The Anatomy of the Conjunctiva
- Anatomy. The conjunctiva is divided into three segments: the bulbar conjunctiva, the palpebral conjunctiva, and the fornix conjunctiva.
- Function. The primary function of the conjunctiva is to keep the front surface of the eye moist and lubricated.
- Associated Conditions. Several conditions can affect the normal functioning of the conjunctiva. ...
What are the 6 functions of connective tissue?
- Fibroblasts – greatest in numbers. ...
- Macrophages – macro means large, phagein means to eat- engulf bacteria and debris by phagocytosis
- Plasma Cells– secrete antibodies for immunity
- Mast Cells – release histamine which is part of the inflammatory process
- Adipocytes and leukocytes(white blood cells) are also present in CT
How to rebuild connective tissue?
- lower your blood pressure
- strengthen your immune system
- reduce chronic pain
What are the signs of connective tissue disease?
Specific symptoms depend on the specific type and may include:
- Blue or gray tint to the whites of the eyes
- Thin skin
- Curved spine
- Breathing problems
- Hearing loss
- Teeth that break easily
Which connective tissue insulates against heat loss?
Insulates against heat loss; provides reserve fuel. adipose connective tissue. ... dense fibrous connective tissue. acts as a storage depot for fat. adipose ...
What does the conjunctive tissue do?
Tissue that supports, protects, and gives structure to other tissues and organs in the body. Connective tissue also stores fat, helps move nutrients and other substances between tissues and organs, and helps repair damaged tissue.
What are conjunctive tissue in plants?
Definition of conjunctive tissue : sometimes lignified parenchymatous ground tissue in which the vascular bundles are embedded in certain dicotyledons (as the beet) and in those monocotyledons in which secondary thickening occurs.
What is conjunctive tissue and where it is present?
Hint: Conjunctive tissue is defined as the tissue which is either parenchyma or sclerenchyma in origin. This tissue is present between the bundles of the xylem and the phloem tissues in the vascular bundles of the root. This is present in both dicot and monocot root.
What is conjugate tissue?
Parenchyma present between xylem and phloem in the vascular bundles of roots is called conjuctive tissue. It is involved in the formation of cambium in dicot stem.
What do you mean by conjunctive?
The definition of conjunctive is something that joins, or is two things combining or co-occurring. Tissue that joins muscle to bone is an example of conjunctive tissue. Two scientific theories that go together and combine in a way that both make sense are an example of conjunctive theories. adjective.
What is the difference between medullary rays and conjunctive tissue?
Answer by Isha Agarwal. In the stem, the parenchyma cells are meant for storage of food and represent the medullary rays while in the root, they store water and represent the conjunctive tissue.
Is conjunctive tissue is a part of stele?
Parenchyma tissue particularly really present between xylem and phloem is called Conjunctive tissue, which for all intents and purposes kind of shows that tetrarch stele essentially mostly is present, generally, for the most part, means stele with four xylem strands, showing how in the stele of dicot root, the ...
What is Conjuctive tissue class 11?
The special tissues which link and support other tissues/organs of the body are called connective tissues. Connective tissues include cartilage, bone, adipose, and blood. In all connective tissues except blood, the cells secrete fibres of structural proteins called collagen or elastin.
What is meant by conjoint vascular bundle?
A. Xylem and phloem on different radii.
Is Conjuctive tissue and cambium same?
The correct word is conjunctive and not conjugative. Interfascicular cambium is parenchymatous and is found between xylem and phloem of dicot stem but conjunctive tissue is the derivatives of interfascicular cambium.
What is the meaning of centripetal xylem?
Xylem development in the roots is from the outer regions in the inward direction and so known as centripetal. The growth of xylem in shoots is centrifugal direction which means towards the outside. Phloem development is in the centripetal direction in roots and shoots.
What are radial and conjoint vascular bundles?
The xylem and phloem within a vascular bundles are arranged in an alternate manner on different radii is called radial vascular bundle. The xylem and phloem are situated at the same radius of the vascular bundles is called conjoint.
What is the function of connective tissue?
One of the important functions of the connective-tissue cells is to maintain conditions in the extracellular spaces that favour this exchange.
What are the different types of connective tissue?
The connective tissues include several types of fibrous tissue that vary only in their density and cellularity, as well as the more specialized and recognizable variants— bone, ligaments, tendons, cartilage, and adipose (fat) tissue. collagenous fibres.
What is the name of the group of tissues that maintain the form of the body and its organs and provide cohe
Professor Emeritus of Anatomy, Harvard Medical School, Harvard University. Coauthor of Textbook of Histology. Connective tissue, group of tissues in the body that maintain the form of the body and its organs and provide cohesion and internal support. The connective tissues include several types of fibrous tissue that vary only in their density ...
Which organ is covered by the greater omentum?
The abdominal organs are supported and protected by the bones of the pelvis and ribcage and are covered by the greater omentum, a fold of peritoneum that consists mainly of fat.
Is connective tissue cellular or fibrous?
In some areas, the connective tissue is loosely organized and highly cellular; in others, its fibrous components predominate; and in still others, the ground substance may be its most conspicuous feature.
What are the three types of connective tissue?
Connective tissues contain three types of fibres: collagen, elastic and reticular. Collagen fibres are the most widespread and made up of fibrous protein, collagen. Collagen fibres are flexible and have high tensile strength (comparable to steel). Elastic fibres form a network and can be stretched like a rubber band.
Which connective tissue is responsible for maintaining correct posture?
Specialised Connective Tissue. Other than these, there are supportive connective tissues, that help in maintaining correct posture and support internal organs, e.g. cartilage and bone. Blood and lymph are fluid connective tissues that circulate in the body and help in interaction and communication among all the organs.
What are reticulate fibres?
Reticulate fibres consist of collagen and glycoproteins. They are thin and form a delicate network. They join connective tissues to neighbouring tissues. There are various kinds of cells present in different types of connective tissues. They secrete different types of fibres and matrices.
What are the different types of cells that are found in developing tissues?
They secrete different types of fibres and matrices. Fibroblasts or adipose cells are stationary and macrophages, mast cells, monocytes, lymphocytes are migrating cells. Fibroblasts are found in developing tissues and play an important part in wound-healing. They are spindle-shaped and present between collagen fibres.
What is the term for a group of cells along with intercellular substances that perform a specific function?
Connective Tissue. A group of cells along with intercellular substances that perform a specific function is called tissue. There are mainly four different types of tissues present in our body. Epithelial- provides covering or lining. Muscular- helps in movement.
What is the function of adipose tissue?
Adipose Tissue: They are present under the skin and store fat. It acts as a shock absorber and helps in maintaining body temperature in colder environments. White adipose tissues protect kidneys and are also found at the back of the eye, in the hump of camels, blubber of whales, etc.
What is the other type of connective tissue disorder?
EB is characterised by skin oversensitivity. The other type of connective tissue disorder is autoimmune. When the immune system of the body starts attacking healthy tissues, it is known as an autoimmune disorder. Some of the autoimmune diseases of connective tissue are the following:
Connective tissue
Connective tissue is mesodermal in origin and form of matrix, fibres and cells. It constitutes the extracellular ground substance and fills up the intercellular spaces between the cells.
Functions of Connective tissues
Connective tissue is basically a binding and a packaging tissue but has many other important functions as well-
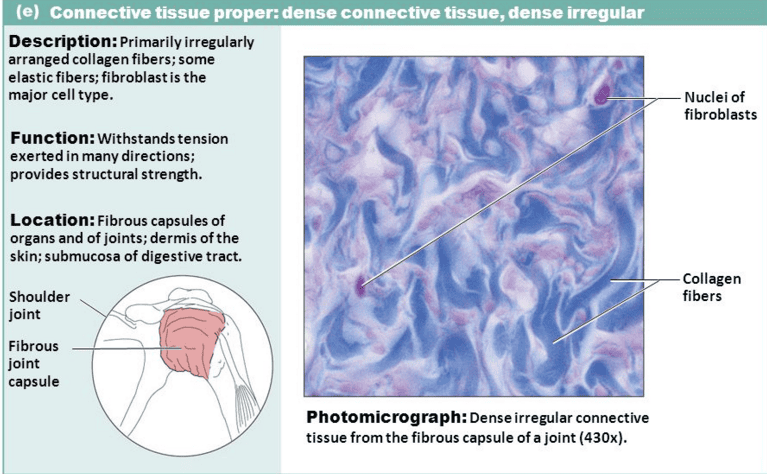
Table of Contents
What Is Connective tissue?
- Connective tissues, as the name implies, support and connect different tissues and organs of the body. They are widely distributed in every part of the body. They originate from the mesoderm (the middle germinal layer of the embryo). Connective tissue is made up of a few cells present in the intercellular framework of protein fibres secreted by the...
Types of Connective Tissue
- The classification of connective tissue is as follows: 1. Loose Connective Tissue 2. Dense Connective Tissue 3. Specialised Connective Tissue
Connective Tissue Disorder
- Connective tissue disorders may be due to mutation of genes or by inherited faulty genes. The two genetic disorders of connective tissue are epidermolysis bullosa (EB) and Marfan syndrome. Marfan syndrome is due to defective genes producing a protein fibrillin-1. The disease is characterised by a very thin and long body. Fingers and toes are spider-like. EB is characterised …