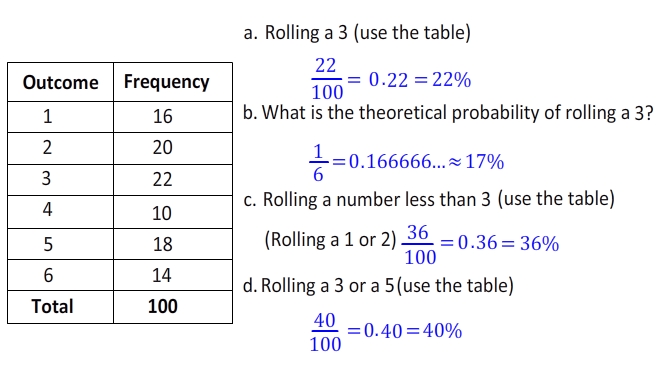
Comparing Empirical (Experimental) and Theoretical Probabilities
- Empirical (experimental) probability is the probability observed in the chart above. The 8 was rolled 8 times out of 50 rolls. ...
- Theoretical probability is based upon what is expected when rolling two dice, as seen in the "sum" table at the right. ...
- The experiment rolled more 8's than would be expected theoretically. ...
What is the difference between theoretical and empirical?
Reference:
- “Empirical Research: Definition, Methods, Types and Examples.” QuestionPro, 14 Dec. 2018, Available here.
- “Empirical Research.” Wikipedia, Wikimedia Foundation, 15 Sept. 2019, Available here.
- “Conceptual Research: Definition, Framework, Example and Advantages.” QuestionPro, 18 Sept. 2018, Available here.
- Patrick. ...
How to calculate empirical probability?
- z = -1 to z = +1 (within 1 sigma) Then,
- z = -2 to z = +2 (within 2 sigma) Lastly,
- z = -3 to z = +3 (within 3 sigma)
What is the formula of theoretical probability?
What is Empirical Probability?
- Formula for Empirical Probability. Total No. ...
- Example of Theoretical Probability. The table below shows a dice thrown three times and the corresponding result. ...
- Advantages and Disadvantages. ...
- Different Types of Probabilities. ...
- Related Readings. ...
What is empirical probability defined?
In probability theory, empirical probability is an estimated probability based upon previous evidence or experimental results. As such, empirical probability is sometimes referred to as experimental probability, and we can distinguish it from probabilities calculated from a clearly-defined sample space.
What is theoretical and empirical probability example?
The empirical probability = 8/50 = 16%. 2) Theoretical probability is based upon what is expected when rolling two dice, as seen in the "sum" table at the right. The theoretical probability of rolling an 8 is 5 times out of 36 rolls. The theoretical probability = 5/36 ≈ 13.9%.
What is the difference between theoretical and experimental probability?
Theoretical probability describes how likely an event is to occur. We know that a coin is equally likely to land heads or tails, so the theoretical probability of getting heads is 1/2. Experimental probability describes how frequently an event actually occurred in an experiment.
What is an example of a theoretical probability?
Theoretical probability is probability that is based on an ideal situation. For instance, since a flipped coin has two sides and each side is equally likely to land up, the theoretical probability of landing heads (or tails) is exactly 1 out of 2.
What do you mean by empirical probability?
An empirical probablility, also called an experimental probability, is closely related to the relative frequency of an event. Empirical probability uses the number of occurrences of a given outcome within a sample set as a basis for determining the probability of that outcome occurring again.
What is the difference between empirical and theoretical research?
Empirical: Based on data gathered by original experiments or observations. Theoretical: Analyzes and makes connections between empirical studies to define or advance a theoretical position.
What is a theoretical probability?
The theoretical probability is defined as the ratio of the number of favourable outcomes to the number of possible outcomes.
How do you determine the theoretical probability?
The theoretical probability formula is equal to the ratio of the number of favorable outcomes to the total number of probable outcomes. This formula is expressed as follows: Theoretical Probability = Number of favorable outcomes / Number of possible outcomes.
Where is theoretical probability used in real?
Probability is used in all types of areas in real life including weather forecasting, sports betting, investing, and more.
What are the different types of probability?
There are three major types of probabilities:Theoretical Probability.Experimental Probability.Axiomatic Probability.
What is an example of empirical probability?
Empirical probability, also called experimental probability, is the probability your experiment will give you a certain result. For example, you could toss a coin 100 times to see how many heads you get, or you could perform a taste test to see if 100 people preferred cola A or cola B.
What is the formula for finding the empirical probability of an event?
Empirical (Experimental) Probability = Number of times an event occurs (in this case the number 6 turns up) × Total number of trails (in this case the total number of times that the dice is cast = 120 times. Thus, the Empirical probability of the number 6 coming up in throws of 120 times of the dice is 120 × 1/6 =20.
What is empirical probability?
This is basically collecting data or running practical experiments to estimate the occurrence of an event. This is called empirical or experimental probability. Thus, the empirical probability is based entirely on experience and observation.
What is probability in math?
Probability is the measurement of chances – the likelihood that an event will occur. If the probability of an event is high, it is more likely that the event will happen. It is measured between 0 and 1, inclusive. So if an event is unlikely to occur, its probability is 0 whereas 1 indicates the certainty for the occurrence.
What is the probability of a coin tossing a coin?
Empirical or Experimental probability. When you toss a coin, there are equal chances of a head or a tail to come up. So we say that probability of head or tail is ½ or 0.5 each. Now repeat the experiment with 100 coins.
How does empirical probability compare to theoretical probability?
The empirical probability of an event comes closer to the theoretical probability as the number of observations becomes larger. The probability could be skewed if a small number of observations are available; in reality only if the number of observations is infinite does the empirical probability become equal to the theoretical probability.
What is the probability that you roll an odd number?
The probability that you roll an odd number is 3/6 (equals 1/2) because three of those outcomes - 1, 3, and 5 - are odd, which makes them "successes.". Empirical probabilities are your calculation of what "did" happen in an experiment.
Is probability theory correct?
The theoretical probability, on the other hand, has only one correct answer. As for professions, consider industries like insurance or casinos and name some of the people who work for those companies. Probability theory is also the foundation of statistical inference, used by statisticians and researchers of all kinds.
What is Theoretical Probability?
Theoretical probability is an approach in probability theory that is used to calculate the probability of an outcome of a specific event. Probability theory is a branch of mathematics that is concerned with finding the likelihood of occurrence of a random event. The probability that an event will occur lies between 0 and 1.
Theoretical Probability Formula
Theoretical probability can be calculated either by using logical reasoning or by using a simple formula. The result of such a type of probability is based on the number of possible outcomes. The theoretical probability formula is equal to the ratio of the number of favorable outcomes to the total number of probable outcomes.
How to Find Theoretical Probability?
Theoretical probability is used to express the likelihood of occurrence of an event without conducting any experiments. Suppose a person has 30 raffle tickets and, in total, 500 tickets were sold. The steps to calculate the theoretical probability of the person winning a prize are as follows:
Theoretical Probability vs Empirical Probability
Empirical probability is also known as experimental probability. Both theoretical probability and empirical probability are approaches to calculating the chance that a random event will occur. The difference between theoretical probability and empirical probability is given in the table below:
Examples on Theoretical Probability
Example 1: If a bag contains 5 red and 7 blue balls then what is the probability of picking up a red ball?
FAQs on Theoretical Probability
Theoretical probability in math refers to the probability that is calculated without any experiment being performed. It can be defined as the ratio of the number of favorable outcomes to the total number of possible outcomes.
What is experimental probability?
Experimental probability and theoretical probability are two aspects of probability, differentiated by the method of calculating the probability of an event. In experimental probability, the success and the failure of the concerned event are measured/counted in a selected sample and then the probability is calculated. In theoretical probability, a mathematical model is used to determine the behaviour responses to an event within the considered sample or the population.
What is the difference between the values obtained from the experiment and the theory?
The difference between the values obtained from the experiment and the theory is of a major concern when designing the statistical experiments. In theoretical probability, the ideal conditions are assumed, and the results are ideal values, but the deviation from ideal values in the experiment is due to the small sample size considered. ...
What is the branch of mathematics that describes the mechanism of probability?
Determining the probability of an event is related to mathematics, and the branch of mathematics explaining the mechanism is known as the probability theory. It gives a mathematical foundation for developing advanced concepts of probability.
What is the measure of expectation that a specific event will occur or a statement will be true?
Probability is the measure of expectation that a specific event will occur or a statement will be true. At all times, probability is given as a number between 0 and 1, where 1 and 0 imply that the event will definitely occur and the event will not occur respectively.