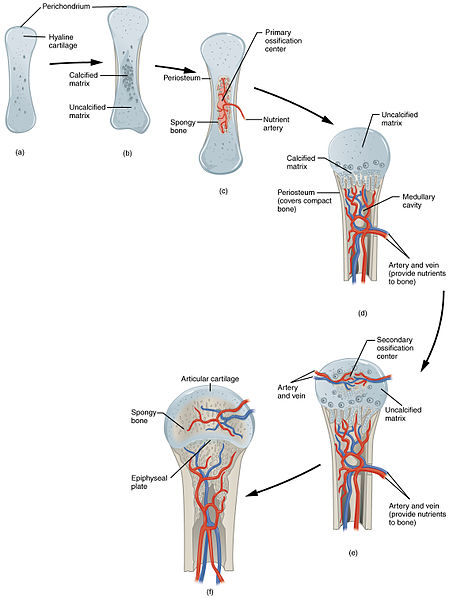
In fact, perichondrium is a fibrous connective tissue while periosteum is a membranous connective tissue. Furthermore, another significant difference between perichondrium and periosteum is that the perichondrium consists of fibroblast cells while periosteum consists of osteoblast cells.
What is the function of perichondrium and periosteum?
Generally, perichondrium is present in the nose, hyaline cartilage in larynx and trachea, elastic cartilage in ear, etc. Periosteum is present in the surfaces of bone tissue. Besides these, the primary function of perichondrium is to cover cartilage to protect the bones from injury.
What is perichondrium made of?
The perichondrium is a fibrous connective tissue. It is a dense layer that covers cartilage in the body. Hence, perichondrium is present in most parts of the body. It is made out of two layers: outer fibrous layer and inner chondrogenic layer. The outer fibrous layer contains collagen-producing fibroblast cells.
What are periosteum and perichondrium grafts?
Periosteum and perichondrium grafts are biomembranes with two layers, an outer fibrous layer and an inner cambium, or osteogenic, layer. Perichondrium lines developing bone, and when vascularized, becomes periosteum, or the nonjoint lining of bone.
What happens if the perichondrium is damaged?
Damage to the perichondrium is known as perichondritis, and can result from cartilage injuries. This often occurs from microtraumas such as piercings, insect bites, or burns to the perichondrium tissue, leading to inflammation and, sometimes, infection.
Is periosteum a perichondrium?
The key difference between perichondrium and periosteum is that perichondrium is the dense membrane of connective tissue that covers cartilages while periosteum is the membrane that covers all the bones in the body. Perichondrium and periosteum are two types of connective tissues present in the body.
What is the perichondrium?
Perichondrium is a type of connective tissue, and also functions in the growth and repair of cartilage. Once vascularized, the perichondrium becomes the periosteum. [
Where is the perichondrium and what is its function?
Perichondrium can be found around the perimeter of elastic cartilage and hyaline cartilage. Perichondrium is a type of irregular collagenous ordinary connective tissue, and also functions in the growth and repair of cartilage. Perichondrium contains type I collagen and type XII collagen.
What is the periosteum also known as?
The periosteum that covers the outer surface of the bones of the skull is known as the pericranium, except when in reference to the layers of the scalp.
What is the perichondrium composed of?
Perichondrium is composed of two layers: an outer fibrous layer and an inner chondrogenic layer. The outer fibrous layer is a dense membrane of connective tissue composed of fibroblast cells which are responsible for collagen fiber production.
What cells are found in the periosteum?
Periosteum and endosteum contain cells (osteoblasts, osteoclasts, and osteoprogenitor cells) required for bone development and remodeling of the bone.
What is the importance of the perichondrium that surrounds cartilage?
What is the importance of the perichondrium that surrounds cartilage? It functions in growth and repair of cartilage. It resists outward expansion when cartilage is subjected to pressure.
Which type of cartilage is surrounded by a perichondrium?
Elastic cartilageElastic cartilage (like hyaline cartilage) has chondrocytes located in lacunae and the tissue is surrounded by a perichondrium .
What are two types of cartilage that do not have a perichondrium?
Correct answer 1. Hyaline cartilage is highly resistant to compression. It does NOT always have a perichondrium (as in articular cartilage). Its matrix consists of type II collagen and hyaluronan, and it is NOT found in the pinna of the ear and epiglottis (elastic cartilage is found there).
What are the two layers of periosteum?
Periosteum can be thought of as consisting of two distinct layers, an outer fibrous layer and an inner layer that has significant osteoblastic potential.
What are 3 functions of the periosteum?
The periosteum is known to have three roles: (1) a source of osteocytes/chondrocytes that differentiate from pluripotent undifferentiated mesenchymal cells, (2) a scaffold for the proliferation of osteocytes/chondrocytes, and (3) a source of growth factors.
Where is the periosteum located?
boneThe periosteum covers all surfaces of the bone except for those capped with cartilage, as in the joints, and sites for attachment of ligaments and tendons. Fibrous cartilage often takes the place of the periosteum along grooves where tendons exert pressure against the bone.
What is the perichondrium quizlet?
A layer of dense irregular connective tissue. Surrounds the cartilage.
Where is perichondrium located?
Perichondrium is mainly found on the surfaces of elastic and hyaline cartilage, which can be found in multiple locations of the body, such as in the ears, nose, joints and ribs. Damage to the perichondrium is known as perichondritis, and can result from cartilage injuries.
What is the importance of perichondrium that surrounds cartilage?
What is the importance of the perichondrium that surrounds cartilage? It functions in growth and repair of cartilage. It resists outward expansion when cartilage is subjected to pressure.
Which type of cartilage is surrounded by a perichondrium?
Elastic cartilageElastic cartilage (like hyaline cartilage) has chondrocytes located in lacunae and the tissue is surrounded by a perichondrium .
What are some interesting facts about Perichondrium?
What are the most important facts to know about perichondrium? The perichondrium is a dense layer of fibrous connective tissue that covers the surface of most of the cartilage in the body. The perichondrium consists of an outer fibrous layer that contains fibroblasts and an inner chondrogenic layer that contains chondroblasts.
Which layer of the perichondrium contains cartilage producing cells?
Additionally, the inner layer of the perichondrium contains cartilage -producing cells, known as chondroblasts, which enable cartilage to grow. Chondroblasts secrete a substance called the extracellular matrix, which contains various components that provide structure and strength to cartilage. In addition, chondroblasts mature into chondrocytes, ...
What is the damage to the perichondrium?
Damage to the perichondrium is known as perichondritis, and can result from cartilage injuries. This often occurs from microtraumas such as piercings, insect bites, or burns to the perichondrium tissue, leading to inflammation and, sometimes, infection. Symptoms can include pain, redness, and swelling, which may require medical treatment.
What is the layer of connective tissue that covers the external surface of most of the body's cartilage?
The perichondrium is a dense layer of connective tissue that covers the external surface of most of the body’s cartilage (a strong, flexible, and semi-rigid tissue found throughout the body).
What is the role of the periosteum in bone growth?
In doing so, the periosteum promotes the development and growth of the bones, while the perichondrium promotes the development and growth of cartilage. The periosteum assists bone growth by facilitating the supply of blood and nutrients to bone tissue. Both types of tissue also provide protection from bone injury, although through different means.
What does it mean when your ear is cauliflower?
Symptoms can include pain, redness, and swelling, which may require medical treatment. Serious ear trauma leading to diminished blood flow from the perichondrium to the cartilage can lead to a puffy, cauliflower-like appearance, and is commonly referred to as cauliflower ear. This condition may require medical treatment, ...
Which connective tissue covers all bones in the body?
The perichondrium is a dense layer of fibrous connective tissue that covers many types of cartilage in the body, whereas the periosteum is a thin layer of membranous connective tissue that covers all bones in the body.
Articular Cartilage
Lily Jeng, ... Myron Spector, in Principles of Regenerative Medicine (Second Edition), 2011
Cartilage tissue engineering
J.M. Patel, M.G. Dunn, in Regenerative Engineering of Musculoskeletal Tissues and Interfaces, 2015
Maintenance Awry – Chondrodysplasias and Achondroplasia
Fgf18 is expressed in perichondria. Fgf18 null mice have a growth-plate phenotype almost indistinguishable from that in FgfR3 null mice except for ossification defects at sites of FgfR2 expression.
Cells to Make and Cells to Break
Tgfß1 is expressed in the perichondria of fetal mouse long bones where it acts to decrease chondrocyte proliferation and hypertrophy in endochondral ossification, providing a feedback system ( Alvarez et al., 2001 ).
Arthroscopic Methods for Cartilage Repair
C. Wayne McIlwraith BVSc, PhD, DSc, Dr med vet (h.c. Vienna), DSc (h.c. Massey), Laurea Dr (h.c. Turin), D vet med (h.c. London), FRCVS, Diplomate ACVS, ECVS & ACVSMR, ... Ian M. Wright MA, VetMB, DEO, Diplomate ECVS, MRCVS, in Diagnostic and Surgical Arthroscopy in the Horse (Fourth Edition), 2015
Growth and Morphogenesis of Long Bones
Igf1 and Igf2 are expressed in the perichondria and proliferating chondrocytes but not in osteocytes of the long bones of growing rats between birth and adulthood.
Skulls, Eyes and Ears
Tenascin, which is located in chondrogenic condensations, perichondria, osteogenic cells and differentiated cartilage and bone, plays a key role in mesenchymal cell condensation ( Chapter 19 ).