Just so, what is the function of the AMPR gene in a vector? The ampr gene on the plasmid codes for an enzyme that is secreted into the periplasmic space of the bacterium, where it catalyzes hydrolysis of the B-lactam ring of ampicillin, with concomitant detoxification of the drug.
What is the function of the AmpR gene Quizlet?
Likewise, people ask, what is the function of the AMPR gene? The ampicillin resistance gene (ampr) codes for an enzyme (b-lactamase) that is secreted into the periplasmic space of the bacterium where it catalyzes hydrolysis of the b-lactam ring of the ampicillin. Thus, the gene product of the ampr gene destroys the antibiotic.
What is a plasmid promoter?
Here, we'll cover the promoter, which is necessary for getting the plasmid express our gene of interest. This element is responsible for initiating the transcription of your insert into RNA. In practice, the term "promoter" describes the combination of the promoter (RNA polymerase binding site) and operators (response elements).
What is a plasmid vector used for?
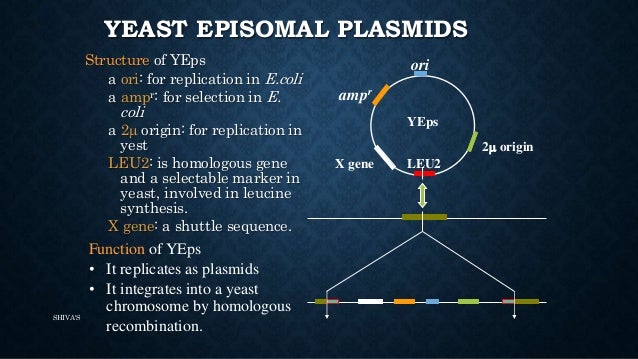
Plasmids that are used experimentally for these purposes are called vectors. Researchers can insert DNA fragments or genes into a plasmid vector, creating a so-called recombinant plasmid. In respect to this, what is the function of the AMPR gene?
What is ampicillin resistant plasmid?
A plasmid containing the ampicillin resistance gene (as well as another target gene within the plasmid) is introduced into the bacterial host. If the bacterium has taken up the plasmid and is expressing the plasmid, it will be resistant to ampicillin.
What is ampR used for?
AmpR acts as a transcriptional activator by binding to a DNA region immediately upstream of the ampC promoter (2, 12, 24). In the absence of a β-lactam inducer, AmpR represses the synthesis of β-lactamase by 2.5-fold, whereas expression is induced 10- to 200-fold in the presence of a β-lactam inducer (22, 23).
What does ampR mean in plasmid?
AmpR promoter is the promoter for ampicillin resistance. It is a weak promoter. Any gene can also be cloned under this promoter and expressed in bacteria like E. Coli. There is a pCutamp plasmid used for plasmid-curing in Escherichia coli by targeting the AmpR promoter.
What is ampR in cloning vector?
(b) Ampicillin resistant gene (ampR): It is a selectable marker which is resistant to the antibiotic amphicillin. The plasmid becomes useful for the cell in the presence of a selectable marker.
What does the ampicillin resistance gene ampR code for?
Abstract. I have determined the nucleotide sequence of the ampicillin resistance gene of pBR322, an Escherichia coli plasmid that encodes a penicillin beta-lactamase. This gene codes for a protein of 286 amino acid residues.
What is the function of the ampR gene in a plasmid vector quizlet?
What is the function of the ampr gene in a plasmid vector? It allows a researcher to separate bacterial cells with a plasmid from those without a plasmid.
What is ampR?
Definition. AMPR. Advanced Microwave Precipitation Radiometer. AMPR. Andria Mitsakos Public Relations (various locations)
What protein does ampR code for?
The ampr gene of Escherichia coli and other Gram-negative bacteria codes for a /3-lactamase (penicillin amido-3-lac- tamhydrolase, EC 3.5. 2.6) of approximately 27,000 daltons that catalyzes the hydrolysis of penicillins to penicilloic acids.
What will happen if the plasmid lack of ampR gene?
The bacterium cannot grow in the presence of the antibiotic ampicillin unless it contains the plasmid, and so there will be no growth on the LB/Amp plate of the bacteria without the plasmid.
What is ampR in pBR322?
pBR322 is 4361 base pairs in length and has two antibiotic resistance genes – the gene bla encoding the ampicillin resistance (AmpR) protein, and the gene tetA encoding the tetracycline resistance (TetR) protein.
Why do you use ampicillin resistance genes in plasmids?
Adding an antibiotic resistance gene to the plasmid solves both problems at once – it allows a scientist to easily detect plasmid-containing bacteria when the cells are grown on selective media, and provides those bacteria with a pressure to keep your plasmid.
What is the enzyme encoded by the ampicillin resistance gene?
Ampicillin resistance on the pBR322 plasmid encodes the enzyme β-lactamase, which is secreted to the periplasm and acts by binding and inactivating the ampicillin molecule (http://wine1.sb.fsu.edu/bch5425/lec13/lect13.htm).
Why are antibiotic resistance genes used as markers in E coli?
Antibiotic resistance genes are used as selectable markers in E. coli as it does not contain antibiotic resistance genes naturally.
Why do you need a promoter for a plasmid?
Aside from choosing a promoter based on type of RNA transcript, you will also need to make sure your plasmid has a promoter suited to working in your host organism. Because transcription machinery differs between cell types or organisms, promoters must be similarly variable.
What are the elements that make up a plasmid?
Once you've gotten to know what a plasmid is in general, it's time to take a look at some of its parts. Elements such as the antibiotic resistance gene and the origin of replication are necessary to replicate plasmids and make sure the cells maintains it. Here, we'll cover the promoter, which is necessary for getting the plasmid express our gene ...
What type of promoter is used for mRNA?
This means that the promoter present in your plasmid backbone must to be compatible with the type of RNA that needs to be made: if you want mRNA (for gene expression) you need to use an RNAP II promoter, whereas small RNAs (such as shRNA) are transcribed from the RNAP III promoters.
How many base pairs are in a promoter?
Promoters are about 100 to 1000 base pairs long and found upstream of their target genes. The sequence of the promoter region controls the binding of the RNA polymerase and transcription factors, therefore promoters play a large role in determining where and when your gene of interest will be expressed.
What is the T3 promoter?
T3. in vitro transcription/general expression. Promoter from T3 bacteriophage. Constitutive, but requires T3 RNA polymerase. When used for in vitro transcription, the promoter drives either the sense OR antisense transcript depending on its orientation to your gene.
Can synthetic promoters kill cells?
This is normally not a big issue for cells, but it may confound research results or even kill your cells if your gene of interest is toxic. To combat this, scientists have created synthetic promoters, which typically include some combination of other promoter elements, and tend to be more tightly regulated.
Is a promoter active all the time?
Some promoters are constitutively active and on all the time while others are more carefully controlled. Regulated promoters might act only in certain tissues or at certain times in development or there may be ways to turn them on or off at will with a chemical, heat, or light.