Chondroblast
- Cells to Make and Cells to Break. A second proto-oncogene, c-myc, is expressed in all chondrocytes of chick and rat long bones. ...
- Initiating Skeletal Growth. ...
- Extracellular Matrix (ECM) Molecules
What is the function of a Chondroblast Quizlet?
What is the function of a Chondroblast? The chondroblasts are cells that secrete the major component of the cartilage, i.e. the extracellular matrix (ECM). Click to see full answer.
What is the difference between osteoblasts and Chondroblast?
Chondroblast. Use of the term is technically inaccurate since mesenchymal progenitors can also technically differentiate into osteoblasts or fat. Chondroblasts are called Chondrocytes when they embed themselves in the cartilage matrix, consisting of proteoglycan and collagen fibers, until they lie in the matrix lacunae.
What is the extracellular matrix of a Chondroblast made of?
Chondroblasts secrete the extracellular matrix which is composed of various substances, including collagen, proteoglycans, glycoproteins, hyaluronic acid, water, and macromolecules. These substances provide strength and structural support to the developing cartilage.
What are the function of chondrocytes?
Chondrocytes in the AC proliferate and secrete extracellular matrix to maintain and sustain the cartilage. The cells themselves are separated from each other by cartilage matrix [2]. They respond to outside stimuli and tissue damage, and are also responsible for degenerative conditions, such as osteoarthritis (OA).
What is the function of chondroblasts quizlet?
Chondroblasts are cells that produce the components of the extracellular matrix. Chondroblasts, along with chondrocytes, are one of two cells that are responsible for producing cartilage. Chondroblasts create the major component, the extracellular matrix, of the cartilage.
What is the function of chondroblasts and chondrocytes?
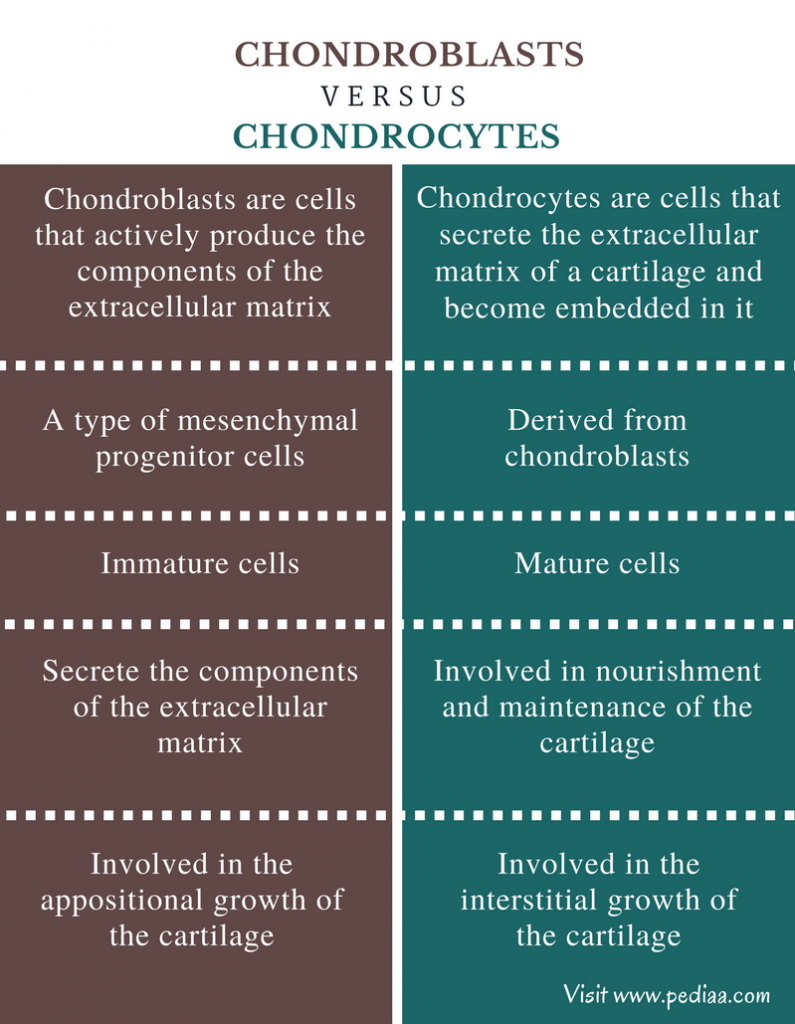
Chondroblasts are a type of immature cells whereas chondrocytes are a type of mature cells. The main difference between chondrocytes and chondroblasts is that chondroblasts secrete the extracellular matrix of the cartilage whereas chondrocytes are involved in the maintenance of the cartilage.
What is the structure of Chondroblast?
It consists of chondrocytes and extracellular matrix (ECM). Chondroblasts originate from the mesenchymal stem cell. Biology definition: Chondroblasts refer to any of the perichondrial cells involved in the formation of chondrocytes and ECM of the cartilage. Etymology: Greek “khondros” (cartilage) and “blastos” (germ).
What do chondrocytes produce?
In the growth plate, chondrocytes undergo a series of highly regulated transformations leading to the replacement of the cartilage template by bone. During this process, known as endochondral ossification, chondrocytes proliferate, produce type II collagen, and form a columnar cell layer.
How do chondrocytes differ from Chondroblasts quizlet?
Terms in this set (51) has chondrocytes that are isogenic (similar cells come together as a group). Chondroblasts are active form of the same cell, they are actively producing the necessary components of ECM. Once they are entrapped in the lacunae surrounded by the ECM they created they turn in chondrocytes.
What is the difference between osteoblast and Chondroblast?
0:000:54osteoblast vs chondroblast - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipBecause this bone is going to connect to another bone you need cartilage in the middle. So the bonesMoreBecause this bone is going to connect to another bone you need cartilage in the middle. So the bones are making up against each other. But that's the main difference between osteoblast.
Do chondroblasts make bone?
Chondroblasts and osteoblasts are, respectively, the cartilage and bone forming cells in mammals.
Who is responsible for chondroblasts?
Matrix formation and composition Due to the proliferative nature of Chondroblasts, cells compose a larger portion of the composition than what is normally found within completed cartilage. Collagen Type II fibers are responsible for giving the future cartilage matrix its tensile strength.
What are the stem cells of chondroblasts?
Chondrogenic differentiation: from stem cell to cartilage Two types of cell are formed during chondrogenesis: chondroblasts, and chondrocytes (Fig. 1). Chondroblasts are progenitor cells that secrete the extracellular matrix (ECM), while chondrocytes are involved in nutrient diffusion and matrix repair.
How are chondrocytes formed?
Chondrocytes arise from cranial neural crest cells (CNCCs) of the neural ectoderm, cephalic mesoderm, sclerotome of the paraxial mesoderm, or somato-pleure of the lateral plate mesoderm. Terminal differentiation of chondrocytes results in different types of cartilage: hyaline; elastic; and fibrous.
What is the function of osteoclasts in bone tissue?
Osteoclasts are the cells that degrade bone to initiate normal bone remodeling and mediate bone loss in pathologic conditions by increasing their resorptive activity. They are derived from precursors in the myeloid/monocyte lineage that circulate in the blood after their formation in the bone marrow.
What are chondroblasts?
Chondroblasts (AKA perichondrial cells) are cells that play an important role in the formation of cartilage (AKA chondrogenesis). They are located...
What do chondroblasts do?
Chondroblasts contribute to the formation of the extracellular matrix and are the precursors of the chondrocytes, which collectively make up cartil...
What are the most important facts to know about chondroblasts?
Chondroblasts, located in the perichondrium, are cells that play an important role in the development of cartilage. By producing extracellular matr...
Why are chondrocytes important in chondrogenesis?
These cells are extremely important in chondrogenesis due to their role in forming both the chondrocytes and cartilage matrix which will eventually form cartilage. Use of the term is technically inaccurate since mesenchymal progenitors can also technically differentiate into osteoblasts or fat. Chondroblasts are called chondrocytes when they embed themselves in the cartilage matrix, consisting of proteoglycan and collagen fibers, until they lie in the matrix lacunae. Once they embed themselves into the cartilage matrix, they grow the cartilage matrix by growing more cartilage extracellular matrix rather than by dividing further.
Why do retinoids need to be repressed?
Retinoic acid, part of a family of molecules called retinoids, need to be repressed in order for Chondroblasts to form. A 2003 study using transgenic mice with a weak, constitutively active retinoic acid receptor found that retinoids maintain cells within condensations in a prechondrogenic, mesenchymal cell state which prevents cell differentiation. It has also been suggested that the inhibition of receptor mediated retinoid signaling induces Sox9 expression which is considered a “master switch” for the differentiation of chondroblasts.
What is the name of the cells that make up the cartilage matrix?
Anatomical terms of microanatomy. Chondroblasts, or perichondrial cells, is the name given to mesenchymal progenitor cells in situ which, from endochondral ossification, will form chondrocytes in the growing cartilage matrix. Another name for them is subchondral cortico-spongious progenitors.
What is the function of the Sox9 gene?
An important genetic component of this process is Sox9, a HMG box transcription factor, which marks progenitor cells for chondrogenic differentiation. Inactivation of the Sox9 gene will result in the loss of all Cartilage, and thus Chondroblast, formation. This factor is also expressed alongside Sox5 and Sox6.
What is the name of the skeletal tissue that is formed by a chondrocyte?
Chondroblast. This article is about the skeletal tissue. For other uses, see cartilage. Chondroblasts, or perichondrial cells, is the name given to mesenchymal progenitor cells in situ which, from endochondral ossification, will form chondrocytes in the growing cartilage matrix.
Which protein inhibits cartilage differentiation?
Differentiation of chondroblasts is favored in an environment with high compressive force and low partial oxygen pressure which combine to inhibit protein 3, a protein which inhibits cartilage differentiation.
What type of growth is maintained by chondroblasts?
The type of growth maintained by chondroblasts is called appositional bone growth and increases the birth of the affected tissue. It is important to note that perichondrium, and thus chondroblasts, are not found on the articular cartilage surfaces of joints.
What are the four cell types of female gametophytes?
The female gametophyte of most flowering plants forms four cell types after cellularization, namely synergid cell, egg cell, central cell and antipodal cell.
What is the role of chondroblasts in cartilage?
They are located in the perichondrium, which is a layer of connective tissue that surrounds developing bone and also helps protect cartilage.
What is fibroblast transfection?
Fibroblast transfection is a commonly used approach in molecular and mobile biology research, fibroblast transfection reagents are commercially to be had for both fibroblast cell strains and primary cells. As depicted underneath, fibroblast cells are massive and flat, with elongated procedures protruding from the body of each mobile, creati
What are the precursors of chondrocytes?
Chondroblasts contribute to the formation of the extracellular matrix and are the precursors of the chondrocytes, which collectively make up cartilage. Chondroblasts secrete the extracellular matrix which is composed of various substances, including collagen, proteoglycans, glycoproteins, hyaluronic acid, water, and macromolecu
How do guard cells work?
Guard cells come in pairs, each one having multiple large vacuoles (pockets designed to withhold water) within them. These vacuoles swell up with water diffused into the cell from the plants veins (forgive me, I can't remember what the vein-like structures are called) and this forces them apart and opens the gap between them, creating a stoma (pl. stomata) or a pore in the leaf's surface. This allows the flow of carbon dioxide to enter the leaf for photosynthesis and the waste product oxygen to leave the leaf. Once this is done, the water diffuses out of the vacuoles of the guard cells again and they shrink, closing the stoma.
Where are synergid cells located?
The synergid cells are located in the female gametophyte and are essential for angiosperm reproduction. During the fertilization process, a pollen tube grows into one of the synergid cells, ceases growth, ruptures, and releases its two sperm cells into this cell. The synergid cells produce an attractant that guides the pollen tube to the female gametophyte and likely contain factors that control arrest of pollen tube growth, pollen tube discharge, and gamete fusion. The synergid cells contain an elaborated cell wall at their micropylar poles, the filiform apparatus that likely plays a role in pollen tube guidance and pollen tube reception. Recent genetic, molecular, and physiological studies in Arabidopsis, maize, and Torenia have provided insights into synergid cell development and the control of pollen tube growth by the synergid cell.
What are fibroblasts made of?
Fibroblasts are the cells that make up the structural framework or stroma composed of the extracellular matrix and collagen in animal tissues. these cells are the maximum commonplace type of connective tissue in animals, and are vital for wound restoration. Fibroblast transfection is a commonly used approach in molecular and mobile biology research, fibroblast transfection reagents are commercially to be had for both fibroblast cell strains and primary cells. As depicted underneath, fibroblast cells are massive and flat, with elongated procedures protruding from the body of each mobile, creating the spindle-like look of the mobile, the nucleus inside the frame of the cellular, is oval.
What is the function of IGF1 in rat ribs?
Igf1 is the main serum factor regulating chondroblast proliferation, binding to proliferating chondrocytes of rat ribs at twice the level at which it binds to resting chondroblasts or to hypertrophic chondrocytes. Both growth hormone and Igf1 stimulate cell function in distinct zones of the rat epiphyseal growth plate, low concentrations enhancing mitosis in the proliferative zone. Igf1 (50 µg) and Tgfß1 (10 µg) also enhance proliferation during the early phases of repair of long bones without compromising callus composition or biomechanical properties b.
What are osteoblasts and chondroblasts?
Chondroblasts and osteoblasts are, respectively, the cartilage and bone forming cells in mammals. Extracellular cues emanating from the neural tube, ectoderm, and notochord structures underlie the specification of somites into the sclerotome and dermomyotome. Our understanding of these early developmental signals has been vital in understanding their contribution to physiological and pathological conditions. For example, a null mutation in mesogenin 1 (msgn 1) in mice results in the absence of a vertebrae [5]. HOX, Notch, and Wnt represent another set of genes that are essential for vertebral development. Mutations in the HOX genes result in severe vertebral defects due to impairment of patterning and specification of somatic cells [6].
What is the difference between a chondrocyte and a chondroblast?
The distinction between chondroblast and chondrocyte is often arbitrary; a chondrocyte is more mature than a chondroblast. As discussed in Chapter 13, distinguishing chondrocytes from hypertrophic chondrocytes (HCCs) is more straightforward, facilitated as it is by the substantial change in morphology, synthesis of new products and altered developmental functions that accompany hypertrophy.
Which is more sensitive, osteoblasts or chondroblasts?
Chondroblasts appear to be more sensitive than osteoblasts, as cartilage proliferation is inhibited at doses of 1800 cGy while osteoid production and mineralization continue. From: Handbook of Toxicologic Pathology (Second Edition), 2002. Download as PDF.
Where is BMP4 expressed?
In Xenopus embryos, Bmp2 and Bmp4 are expressed in the neural crest, fin mesenchyme, olfactory placodes and craniofacial primordia. Bmps2, 4 and 7 all are differentially transcribed in early embryos.
How is the Roman arch held in place?
Application of the principle of tensional integrity goes back to the Romans; the Roman arch is held in place by gravity pulling the arch tensionally downward. R. Buckminster Fuller pulled exactly the opposite way when he argued that a structure is pulled outward (and thus supported) by tensional forces inherent in and restrained by the structure, rather than structural weight providing compressive continuity. Ingber (*1993) extended this theory to the cytoskeleton in his theory of cellular tensegrity. Although little empirical information is available, it is known that ßeta 1 integrin promotes formation of focal adhesions in mediating changes in the ECM to the cell surface and then to cytoskeletal mechanotransduction. Integrin subtypes change as osteoblasts differentiate. Whether such changes drive or react to changing mechanotransduction was unclear until it was demonstrated that both ßeta 1 integrin and focal adhesion kinase are up-regulated in experimentally expanded (stretched) rat midpalatal sutures ( I. Takahashi et al., 2003) 17.
What causes progressive bone loss?
Other conditions such as osteoporosis lead to progressive bone degeneration. Bone loss in osteoporosis or in other pathological conditions results from an imbalance between bone-forming and bone resorption processes commonly known as bone remodeling.
What is the structure of cartilage made of?
The structure made up of the extracellular matrix, chondrocytes, and other densely packed components is what makes up cartilage.
Which cell group is responsible for the formation of cartilage?
The dense, circular group of cells is known as the "chondrogen node"; These are mesenchymal or ectomesenchymal cells that generally mark the site of hyaline cartilage formation. At this point, the transcription factor SOX-9 is expressed, which triggers the differentiation of cells from the "chondrogen node" into new chondroblasts.
How does chondroblast synthesis occur?
Chondroblast synthesis can occur by appositional growth or interstitial growth.
What is the process of cartilage growth?
When cartilage growth begins, cells go through a process of "dedifferentiation" guided by the expression of the transcription factor SOX-9. The cytoplasmic processes of these cells disappear, the cell nucleus condenses and acquires a completely circular shape.
Which type of cartilage is found in all three types of animals?
Although all three types of cartilage tissue in animals possess chondrocytes, chondroblasts are only found in two of these: hyaline cartilage and elastic cartilage.
What are the factors that regulate chondrogenesis?
Chondrogenesis, or the origin of chondroblasts, is highly regulated by numerous factors and molecules, including extracellular ligands, nuclear receptors, transcription factors, adhesive molecules, and matrix proteins.
What is the diameter of a chondroblast?
Chondroblasts found in the periphery of tissues have an ovoid or elliptical shape, while those inside the tissues are round in shape, with a diameter of between 10 and 30 μm.
What are Chondroblasts?
Chondroblasts, also called chondroplasts, are immature cells, that are essential for cartilage development. They are located along the edges of the cartilage under the perichondrium where the cell division occurs as two oppositional areas. Chondroblasts are also known as perichondrial cells or mesenchymal progenitor cells, which give rise to chondrocytes and components of the extracellular matrix. Chondroblasts mainly secrete type two collagen and other types of extracellular matrix components.
What are the cells that make up the extracellular matrix called?
Chondroblasts are also known as perichondrial cells or mesenchymal progenitor cells, which give rise to chondrocytes and components of the extracellular matrix. Chondroblasts mainly secrete type two collagen and other types of extracellular matrix components.
What is cartilage made of?
Cartilage is a specialized connective tissue found in many places of the body. Chondrogenesis is the process which forms cartilage from mesenchyme tissue. There are two main cell types in the cartilage known as chondroblasts and chondrocytes. Chondroblasts are actively dividing immature cells which form extracellular matrix and the chondrocytes. Chondrocytes are the differentiated cells which are involved in the diffusion of the nutrients, maintenance, and repair of the extracellular matrix of the cartilage. The key difference between chondrocytes and chondroblasts is that chondroblasts are immature cartilage cells found near the perichondrium while chondrocytes are mature cartilage cells found embedded within the extracellular matrix.
What is the difference between a chondrocyte and a chondroblast?
The key difference between chondrocytes and chondroblasts is that chondroblasts are immature cartilage cells found near the perichondrium while chondrocytes are mature cartilage cells ...
What is the function of chondrocytes?
The major function of the chondrocyte is to synthesis, maintain and remodel the extracellular matrix of the cartilage. Extracellular matrix is composed of equal proportions ...
What is the term for a disease that occurs when a chondrocyte malfunctions?
Chondrocytes malfunction can lead to a disease called osteoarthritis. It is a cartilage degenerative disease caused due to the breakage of tissue homeostasis. The flexibility of the cartilage is decided by the number of chondrocytes present in the cartilage.
Where are chondrocytes and chondrocytes found?
Chondroblasts and chondrocytes are two types of cells found in the cartilage. Chondroblasts are actively dividing immature cells located near the perichondrium of the cartilage. They are the actual cells which create the cartilage. Chondroblasts are the progenitors of the chondrocytes and extracellular matrix of the cartilage.
What is the role of chondrocytes in cartilage?
The main difference between chondroblasts and chondrocytes is the maturity and the role each play in the cartilage.
What are the two types of cells that are involved in the growth of cartilage?
Both chondroblasts and chondrocytes are involved in the growth of cartilage. Chondroblasts are an immature type of cells, which secrete the extracellular matrix of the cartilage. Once the matrix surrounds the chondroblasts, the cells become chondrocytes. Chondrocytes are mainly involved in the maintenance of the cartilage by providing nutrients.
What is the mature form of chondrocytes?
Chondrocytes are the mature form of the chondrocytes, which are embedded in the self-secreted, extracellular matrix of the cartilage. These cells are formed from chondroblasts, which secrete the extracellular matrix. This extracellular matrix form lacunae in which the chondrocytes are located in.
What are the cells that make up cartilage?
Chondroblasts are an immature type of cells found in the cartilage. Chondroblasts are also known as perichondrial cells. Chondroblasts are a type of mesenchymal progenitor cells. They secrete the extracellular matrix of the cartilage. The extracellular matrix of the cartilage is composed of collagen, hyaluronic acid, glycoproteins, proteoglycans, ...
How do chondrocytes help the cartilage?
Chondrocytes help the diffusion of nutrients into the cartilage from nearest blood vessels. Moreover, chondrocytes are involved in the interstitial growth of the cartilage by increasing the cell number and secreting more matrix. Chondrocytes secrete proteoglycans, collagen, and elastin fibers. Chondrocytes in lacunae are shown in figure 2.
What is the difference between chondrocytes and chondrocytes?
The main difference between chondrocytes and chondroblasts is that chondroblasts secrete the extracellular matrix of the cartilage whereas chondrocytes are involved in the maintenance of the cartilage. Once the chondroblasts are trapped in the extracellular matrix, which is secreted by the chondroblasts itself, chondrocytes are formed. Chondrocytes are involved in the diffusion of nutrients to the cartilage as well as the repair of the cartilage.
Which cells secrete the components of the extracellular matrix?
Chondroblasts: Chondroblasts secrete the components of the extracellular matrix.
Overview
Function
Chondroblasts appear to migrate to cartilage whenever chondrocytes are destroyed via mechanical force. Remaining chondrocytes divide in order to form more chondroblasts. HMGB-1, a growth factor which promotes chondrocyte division while receptors for advanced glycation products (RAGE) mediated chemotaxis to clean up cell debris resulting from the damage. Chondroblasts then secrete cartilage matrix around themselves in order to reform the lost cartil…
Structure
Within adults and developing adults, most chondroblasts are located in the perichondrium. This is a thin layer of connective tissue which protects cartilage and is where chondroblasts help to expand cartilage size whenever prompted to by hormones such as GH, TH, and glycosaminoglycans. They are located on the perichondrium because the perichondrium, located on the outside of developing bone, is not as heavily ensheathed in cartilage extracellular matrix as the interior an…
Development
As suggested in the name, mesenchymal progenitors originate from the mesoderm. These cells, when forming from the mesoderm, specifically form from embryonic stem cells via induction through BMP4 and fibroblast growth factor FGF2 while the fetus is inside the womb. It has been suggested that differentiating embryonic stem cells with these growth factors could prevent stem cells, once injected into potential patients, from forming teratomas, or stem cell caused tumors.
Pathology
Chondroblastomas can sometimes form, which are benign tumors that form at the sites of endochondral ossification due to over stimulation of the chondroblasts. When they form, they are usually found on the upper or lower tibia as well as the upper humerus where chondroblast activity is most apparent. Rarely, they can be found on the feet, hands, flat bones, or spine. 30–50% of these sarcomas have an accompanying osteoblastoma which is similarly benign.
See also
• List of human cell types derived from the germ layers