents.
- The outer 2 layers, the subserosa and the outermost serosa, wrap the stomach.
What does gastric fundus stand for?
Here are all the possible meanings and translations of the word gastric fundus. The superior portion of the body of the stomach above the level of the cardiac notch. How to pronounce gastric fundus? How to say gastric fundus in sign language? Notify me of new comments via email.
Where is the gastric fundus?
gas·tric fun·dus [ gas-trik fuhn-duhs ] The superior portion of the body of the stomach above the level of the cardiac notch. (fundus of the stomach) The portion of the stomach that lies above the cardiac notch. It allows for the accumulation of gases produced by chemical digestion.
See more
What is the fundus region of the stomach?
The fundus is a rounded section next to the cardia. It's below your diaphragm (the dome-shaped muscle that helps you breathe). The body (corpus) is the largest section of your stomach. In the body, your stomach contracts and begins to mix food.
Why is it called fundus of stomach?
In classical anatomy the human stomach is divided into four sections, beginning at the cardia. The cardia is where the contents of the oesophagus empty into the stomach. The fundus (from Latin 'bottom') is formed in the upper curved part. The body is the main, central region of the stomach.
What is present inside the fundus of stomach?
The mucosa of the gastric fundus contains parietal cells, which secrete hydrochloric acid and intrinsic factor, and chief cells, which secrete pepsinogen. The antrum and pylorus contain G cells, which secrete the hormone gastrin.
What is the difference between the gastric antrum and fundus?
The gastric fundus receives and stores food, and the antrum triturates ingested food into chyme.
What is the fundus medical term?
(FUN-dus) The part of a hollow organ that is across from, or farthest away from, the organ's opening. Depending on the organ, the fundus may be at the top or bottom of the organ. For example, the fundus of the uterus is the top part of the uterus that is across from the cervix (the opening of the uterus).
What is fundus in endoscopy?
The reasons may be as follows: i) The gastric fundus is in the upper portion of the stomach and the operation requires retroflexion of the endoscope. ii) The muscularis propria is a deep layer of gastric wall and adjacent to the serosal layer.
What causes thickening of the gastric fundus?
The gastric wall thickening is a diagnostic challenge for gastroenterologists and can be caused by a wide variety of benign and malignant disorders including lymphoma, adenocarcinoma, Menetriers' disease, Crohn's disease, peptic ulcer disease, sarcoidosis and tuberculosis.
What is Fundic relaxation?
Fundic relaxant drugs are a recent different approach to treatment of gastric motility disorders. Recently studied drugs include drugs under investigation including nitrates, serotonin reuptake blockers, 5-HT(1A) receptor agonists (buspirone and R137696), and muscarinc M1/M2 receptor antagonists (acotiamide or Z-338).
What is the function of the stomach?
The function of the stomach to store food, grind it, and release it slowly into the stomach is reviewed. The functional regions of the stomach—fundus, body, and antrum—are discussed. Receptive relaxation and gastric accommodation of the fundus are described, and the mechanisms that bring these about. The cardiac pacemaker is described. Gastric motility is discussed along with gastric emptying and the enterogastric inhibitory reflex and the function of GI hormones cholecystokinin and secretin. The migrating motility complex or migrating myoelectric complex during the interdigestive period is described. Stomach secretions are considered, beginning with a description of the secretory glands and cells. Secretion of mucus by neck cells, pepsinogen by chief cells, and HCl and intrinsic factor by parietal cells is discussed. The mechanism of acid secretion is covered and its regulation by nerves, hormones, and paracrine substances such as histamine.
What is gastric accommodation?
Gastric accommodation is a physiological phenomenon whereby the proximal stomach (fundus) relaxes to serve as a food reservoir in response to meal ingestion, which is controlled by a vagal reflex. [42] Up to 40% of patients with FD have been reported to have an impaired gastric accommodation. [43] Impaired gastric accommodation in patients were particularly found to be associated with symptoms of bloating, pain and nausea in FD [44].
Is the barium upper GI hernia a paraesophageal hernia
First of 2 films from barium upper GI series shows herniation of the gastric fundus as well as the gastric cardia. This constitutes a paraesophageal hernia and is considered a more compelling indication for surgical repair than a simple sliding hiatal hernia, which involves only the cardia.
Overview
The digestive system is made up of the gastrointestinal tract-mouth, esophagus, stomach, small & large intestine, and rectum.
Function
Your stomach’s purpose is to digest food and send it to your small intestine. It has three functions:
Anatomy
Your stomach sits in your upper abdomen on the left side of your body. The top of your stomach connects to a valve called the esophageal sphincter (a muscle at the end of your esophagus). The bottom of your stomach connects to your small intestine.
Conditions and Disorders
Gastrointestinal diseases may affect your stomach. You may have gastrointestinal symptoms only under specific circumstances, such as getting heartburn during pregnancy. Or you may have a chronic (long-lasting) condition.
Care
You can make lifestyle changes to keep your stomach and digestive system healthy. You may:
Frequently Asked Questions
If you have chronic stomach symptoms, you may speak with a gastroenterologist. Gastroenterologists are doctors who specialize in treating the digestive system. You may ask:
What is the fundus of the stomach?
fundus of stomach the part of the stomach to the left and above the level of the opening between the stomach and esophagus. fundus tym´pani the floor of the tympanic cavity. fundus u´teri ( fundus of uterus) the part of the uterus above the orifices of the fallopian tubes. Miller-Keane Encyclopedia and Dictionary of Medicine, Nursing, ...
What is the fundus of the eye?
fundus of eye the back portion of the interior of the eyeball, visible through the pupil by use of the ophthalmoscope. (See Atlas 4, Part A). fundus of gallbladder the inferior, dilated portion of the gallbladder. fundus of stomach the part of the stomach to the left and above the level of the opening between the stomach and esophagus.
Words nearby fundus of stomach
The American Heritage® Stedman's Medical Dictionary Copyright © 2002, 2001, 1995 by Houghton Mifflin Company. Published by Houghton Mifflin Company.
How to use fundus of stomach in a sentence
Is there a more dreadful sensation than that of your stomach wringing itself out like a washcloth?