What is the chemical reaction in copper corrosion?
Well copper corrosion can be due to many reasons and reactants including ammonia, chlorine, Sulfur and the reaction is electrochemical in nature (not chemical) the patina is normally green, but can be also blue depending on the reactants. So the copper corrosion/electrochemical reaction is.
What is the chemical equation for copper and oxygen?
When copper reacts with oxygen, then it produces copper oxide. The chemical equation of this reaction is 4Cu + O2 = 2Cu2O, and forms Copper Oxide. Silver objects corrode slowly in the air due to the presence of H2S in the air. The chemical equation of this reaction is 2Ag + O2 = Ag2O.
What is the chemical equation for the green coating of copper?
The green coating is mainly Copper (II) Carbonate CuCO3 caused by slow chemical reactions involving the copper metal and water and carbon dioxide. 2 Cu + H2O + CO2 + O2 → Cu (OH)2 + CuCO3 The chemistry of the reaction resulting in the formation of rust can be summarized as follows: The chemical equations for rust formation
What is the chemical equation for the corrosion reaction of silver?
The chemical equation of this reaction is 4Cu + O2 = 2Cu2O, and forms Copper Oxide. Silver objects corrode slowly in the air due to the presence of H2S in the air. The chemical equation of this reaction is 2Ag + O2 = Ag2O.
See more
What is the formula for corrosion of copper?
Answer. When copper or silver combines with oxygen, the process is known as corrosion or oxidation. When copper reacts with oxygen, then it produces copper oxide. The chemical equation of this reaction is 4Cu + O2 = 2Cu2O, and forms Copper Oxide.
What is the equation of corrosion?
The chemical formula for rust is Fe2O3 and is commonly known as ferric oxide or iron oxide. The final product is a series of chemical reactions simplified below as- The rusting of the iron formula is simply 4Fe + 3O2 + 6H2O → 4Fe(OH)3.
What is the chemical formula and Colour of corroded copper?
Corrosion of copper Cu2O is further oxidized to form black-colored CuO. This CuO reacts in the atmosphere to form Cu2(OH)2(s)(Malachite) that is blue and Cu4SO4(OH)6(s)(Brochantite) that is green with CO2, SO3 and H2O.
What is corrosion give the reaction of corrosion of copper?
Corrosion causes damage to car bodies, bridges, iron railings, ships and to all objects made of metals, specially those of iron. In case of rusting of copper, the metallic copper reacts with oxygen, carbon-dioxide and atmospheric moisture and develops a green coloured coating of copper hydroxide and copper carbonate.
What is the chemical reaction of corrosion?
Corrosion reactions of metallic materials are of electrochemical nature, that is, the reaction can be divided into an oxidation reaction (anodic reaction) and a reduction reaction (cathodic reaction).
What is rust write its formula?
Rust is a general term for a series of iron oxides, usually, red oxides, formed by the reaction of iron with oxygen in the presence of water or air moisture. The chemical formula for rust is Fe2O3, which is called iron oxide but is also known as ferric oxide.
What is the equation of green coating on copper?
A greenish coating that develops on copper utensils is due to the formation of. The Correct Answer is (D) Cu(OH)2. CuCO3.
What is chemical name of corrosion?
iron oxideRust is hydrated ferric oxide and its chemical formula is Fe2O3. xH2O. The generic name of a very common compound, iron oxide, is rust.
Is corrosion of copper a chemical change?
Oxidized Copper Lion. The process of rusting, or oxidization, exemplifies a chemical reaction.
What is the color of copper oxide?
Copper reacts with oxygen in the atmosphere to form copper (I) oxide that is red when copper metal is exposed to the environment. Cu2O is further oxidized to form black-colored CuO. This CuO reacts in the atmosphere to form Cu2 (OH)2 (s) (Malachite) that is blue and Cu4SO4 (OH)6 (s) (Brochantite) that is green with CO2, SO3 and H2O. ...
What is the reaction of silver to sulphur?
Silver reacts with sulphur and sulphur compounds in the air to give silver sulphide (Ag 2 S) which is black. Exposed silver forms Ag 2 S as it reacts with the H 2 S (g) in the atmosphere which is present due to certain industrial process.
What is the process of interacting with water or air that causes the transformation of pure metals to undesirable substances?
Answer: Corrosion is described as the natural process that when interacting with substances such as water or air, causes the transformation of pure metals to undesirable substances. The reaction causes the metal to damage and decompose, beginning with the portion of the metal that is exposed to the atmosphere and spreading across ...
What color is corrosion thin coating?
Therefore, on corrosion thin coating formed on silver metal is black in colour and that on copper metal is green in colour.
What is the effect of oxidation reaction on metals?
Corrosion is an effect of oxidation reaction. Hence, we can say that it is a process in which metals are attacked by substances such as air, moisture or acids around it. Most commonly metals are oxidised by the oxygen present in air. The metal is said to be corroded and the process is corrosion .
What is the black coating of silver sulphide?
The silver sulphide formed is black in color and thus, we can understand that a thin black coating of silver sulphide is formed on the surface when silver gets corroded.
Why is copper corrosion inhibitor important?
A copper corrosion inhibitor is often needed to reduce the amount of soluble copper generated via corrosion and to complex any soluble copper to the cooling water.
What is the dielectric constant reduction?
The dielectric constant reduction is based on increased fluorine concentration in the dielectric film. Indeed, O-Si-F has less polar bonds than O-Si-O. However, the major drawback with a high amount of flourine in the material is the reaction of this element with water leading to the formation of hydrofluoric acid (HF) impacting the copper line integrity with copper corrosion [TRE 98, PAS 97 ]. Furthermore, different studies have suggested that to achieve stable low- k films, the amount of fluorine incorporated (atom %) should be less than 10% [ SEN 97 ]. They demonstrated that the Young modulus and the hardness decrease with increasing fluorine incorporation. Despite these drawbacks, fluorosilicate glass ( k = 3.8) was successfully implemented for the 130 nm technology node by ST Microelectronics.
What are the requirements for sampling and testing for solvents used in the paint industry?
Sampling and testing requirements for solvents used in the paint industry are summarized in a special standard. 74 This comprehensive list of standards used by paint industry also includes a brief discussion of each method of testing, including sampling, specific gravity, color, distillation range, nonvolatile matter, odor, water, acidity, alkalinity, ester value, copper corrosion test, sulfur, permanganate time test for acetone and methanol, flash point, purity of ketones, solvent power evaluation, water miscibility, analysis of methanol, analysis of ethylene and propylene glycols, acid wash color of aromatic hydrocarbons, paraffins and other nonaromatic hydrocarbons in aromatics, and aromatics in mineral spirits.
How thick is a copper canister?
There has already been a trend in this direction with, for example, the reference thickness of the copper canister in the Swedish programme being reduced, first from the original thickness of 20 cm to a thickness of 10 cm and now to the current reference thickness of 5 cm. Even this thickness is more than is required as a corrosion barrier. It is impractical to fabricate a separate copper shell of this size with a significantly smaller wall thickness, but perhaps the copper corrosion barrier could be applied as a thinner cladding instead.
Does gasoline have copper corrosion?
Although iron oxidation is a major cause of fuel system corrosion, other non-ferrous components are also susceptible to corrosion caused by reactive sulphur species found in some diesel fuels and gasoline. As a result, many fuel specifications have copper corrosion limits as determined by a copper strip test. Typically thiadiazole chemistry is effective at controlling copper corrosion. More recently, there have been cases of silver contacts in fuel sending/sensing units suffering damaged from free sulphur and other sulphur species remaining in gasoline after the desulphurisation process. This problem has occurred sporadically in North America and other regions. In the US, the ASTM requirements now stipulate that gasoline pass a silver corrosion test, whilst in other markets, fuels distributors regularly check that products meet their own internal specifications. Figure 7.5 illustrates the effect of free sulphur on silver strip ratings. The protection provided by two different fuel additives is shown in Fig. 7.6.
Does thiadiazole help with copper corrosion?
Typically thiadiazole chemistry is effective at controlling copper corrosion. More recently, there have been cases of silver contacts in fuel sending/sensing units suffering damaged from free sulphur and other sulphur species remaining in gasoline after the desulphurisation process.
Does pure water corrode copper?
However, new research activity was started to resolve the speculative issue regarding copper corrosion by pure water: studies conducted at the Royal Institute of Technology (KTH) in Sweden claimed to show that copper could corrode in pure water. Similar claims had been presented already in the 1980s by the same researchers, but, because of lacking information on the experimental design, attempts to reproduce the test results elsewhere turned out inconclusive at that time. The published new results made it possible to duplicate the tests and, indeed, presence of hydrogen could be observed also in other tests. Hydrogen could indicate corrosion, but other explanations could be possible as well—especially as the test results seemed to be in contradiction to standard thermodynamic knowledge. Therefore, SKB decided to launch an extensive research program to explain the origin of hydrogen in the tests. As the corrosion issue was, of course, relevant for the Olkiluoto repository as well, Posiva followed suit.
What Does Copper Corrosion Mean?
Copper corrosion is the corrosion of materials made of copper or copper alloys. When exposed to the atmosphere, copper oxidizes, causing normally bright copper surfaces to tarnish. After a few years, this tarnish gradually changes to dark brown or black, and finally to green.
Why is copper immune to corrosion?
The metal is basically immune to corrosion due to a naturally occurring protective film known as a patina that forms on the metal's surface. If this protective film, usually consisting of reddish-brown cuprous oxide (Cu 2 O), is destroyed, then copper will eventually corrode.
What is uniform corrosion?
Uniform corrosion, which is identified by the presence of a relatively uniform layer of copper corrosion byproducts across the inner surface of a pipe wall. It is typically associated with elevated copper levels at the taps.
What are the effects of air pollutants on copper?
This change promotes the failure of printed circuit boards in microelectronic devices.
Can copper be corroded?
Coupling of copper with aluminum or steel can lead to severe galvanic corrosion. Cyanides are also very corrosive to copper pipes.
Is copper bad for you?
This leaching is a product of corrosion. A small amount of copper consumption is acceptable for humans because it serves as an essential nutrient, but too much may cause gastrointestinal problems.
Is copper a crevice?
Copper is also susceptible to crevice corrosion attack. Copper corrosion occurs at negligible rates in unpolluted air, water and deaerated non-oxidizing acids. However, it is susceptible to more rapid attack in oxidizing acids, oxidizing heavy-metal salts, sulfur, ammonia, and some sulfur and ammonia compounds.
What is corrosion in metal?
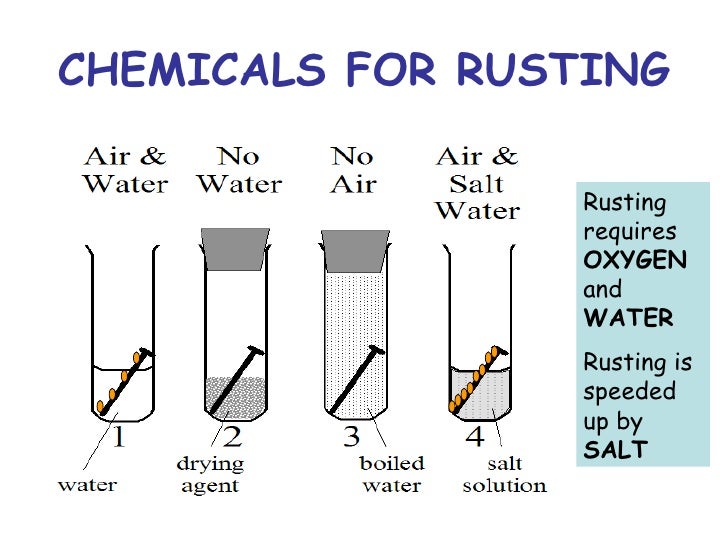
CORROSION or RUSTING : Corrosion is defined as the oxidation of metal by air. Although presence of moisture makes corrosion faster but it is not necessary condition. In corrosion, the metal is slowly oxidized by the air. Corrosion of Iron is also called Rusting of iron.
What are some examples of corrosion?
The black coating on silver and the green coating on copper are other examples of corrosion.
What is the process of rusting iron?
Corrosion of Iron is also called Rusting of iron. Iron articles are shiny when new, but get coated with a reddish brown powder called rust (Fe2O3.n H2O) when left for some time. This process is commonly known as rusting of iron. The black coating on silver and the green coating on copper are other examples of corrosion.
How is corrosion prevented?
Corrosion of metals is prevented by not allowing them to come in contact with moisture and O2.
What is the green coating on copper called?
COPPER CORROSION. The green coating on copper metal called a Patina. The green coating is mainly Copper (II) Carbonate CuCO3 caused by slow chemical reactions involving the copper metal and water and carbon dioxide. The chemistry of the reaction resulting in the formation of rust can be summarized as follows:
How to make a metal alloy?
This is achieved by the following methods: 1 By coating with paints: Paint coated metal surfaces keep out air and moisture. 2 By coating with oil and grease: Application of oil and grease on the surface of iron tools prevents them from moisture and air. 3 By alloying with other metals: Alloys (mixture of metals) is more resistant to corrosion. Example: stainless steel. 4 By the process of Galvanization: This is a process of coating zinc on iron sheets by using electric current. In this Zinc forms a protective layer of zinc carbonate on the surface of iron.This prevents corrosion. 5 Electroplating: It is a method of coating one metal over the surface of Iron (or other metal) by passing electric current. Example: silver plating, nickel plating. This method not only lends protection but also enhances the metallic appearance. 6 Sacrificial Protection: Sometime more electropositive metal like Magnesium is used to protect Iron. The more electropositive metal is connected with iron surface or articles . The electropositive reduces Iron if it is oxidized and saves Iron. Thus finally Electropositive metal like Magnesium is sacrificed to prevent Iron from oxidation.
What is the chemical equation for silver corroded?
Silver objects corrode slowly in the air due to the presence of H2S in the air. The chemical equation of this reaction is 2Ag + O2 = Ag2O.
What is the chemical reaction of copper and oxygen?
When copper or silver combines with oxygen, the process is known as corrosion or oxidation . When copper reacts with oxygen, then it produces copper oxide. The chemical equation of this reaction is 4Cu + O2 = 2Cu2O, and forms Copper Oxide. Silver objects corrode slowly in the air due to the presence of H2S in the air.
What is the effect of copper on air?
Copper Corrosion: When copper is exposed to air for a longer time , then copper reacts with Carbon Dioxide and water of air to form a green coating of basic copper carbonate on the surface of the object.The formation of this green coating on the surface of a copper object corrodes it.