What is the main function of the palate?
Which muscles elevate the soft palate quizlet?
- levator veli palatini. elevates soft palate.
- tensor veli palatini. …
- Palatoglossus. …
- Palatopharyngeus. …
- musculus uvulae. …
- nerve innervation for levator veli palatini. …
- nerve innervation for tensor veli palatini. …
- nerve innervation for palatoglossus, palatopharyngeus, musculus uvulae.
What is hard palate and soft palate?
Soft palate cancer has some similar signs and symptoms, which can include the following:
- Bad breath
- Loose teeth
- Bleeding
- Difficulty swallowing or speaking
- Pain when swallowing
- Mouth pain and/or sores that don't heal
- Weight loss
- Ear pain
- Swelling in your neck that may hurt
What bones are in the hard palate?
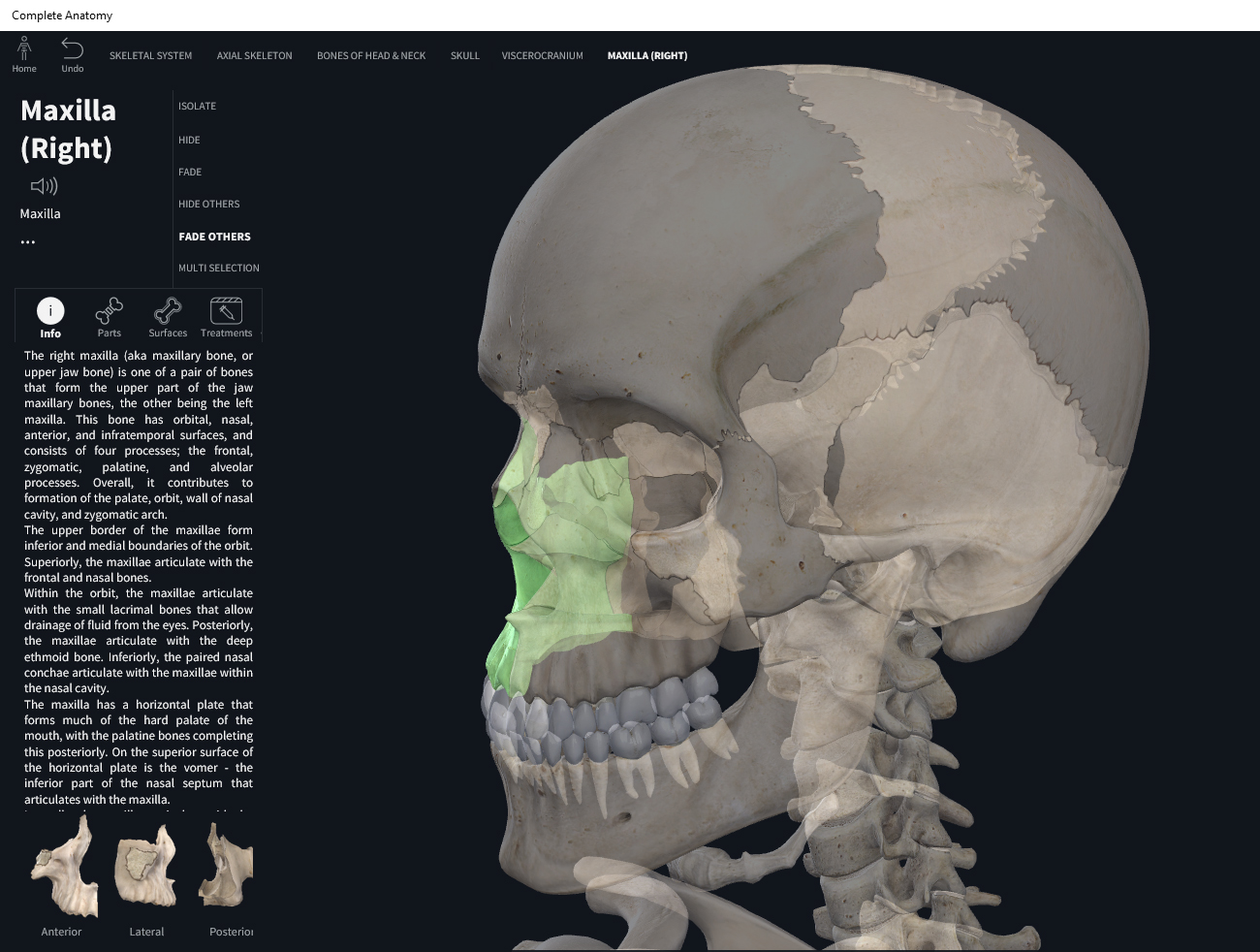
- palatine process of maxilla. The portion of the maxillary bone that forms most of the hard palate.
- horizontal plate of palatine bone. forms posterior part of hard palate.
- medial pterygoid process.
- lateral pterygoid process.
- vomer.
- alveolar arch.
- sphenoid.
What does the hard palate separate?
- Bearing the weight of the torso
- Ryggraden under ribbein
- Connects to the pelvis
What is the function of the hard and soft palate of the mouth?
The soft palate is continuous with the hard palate, which forms in the anterior roof of the mouth. The soft palate plays an essential role in blocking food and other substances from entering the nasal passages during swallowing and is important in the formation of certain sounds in speech production.
What is the function of the hard palate quizlet?
The hard palate holds the root of the teeth. The soft palate pressed down for swallowing. What mechanical and chemical digestion occurs in the oral cavity?
What is the function of palate?
The function of the soft palate is to facilitate speech, breathing and swallowing by making sure that the proper communication channels between the oral, pharyngeal and nasal cavities are open or closed during each of these processes.
Where is the hard palate located and what are their functions?
Palate Anatomy With a hard palate comes a soft palate located in the back of your oral cavity with a much more fleshy-like surface. Your hard palate plays a significant role as it separates the oral cavity from the nasal cavity while also aiding swallowing and speaking. Translation — it's a big deal.
What is the difference between the hard and soft palate?
The hard palate is the front part of the roof of the mouth, and the soft palate is the back part.
What is the hard palate made of?
The hard palate comprises about two-thirds of the total palate surface area, and its underlying bony structure consists of the palatine processes of the maxilla and the horizontal plates of the palatine bones.
What are the parts of the hard palate?
The hard palate is a horizontal bony plate that forms a subsection of the palate of the mouth. It forms the anterior two-thirds of the roof of the oral cavity. The hard palate is comprised of two facial bones: the palatine process of the maxilla and the paired palatine bones.
What is your palate?
The roof of the mouth. The front portion is bony (hard palate), and the back portion is muscular (soft palate). Anatomy of the oral cavity.
What is the hard palate?
What is hard palate. The palate forms the roof of the mouth and floor of the nasal cavity. The palate is divided anatomically into the bony hard palate anteriorly (part of the oral cavity) and the fleshy soft palate posteriorly (part of the oropharynx). Most of the hard palate is formed by horizontal extensions of the maxilla called palatine ...
What is the name of the bone that grows out of the hard palate?
Torus palatinus is a common developmental exostosis or outgrowth of the bone of the hard palate that manifests itself in adults during the second or third decade of life 10). It is more common in women and is always located in the midline. Torus palatinus is an extension of the bone of the hard palate and and not a true neoplasm. Torus palatinus are benign anatomical bony protuberances 11) and rarely needs treatment. Occasionally, it is removed because it interferes with the fitting of dentures. In rare instances, multiple tori grow on the hard palate.
What is the best treatment for squamous cell carcinoma of the hard palate?
Surgery is the preferred treatment for squamous cell carcinoma of the hard palate. However, megavoltage radiation has also been used with some success as a viable alternative in treating patients with these tumors.
Is hard palate cancer treated?
Hard palate cancer treatment. Specific treatment of palate cancer depends on the location of the tumor (hard vs soft palate), stage of the tumor and pathologic type of the cancer. For this reason, management of squamous cell carcinoma and carcinomas of minor salivary gland origin are discussed separately.
Why do we have two palates?
That’s because the passage remains open when a person is not swallowing food, thus allowing him to breathe through the mouth and nose.
Which nerve innervates the posterior portion of the hard palate?
The nasopalatine nerve emerges from the incisive foramen and supplies the anterior part of the hard palate. The greater palatine nerve gains the hard palate via the greater palatine foramen and innervates its posterior portion. Figure 1. Hard palate anatomy.
Where is the L-shaped palatine bone located?
The L-shaped palatine bones are located behind the maxillae (see Figure 1). The horizontal portions form the posterior section of the hard palate and the floor of the nasal cavity. The palate’s function is to separate the nasal cavity from the oral cavity, enabling you to continue breathing while chewing.
What is the palate?
The palate (also known as the ‘roof of the mouth’), forms a division between the nasal and oral cavities. It is separated into two distinct parts: Hard palate – comprised of bone. It is immobile. Soft palate – comprised of muscle fibres covered by a mucous membrane.
What are the two parts of the soft palate?
It is separated into two distinct parts: Hard palate – comprised of bone. It is immobile. Soft palate – comprised of muscle fibres covered by a mucous membrane. It can be elevated to close the pharyngeal isthmus during swallowing – this prevents the food bolus from entering the nasopharynx.
What is a cleft lip?
Cleft lip – occurs when the medial nasal prominence and maxillary prominence fail to fuse. Cleft palate – can occur in isolation when the palatal shelves fail to fuse in the midline, or in combination with cleft lip. Cleft lip and cleft palate are relatively common, occurring in approximately 1/1000 births.
Where does the palate receive arterial supply?
Vasculature. The palate receives arterial supply primarily from the greater palatine arteries, which run anteriorly from the greater palatine foramen. In addition, the anastomosis between the lesser palatine artery and ascending palatine artery provide collateral supply to the palate.
What is the posterior border of the soft palate?
The posterior border of the soft palate is free (i.e. not connected to any structure), and has a central process that hangs from the midline - the uvula. The soft palate also forms the roof of the fauces ; an area connecting the oral cavity and the pharynx.
Which surface of the palate has a mucosal lining?
Reflecting this, the superior and inferior palatal surfaces have different mucosal linings: Superior aspect of palate (nasal cavity) - respiratory epithelium. Inferiorly aspect of palate (oral cavity) - oral mucosa, populated by secretory salivary glands. The hard palate forms the anterior aspect of the palate.
Which structure divides the nasal cavity and the oral cavity?
Structure. The palate divides the nasal cavity and the oral cavity, with the hard palate positioned anteriorly and the soft palate posteriorly. It forms both the roof of the mouth and the floor of the nasal cavity.
What causes a hard palate?
Your hard palate can also be affected in other ways, including sexually transmitted infections (STIs). Two specific ones could impact the health of your hard palate: 1 Syphilis#N#This disease can leave lesions on both palates, lip, and tongue 2 HPV#N#Papillary or ulcerative white patches or warts have been known to form on the hard and soft palate if infected with this STD
Where is the hard palate located?
Your hard palate is that bony part found at the top of your mouth near the front of your oral cavity. With a hard palate comes a soft palate located in the back of your oral cavity with a much more fleshy-like surface. Your hard palate plays a significant role as it separates the oral cavity from the nasal cavity while also aiding swallowing ...
Why does my palate get cancer?
There's a natural opening in the hard palate for nerves and blood vessels that's an ideal route for a tumor to make its way into the oral cavity. Possible causes for palate cancer include drinking, smoking, and reverse smoking (inserting the lit end of a cigarette into your mouth instead). Symptoms may include:
Why do you need to see a dentist for hard palate?
It allows them to properly examine your hard palate during regular checkups or if something irregular occurs. So make it easy on yourself and keep that hard palate of yours healthy.
What are the factors that can cause a baby to have a cleft palate?
Speech difficulties. Social, emotional, behavioral issues. Some factors might put your baby at a higher risk of developing a cleft palate, notes the Mayo Clinic, including genetic family history, as well as smoking, drinking, or drug use during pregnancy, and other health issues.
What diseases can affect the hard palate?
Your hard palate can also be affected in other ways, including sexually transmitted infections (STIs). Two specific ones could impact the health of your hard palate: Syphilis. This disease can leave lesions on both palates, lip, and tongue. HPV.
Can a baby with a cleft palate break your heart?
Feeding and Speech Complications. If you've ever seen a baby with a cleft palate, it can break your heart. It's a disorder that consists of an opening within the hard palate that doesn't entirely fuse as it should and could extend to their nose or lips.
Why is the hard palate important?
The hard palate is important for feeding and speech. Mammals with a defective hard palate may die shortly after birth due to inability to suckle. It is also involved in mastication in many species. The interaction between the tongue and the hard palate is essential in the formation of certain speech sounds, notably high-front vowels, palatal consonants, and retroflex consonants such as [i] like "s ee ", [j] like " y es", [ç] (realization of /hj/ in English) like " h ue", and [ɻ] (/r/, only for some speakers) like " r ed".
What is the hard palate?
The hard palate is formed by the palatine process of the maxilla and horizontal plate of palatine bone. It forms a partition between the nasal passages and the mouth. On the anterior portion of the hard palate are the plicae, irregular ridges in the mucous membrane that help facilitate the movement of food backward towards the larynx.
What is the birth defect of the left and right palate?
In the birth defect called cleft palate, the left and right portions of this plate are not joined, forming a gap between the mouth and nasal passage (a related defect affecting the face is cleft lip ).
What drug causes bluish grey color in the palate?
Long-term use of the drug chloroquine diphosphatase, used in malaria prophylaxis, rheumatoid arthritis and other conditions, was found to cause bluish - grey pigmentation in the hard palate.
Where is the hard palate located?
Anatomical terminology. The hard palate is a thin horizontal bony plate made up of two bones of the facial skeleton, located in the roof of the mouth. The bones are the palatine process of the maxilla and the horizontal plate of palatine bone. The hard palate spans the alveolar arch formed by the alveolar process that holds the upper teeth ...
Is smoking a risk factor for cleft palate?
As for the environmental risk factors, maternal smoking is the most influential risk factor. Based on a recent study of 103 German patients with cleft palates, it was found that 25.2% of them developed the defect due to excessive maternal smoking during pregnancy.