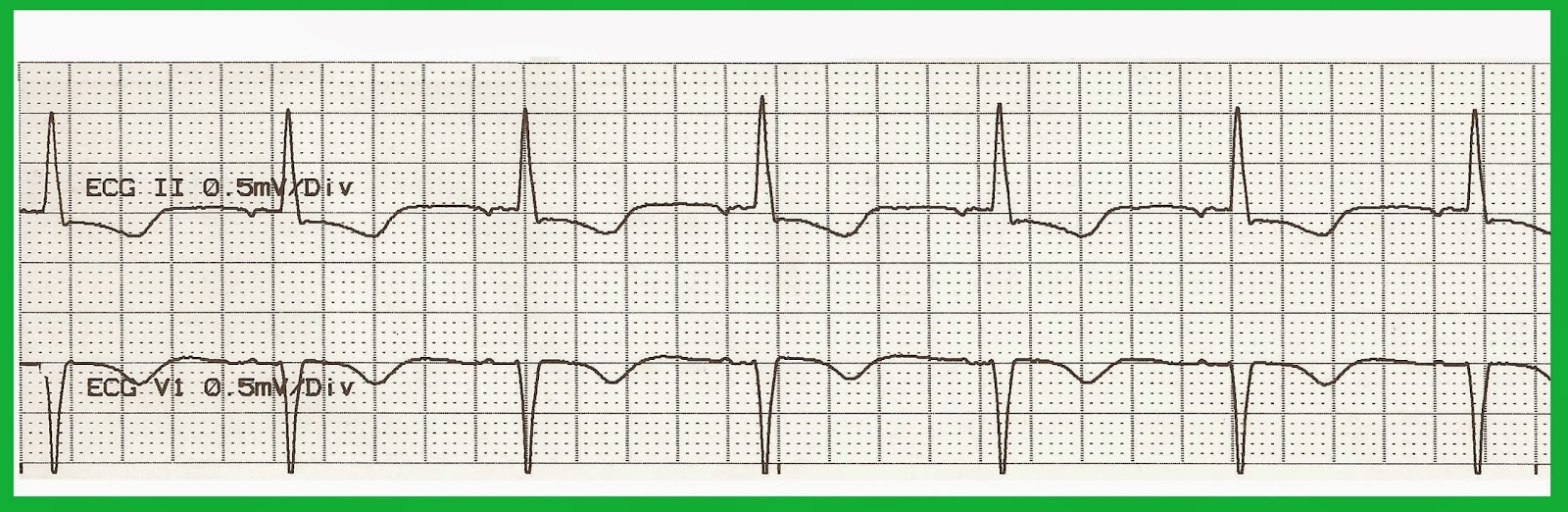
Idioventricular rhythm is a cardiac rhythm caused when ventricles act as the dominant pacemaker. So, this is the key difference between junctional and idioventricular rhythm. Junctional rhythm can be without p wave or with inverted p wave, while p wave is absent in idioventricular rhythm.
Is junctional rhythm a bad thing?
Junctional rhythm usually is associated with a benign course, but it can cause symptoms due to AV dyssynchrony (pseudo “pacemaker syndrome”). Junctional rhythm can cause symptoms due to bradycardia and/or loss of AV synchrony.
How do you identify idioventricular rhythm?
Ventricular rhythm and accelerated ventricular rhythm (idioventricular rhythm)
- Causes of ventricular rhythm and idioventricular rhythm. The usual mechanisms are responsible for all ventricular rhythms. ...
- Definitions and ECG criteria for ventricular rhythm and idioventricular rhythm. Ventricular rhythm exists if 3 or more consecutive beats have a ventricular origin. ...
- Management and treatment of ventricular rhythms. ...
How to identify a junctional rhythm?
Junctional rhythm can cause symptoms due to bradycardia and/or loss of AV synchrony. These symptoms (which can be vague and easily missed) include lightheadedness, palpitations, effort intolerance, chest heaviness, neck tightness or pounding, shortness of breath, and weakness.
What are the treatment options for junctional rhythm?
- Junctional beats and junctional rhythm. If the normal sinus impulse disappears (e.g sinus arrest) cells around the atrioventricular node may discharge impulses.
- Treatment of junctional beats and rhythm. Symptomatic junctional rhythm is treated with atropine. ...
- Junctional tachycardia. ...
- Treatment of junctional tachycardia. ...
How do you identify idioventricular rhythm?
0:181:47Idioventricular Rhythm ECG - EMTprep.com - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipThe rate of an idioventricular rhythm will be generally between 20 and 40 beats per minute theMoreThe rate of an idioventricular rhythm will be generally between 20 and 40 beats per minute the rhythm will be regular. There will be no P waves. And therefore no PR interval.
What is an idioventricular rhythm?
Idioventricular rhythm is a slow regular ventricular rhythm, typically with a rate of less than 50, absence of P waves, and a prolonged QRS interval.
What's another name for idioventricular rhythm?
An idioventricular rhythm is frequently referred to as a “slow ventricular tachycardia” for this reason. When the ventricular rate is between 60 and 100 bpm, it is referred to as an accelerated idioventricular rhythm.
What is the difference between IVR and AIVR?
Idioventricular Rhythm (IVR) When Idioventricular Rhythm has a rate greater than 40 bpm it is referred to as Accelerated Idioventricular Rhythm or AIVR.
Is idioventricular rhythm shockable?
Non-shockable rhythms included asystole, pacing, slow VT, idioventricular rhythms, sinus and atrial based rhythms, some of which contained ventricular ectopic activity of differing grades.
Does idioventricular rhythm have a pulse?
An idioventricular rhythm — not accelerated — has a heart rate of < 60 beats per minute. AIVR is hemodynamically stable, and thus no specific treatment is needed.
What rate is idioventricular rhythm?
Idioventricular rhythm is a slow regular ventricular rhythm with a rate of less than 50 bpm, absence of P waves, and a prolonged QRS interval.
Can junctional rhythm have wide QRS?
If the QRS complex is wide, an accelerated junctional rhythm resembles an accelerated ventricular rhythm. The rate of the ectopic ventricular rhythm is usually 70 to 110 beats/min.
What are the characteristics of a junctional rhythm?
Junctional Escape Rhythm produces a heart rate between 40-60 beats per minute and has a relatively narrow QRS. The P waves may be hidden (Example Strip 1), inverted, retrograde, or short/upright. If there is only one late Junctional beat (Example Strip 2) this is referred to as a Junctional Escape Beat.
What is junctional rhythm?
Similarly, you may ask, what is a junctional rhythm? Junctional rhythm describes an abnormal heart rhythm resulting from impulses coming from a locus of tissue in the area of the atrioventricular node, the "junction" between atria and ventricles.
What is the rate of ventricular rhythm?
Accelerated idioventricular rhythm is a ventricular rhythm with a rate of between 40 and 120 beats per minute. Accelerated idioventricular arrhythmias are distinguished from ventricular rhythms with rates less than 40 (ventricular escape) and those faster than 120 (ventricular tachycardia).
What is less than 40 BPM?
Less than 40 BPM is termed junctional bradycardia, more than 60 BPM and less than 100 BPM is accelerated junctional rhythm. Click to see full answer.
What is the ventricular rate?
Ventricular rhythm exists if 3 or more consecutive beats have a ventricular origin. The ventricular rate is between 20 to 40 beats per minute and the rhythm is regular. There is always secondary ST-T changes, meaning that the ST-T segment is discordant ( Figure 1 ).
Is ventricular rhythm reliable?
Importantly, ventricular rhythm is not a reliable rhythm as it may cease working. Figure 1 exemplifies a ventricular rhythm. Accelerated ventricular rhythm (idioventricular rhythm) is a rhythm with rate at 60–100 beats per minute. As in ventricular rhythm the QRS complex is wide with discordant ST-T segment and the rhythm is regular (in most cases).
How many beats per minute is a junctional rhythm?
Junctional escape rhythm is a regular rhythm with a frequency of around 40–60 beats per minute.
What is junctional tachycardia?
Junctional tachycardia. Junctional tachycardia is caused by abnormal automaticity in the atrioventricular node, cells near the atrioventricular node or cells in the bundle of His. It is very rare among adults and elderly, but is relatively common in children. When occurring in adults and elderly it is referred to as nonparoxysmal junctional ...
What is the difference between JET and NPJT?
When occurring in adults and elderly it is referred to as nonparoxysmal junctional tachycardia (NPJT) whereas it is referred to as junctional ectopic tachycardia (JET) in children. NPJT is caused by ischemia, digoxin overdose, theophylline, overdose cathecholamines, electrolyte disorders and perimyocarditis.
What is the most common rhythm in the AV node?
The most common rhythm arising in the AV node is junctional rhythm , which may also be referred to as junctional escape rhythm. Junctional tachycardia is less common. Basic knowledge of arrhythmias and cardiac automaticity will facilitate understanding of this article.
What is the vagal tone of a well trained athlete?
Well-trained athletes may have very high Vagal tone which lowers the automaticity in the sinoatrial node to the point where cells in the AV-junction establishes an escape rhythm. This is asymptomatic and benign.
What is the primary objective of junctional tachycardia?
Treatment of junctional tachycardia. The primary objective is to treat the underlying cause and/or eliminate provocative medications. Electrical cardioversion is ineffective and should be avoided (electrical cardioversion may be pro-arrhythmogenic in patients on digoxin).
What happens when cells in bundle of His are not reached by the atrial impulse?
In such scenarios, cells in the bundle of His (which possess automaticity) will not be reached by the atrial impulse and hence start discharging action potentials and an escape rhythm. This will also manifest as a junctional escape rhythm on the ECG.
How many junctional rhythms are there?
There are 4 Junctional Rhythms to be discussed: 1. Junctional Escape Rhythm, 2. Accelerated Junctional Rhythm, 3. Junctional Tachycardia, and 4. Junctional Bradycardia. There are also 2 ectopic Junctional Beats that you may see as well that we will discuss as well: Junctional Escape Beats and Premature Junctional Contractions (PJCs).
Where does the impulse originate in Junctional Ectopic Beats?
The main thing to understand about Junctional Rhythms or Junctional Ectopic Beats is that the impulse originates in the AV node. To know that a rhythm is a type of Junctional Rhythm, look at the P-waves to see if it is inverted before or after the QRS complex or hidden in the QRS.
What is junctional escape beat?
A junctional escape beat is essentially a junctional ectopic beat that occurs within the underlying rhythm. Example: Junctional Escape Beat. Note the pause and then the Junctional Escape Beat within the underlying rhythm. Image from researchgate.com.
Where are P waves in a rhythm?
P-waves can present themselves in a Junctional Rhythm as inverted. P-waves can be in front of the QRS complex, behind the QRS complex, or hidden altogether. Image from Thoracic Key.
How many beats per minute is junctional rhythm?
The inherent rate of a junctional rhythm is a little slower, so it's between 40 and 60 beats per minute. And the key characteristic of a junctional rhythm is that the P wave is messed up. It's either absent, it's inverted, it happens after the QRS complex instead of before, or we have a very short PR interval.
What is the heart rate of junctional tachycardia?
With accelerated, it's between 60 and 100. With junctional tachycardia, the heart rate will be over 100. In this case, we have approximately 115 beats per minute, so that fits the bill for junctional tachycardia.
How many beats per minute is 1500?
If we use the small box method to calculate this heart rate shown above, we can see that there are 18 small boxes between the R waves. 1500 divided by 18 is 83. This means 83 beats per minute. We know it's not a regular junctional rhythm because that inherent rate is supposed to be between 40-60 BPM, and this rate is higher at 83. Accelerated junctional rhythms have an expected rate of 60-100 BPM.
Is the ventricular rhythm regular?
There are equal distances between the R waves, meaning the ventricular rhythm is regular. The P waves, though they look strange, are also regular; they have an equal distance between them. So the atrial rhythm is also regular.
Can digoxin be used for junctional dysrhythmias?
Again, remember that you would NOT use digoxin in patients with junctional dysrhythmias as it is contraindicated.