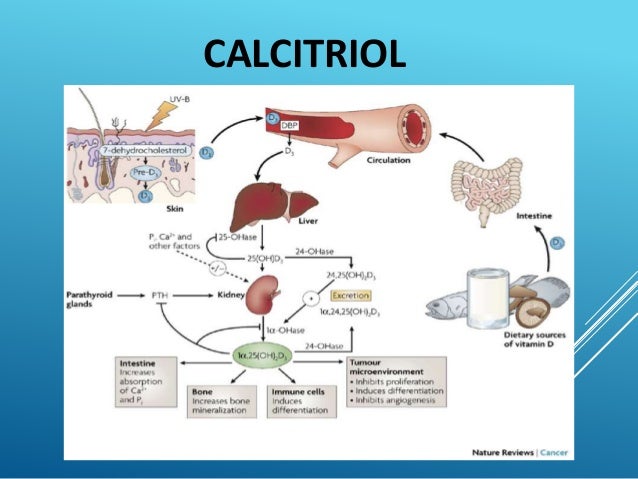
Calcitriol is used in patients with kidney disease who can't make enough of the active form of Vitamin D. This medication is also used to prevent and treat certain types of calcium/phosphorus/parathyroid problems that can happen with long-term kidney dialysis or hypoparathyroidism.
What does high levels of calcitonin mean?
If your calcitonin levels were high, it may mean you have C-cell hyperplasia or medullary thyroid cancer. If you are already being treated for this thyroid cancer, high levels may mean the treatment is not working or that cancer has returned after treatment.
What factors affect calcitonin levels?
- Abstract. To investigate the factors that affect postoperative recurrence in medullary thyroid carcinoma (MTC) patients, including preoperative ultrasonic characteristics and other factors.
- Background. ...
- Methods. ...
- Results. ...
- Discussion. ...
- Conclusions. ...
- Availability of data and materials. ...
- Abbreviations. ...
- Acknowledgements. ...
- Funding. ...
What are the differences between parathyroid and calcitonin?
- Promoting reabsorption of Ca2+ ion from renal tubule
- Stimulating demineralisation (resorption) of bones
- Stimulating absorption of Ca2+ ions from digested food
What gland produces calcitonin?
What side effects can calcitonin salmon injection cause?
- How should calcitonin salmon injection be used?
- Other uses for calcitonin salmon injection
- What special precautions should I follow?
- What special dietary instructions should I follow?
- Calcitonin salmon injection dosage
- What should I do if I forget a dose?
- What side effects can calcitonin salmon injection cause?
What are the roles of calcitriol calcitonin and parathyroid hormone?
These three hormones are: parathyroid hormone, calcitriol, and calcitonin. The hormones work by shuttling free calcium ions among the bones, kidneys, intestines, and blood. Combinations of parathyroid hormone, calcitriol, and calcitonin levels trigger the actions of osteoblasts and osteoclasts.
What is the function of the calcitonin?
Calcitonin is involved in helping to regulate levels of calcium and phosphate in the blood, opposing the action of parathyroid hormone. This means that it acts to reduce calcium levels in the blood.
What is the difference between calcitonin and parathyroid hormone?
The main difference between calcitonin and parathyroid hormone is that calcitonin reduces the calcium concentration in the blood, whereas parathyroid hormone increases calcium concentration in the blood.
What is the role between calcitriol and calcium?
Calcitriol is in a class of medications called vitamin D analogs. It works by helping the body to use more of the calcium found in foods or supplements and regulating the body's production of parathyroid hormone.
Does calcitriol increase blood calcium levels?
It is a hormone which binds to and activates the vitamin D receptor in the nucleus of the cell, which then increases the expression of many genes. Calcitriol increases blood calcium (Ca2+) mainly by increasing the uptake of calcium from the intestines.
Where is calcitriol produced?
Calcitriol is produced in the cells of the proximal tubule of the nephron in the kidneys by the action of 25-hydroxyvitamin D3 1-alpha-hydroxylase, a mitochondrial oxygenase and an enzyme which catalyzes the hydroxylation of 25-hydroxycholecalciferol (calcifediol).
Why is calcitonin not a thyroid hormone?
What is calcitonin? Calcitonin is a hormone that your thyroid gland makes and releases to help regulate calcium levels in your blood by decreasing it. Calcitonin opposes the actions of the parathyroid hormone, which is a hormone that increases your blood calcium levels.
How does calcitonin treat hypercalcemia?
In response to hypercalcemia, calcitonin is secreted by the parafollicular C cells. Calcitonin lowers serum calcium by decreasing renal calcium and phosphorus reabsorption and also by decreasing bone reabsorption. Calcitonin is not significant in overall calcium homeostasis, but it is an important therapeutic option.
How does calcitonin work for osteoporosis?
Calcitonin. Calcitonin is a hormone naturally produced in the thyroid. When given to patients with osteoporosis, calcitonin produces modest increases in bone mass because it slows the rate at which osteoclasts absorb bone.
What is the difference between calcitriol and calcium?
Calcitriol increases blood levels of calcium by increasing the absorption of calcium in the kidneys, increasing the absorption of calcium and phosphorus from the intestine, and increasing the release of calcium and phosphorus from the bones. Calcitriol helps the body to use calcium found in foods and supplements.
What is another name for calcitriol?
Calcitriol (Rocaltrol) is a strong form of vitamin D used to raise calcium levels. It's commonly used in people with kidney and parathyroid problems.
Is calcitriol for hypocalcemia?
Calcitriol is a hormonally-active, synthetic vitamin D analog prescribed to treat hypocalcemia, osteoporosis, and the prevention of corticosteroid-induced osteoporosis.
What is the active form of vitamin D?
Calcitriol is the active form of vitamin D. It does not exist in foods, but your body can make it provided it receives an adequate supply of vitamin D2 or D3. These food-form nutrients first undergo conversion into calcidiol, the storage form of vitamin D.
Where does vitamin D3 come from?
Vitamin D3. Along with vitamin D2, vitamin D3 occurs naturally in foods. However, the greatest effect normally comes from the manufacture of vitamin D3 in specialized cells under the skin; these localized zones produce the nutrient following exposure to sunlight of sufficient intensity. Dr.
Side Effects
Commonly reported side effects include: hypercalcemia, hypercalciuria, and increased serum creatinine.
Half Life
The half-life of a drug is the time taken for the plasma concentration of a drug to reduce to half its original value.
What is the difference between vitamin D3 and calcitriol?
Vitamin D3 And Calcitriol: Why The Difference Between The Two Is The Difference Between Strong and Weak Bones. You surely know by now how important Vitamin D3 is to building younger, healthier bones. But you may be surprised to learn that getting this essential vitamin to where it needs to go, in a form that your body can use, ...
What is the receptor for calcitriol?
Additionally, calcitriol needs to connect with a specific receptor called the Vitamin D Receptor, or the calcitriol receptor. When we talk about the benefits of Vitamin D3, we’re talking about the benefits of calcitriol, because unless it makes this transformation, it can’t be absorbed and used.
What is the role of vitamin D3 in the human body?
Bioactivated Vitamin D3, or calcitriol, plays many important roles in the human body. It has been shown in medical studies 1 to protect against a litany of issues including: The most relevant benefit for Savers of course, is protection against Osteoporosis, through the building of stronger bones.
Does calcitriol help with inflammation?
Calcitriol has additional health benefits, such as reducing inflammation by lowering the “adaptive” immune system, while stimulating the parts of your immune system that control viral infections and help prevent autoimmune disease. 2
Does calcitriol work in bone?
Otherwise it would escape your body without ever getting used! Only after calcium enters the bloodstream, it becomes bioavailable to build new bone. If this were the only function of calcitriol, it would already rank as possibly the most important hormone at work in bone health.
Does vitamin D affect calcitriol?
Everyone’s body is a little different, and because Vitamin D production happens naturally in the body mostly through sun exposure, where you live can impact your calcitriol levels as much as what you do.
What is calcitonin hormone?
What Is Calcitonin? Calcitonin is a hormone released when a person experiences hypercalcemia, a condition that causes elevated calcium levels in the blood. There are two ways in which calcitonin works. First, calcitonin opposes osteoclasts, cells that break down bone in the body.
What happens if calcium levels in the blood decrease?
On the other hand, if calcium levels in the blood decrease, the secretion of calcitonin dwindles. A lack of calcitonin in the blood may increase a person’s risk of bone degradation and osteopenia, a condition that occurs when the rate in which the body reabsorbs old bone exceeds the rate in which it produces new bone.
What hormones help regulate calcium levels in the body?
PTH is a hormone produced by the parathyroid glands; there are four parathyroid glands, and together, they help regulate calcium levels in the body. PTH increases calcium in several ways; it breaks down bone, improves the body’s ability to obtain calcium from food, and increases the kidney’s ability to contain calcium.
What causes hypercalcemia?
There are other possible causes of hypercalcemia as well. These include: 1 Cancer: Lung and breast cancer and different cancers of the blood increase a person’s risk of hypercalcemia. Moreover, metastasis (spread of cancer) to the bones may make a person susceptible to hypercalcemia. 2 Disease: Tuberculosis, sarcoidosis, and other diseases that raise vitamin D levels in the blood can stimulate the digestive tract. The result: the digestive tract absorbs more calcium, increasing the risk of hypercalcemia. 3 Genetics: Hypocalciuric hypercalcemia is a rare genetic disorder that occurs due to faulty calcium receptors in the body. 4 Dehydration: Severe dehydration means there is less fluid in the blood, raising the body’s calcium concentrations. 5 Medication: Lithium and other medications sometimes increase the release of PTH in the body, leading to an increase in calcium. 6 Supplements: Taking too much of a calcium or vitamin D supplement may result in elevated calcium levels in the blood.
What is hypocalciuric hypercalcemia?
Genetics: Hypocalciuric hypercalcemia is a rare genetic disorder that occurs due to faulty calcium receptors in the body. Dehydration: Severe dehydration means there is less fluid in the blood, raising the body’s calcium concentrations.
What is the highest risk for hypercalcemia?
Research shows that the risk of hypercalcemia is highest among women 50 years of age and older. For women or men who experience hypercalcemia, they may be prone to different complications, such as osteoporosis, kidney failure, and abnormal heart rhythm.
Is calcitonin a weaker than PTH?
Calcitonin and PTH help regulate the body’s calcium levels, but each functions in a different way. It is important to note that calcitonin is weaker than PTH. While HPT occurs when one or more malfunctioning parathyroid glands produce an excess amount of PTH and raise the blood calcium level, calcitonin does not play a major role in HPT. ...
Side Effects
Commonly reported side effects include: hypercalcemia, hypercalciuria, and increased serum creatinine.
Half Life
The half-life of a drug is the time taken for the plasma concentration of a drug to reduce to half its original value.