Difference Between Angiosperms and Gymnosperms
| Angiosperms | Gymnosperms |
| The flowering plants produce seeds | The non-flowering plants produce seeds |
| The seed is enclosed in the ovary | The seeds are naked as there is no ovary |
| These plants have season lifecycle | They are evergreen |
| They have triploid tissues | These have haploid tissues |
What is the similarity between gymnosperms and angiosperms?
Ø The main plant body in both gymnosperms and angiosperms is the diploid sporophyte. Ø In both groups, the sporophyte is differentiated into root, stem and leaves. Ø Vascular bundles are conjoined, collateral and open. Ø Anomalous secondary thickening occurs in some gymnosperms and angiosperms.
What are facts about gymnosperms?
- Flowering plants form an extremely important part of Earth’s ecology as an amazingly huge number of insects feed on the nectar of flowers. ...
- Angiosperms are further classified as monocotyledonous and dicotyledonous plants. ...
- The female reproductive organs of an angiosperm are the stigma, style and the ovary which are collectively known as the carpel. ...
What are the four types of gymnosperms?
Types of Gymnosperm Plants
- The Conifer Species. Around 550 species of conifer trees exist worldwide and make up the largest group of gymnosperms. ...
- Not Palms, but Cycads. Found primarily in the warmer climates of the world, in USDA zones 8 through 11, cycads comprise the next largest group of gymnosperms.
- The Ancient Ginkgoes. ...
- History of Gymnosperm Plants. ...
Do gymnosperms reproduce sexually or asexually?
In the gymnosperm life cycle, plants alternate between a sexual phase and an asexual phase. This type of life cycle is known as alternation of generations. Gamete production occurs in the sexual phase or gametophyte generation of the cycle. Spores are produced in the asexual phase or sporophyte generation.
How are angiosperms different from the gymnosperms and seedless plants?
Gymnosperms. Angiosperms, also called flowering plants, have seeds that are enclosed within an ovary (usually a fruit), while gymnosperms have no flowers or fruits, and have unenclosed or “naked” seeds on the surface of scales or leaves.
What is the difference between gymnosperms and angiosperms plants?
The biggest difference between gymnosperm and angiosperms lies in their seeds. Gymnosperm seeds are typically formed in unisexual cones and are known as “naked” seeds since they lack the protective cover angiosperms provide their seeds.
What are three differences between gymnosperms and angiosperms?
Difference between Angiosperms and GymnospermsAngiospermsGymnospermsHardwood typeSoftwood typeReproduction rely on animalsReproduction rely on windReproductive system present in flowers (unisexual or bisexual)Reproductive system present in cones and are unisexual4 more rows
What is the main difference and similarity between gymnosperms and angiosperms?
AngiospermGymnospermThe angiosperms have plant parts including the leaves, stems, and roots.The plant parts of gymnosperms are also the same as the angiosperms which include the leaves, stems, and roots.Angiosperms produce seeds that are enclosed in a coveringGymnosperms produce naked seeds with no outer covering.4 more rows
What is the difference between gymnosperms and angiosperms quizlet?
Gymnosperms have naked seeds, don't have flowers or fruits, and have a haploid endosperm in the seeds (endosperm is produced before fertilization), while Angiosperms have enclosed seeds, flowers, fruits, and have a triploid endosperm in the seed (endosperm produced during triple fusion).
How does the reproduction of seedless plants differ from that of seed plants?
Explanation. The major difference between seed plants and seedless plants is that seedless plants do not contain propagation seeds, whereas seed plants do. Seed plants reproduce sexually and create spores, whereas seedless plants reproduce asexually on their own.
What are the characteristics of seedless vascular plants?
Characteristics of Seedless Vascular PlantsHave vascular tissue.Xylem.moves water.contains lignin.formed through programmed cell death.Phloem.moves nutrients, minerals and organics through plant.living tissue.More items...
Do angiosperms have seeds?
Angiosperm means "covered seed". The ovules develop into seeds, and the wall of the ovary forms a fruit to contain those seeds. Fruits attract animals to disperse the seeds.
What is gymnosperm plant?
gymnosperm, any vascular plant that reproduces by means of an exposed seed, or ovule—unlike angiosperms, or flowering plants, whose seeds are enclosed by mature ovaries, or fruits. The seeds of many gymnosperms (literally, “naked seeds”) are borne in cones and are not visible until maturity.
Which character most differentiates angiosperms from gymnosperms?
angiosperms are also called as flowering plants. Seeds of angiosperms are enclosed in the ovary (usually a fruit). Gymnosperms do not have flowers or fruits. In gymnosperms, the ovules are not enclosed in an ovary.
What is the difference between angiosperms and gymnosperms?
Angiosperms, also called flowering plants, have seeds that are enclosed within an ovary (usually a fruit), while gymnosperms have no flowers or fruits, and have unenclosed or “naked” seeds on the surface of scales or leaves. Gymnosperm seeds are often configured as cones.
What are the characteristics of gymnosperms?
Gymnosperm seeds are often configured as cones. The characteristics that differentiate angiosperms from gymnosperms include flowers, fruits, and endosperm in the seeds.
What are some examples of angiosperms?
Examples of angiosperms are monocots like lilies, orchids, agaves (known for agave nectar) and grasses; and dicots like roses, peas, sunflowers, oaks and maples. Gymnosperm examples include non-flowering evergreen trees such as pine, spruce and fir. Apple tree, a flowering, fruit-bearing angiosperm.
What is the dominant plant life on Earth?
Between 250 and 200 million years ago, angiosperms started to evolve. Now, angiosperms are more widely distributed and populous, and can be considered the dominant plant life on the planet. Angiosperms comprise a far more diverse range of plants, with a range of 250,000 to 400,000 species. They inhabit every kind of land and aquatic environment except the most extreme habitats. Angiosperms may be dicots or monocots .
How do angiosperms reproduce?
Reproduction in angiosperms can be unisexual or bisexual. The gametes are spread by wind and by insect and animal pollinators attracted by their flowers. Flowers often have both female and male gametes inside them, and after fertilization, the ovules develop into a fruit.
How many species of angiosperms are there?
Angiosperms comprise a far more diverse range of plants, with a range of 250,000 to 400,000 species. They inhabit every kind of land and aquatic environment except the most extreme habitats. Angiosperms may be dicots or monocots .
What are angiosperms used for?
Uses. Angiosperms provide virtually all plant-based food, as well as most livestock feed. Grains, fruit, legumes, nightshades (including potatoes and tomatoes), gourds, and cabbages are all angiosperms.
Why are angiosperms not visible?
Unlike those in the gymnosperms, these seeds are not immediately visible because they are enclosed and concealed by a fruit.
What are the phyla of gymnosperms?
The phyla (or divisions) of the plant kingdom that comprise the gymnosperms are the Cycadophyta (ex. Cycas revoluta ), Ginkgophyta (i.e. , Ginkgo biloba ), Pinophyta ( ex. Pinus spp.), and Gnetophyta (ex. Gnetum gnemon) (Moore et al. 2003). However, Simpson (2010) listed only three having placed the gnetophytes under Coniferae (also called Pinophyta or Coniferophyta). He noted that the exact placement of Gnetophyta (or Gnetales) is still uncertain.
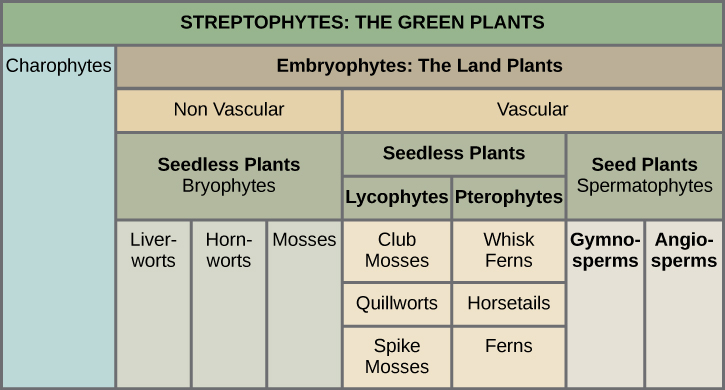
What is a seed plant?
Seed plants or seed-bearing plants, also called spermatophytes or Spermatophyta, are vascular plants with numerous members belonging to the lignophytes or woody plants. They have the natural ability to produce seeds, a characteristic that likewise distinguishes them from earlier plants. The seed has been defined as an embryo surrounded by nutritive tissue and enveloped by a seed coat. The embryo is an immature diploid sporophyte developing from the zygote (Simpson 2010).
When did gymnosperms first appear?
The gymnosperms are more ancient in terms of evolutionary history. It was some 360 million years ago that the spermatophytes first appeared. But the earliest evidence of angiosperms is those of fossilized pollen grains from the Cretaceous period about 140 million years ago and flowers from sediments about 130 million years ago (Simpson 2010).
What is the division of angiosperms?
The angiosperms (Angiospermae, flowering plants, or covered-seed plants) consist of the division Anthophyta, also called Magnoliophyta.
What is a plant that does not produce seeds called?
Those which do not produce seeds are called seedless plants or non-seed plants. They consist of both nonvascular and vascular plants and reproduce by means of spore. The spore is defined by Simpson (2010) as a haploid cell that, in the land plants, originates from meiotic divisions of sporocytes within a sporangium, ultimately growing into a gametophyte.
Why is water important for seed formation?
Water is essential to fertilization with spores because the sexual gametes have to swim to find each other and unite, but it is not a requirement in seed formation. Pollination, the transfer of pollen grains from the male to the female reproductive organ, which precedes fertilization, is accomplished in many ways. The wind, insects, birds, bats, and other animals serve as vectors or agents of pollination. In relation to species perpetuation, therefore, the seed is one of plants’ most ingenious and powerful evolutionary innovations. Reproduction is the main function of seeds.
Which is better, angiosperms or gymnosperms?
The fruits aid in the dispersing seeds whereas the flowers provide the protection for the ovule. Therefore, angiosperms are better than gymnosperms.
Why are angiosperms more diverse than gymnosperms?
Angiosperms are more diverse in comparison to the gymnosperms. The higher diversity of angiosperms is due to their wide adaptability in terrestrial ecosystems. Angiosperms, are also known as flowering plants and having seeds enclosed within their fruit.
What are Angiosperms?
The angiosperms are vascular plants bearing the seeds in fruits or mature ovaries. Angiosperm forms the flower which carries reproductive organs and fruits. These plants can easily adapt to the terrestrial habitat and also have a very wide distribution, around 250000 species. Fruit trees including Mango, Apple, Banana, Peach, Cherry, Orange, Pear, etc are the examples of Angiosperms. These show the flowers before they bear fruits. Grains like rice, corn, and wheat are also examples of Angiosperm. In such type of plants, the pollination process is carried out by the wind. Some other examples of Angiosperms are roses, lilies, Broccoli, kale, Petunias, Eggplant, Tomato, Peppers, and sugarcanes.
How are gametes spread?
The gametes are being spread by wind and by the insect as well as by animal pollinators, attracted by their flowers. Their flowers are having both female and male gametes inside themselves. Also, after fertilization, the ovules develop into a fruit. The gametes of the gymnosperms are found in as cones.
What is gymnosperm used for?
The hardwood of angiosperms is useful to make the hardwood floors. Gymnosperms are from the conifer group like pine, spruce, and fir and are commonly in use for the lumber. Other gymnosperms are processed into other products such as soap, varnish, and perfumes.
What are some examples of angiosperms?
Answer: Examples of the angiosperms are monocots such as lilies, orchids, agaves, and grasses. Some others are the dicots like roses, peas, sunflowers, oaks, and maples. Gymnosperm examples are including the non-flowering evergreen trees such as pine, spruce, and fir.
Why are there so few species of seeds?
The main reason for having such a less number of species is the lack of protection of the seeds. The seeds are naked and hence is unprotected after of its release. Therefore they need to get into the ground quickly to take root. Otherwise, the animals, weather conditions, or any other negative factors will damage them.
How many types of angiosperms are there?
There are two types of angiosperms. Let’s look at them –
What kingdom are angiosperms in?
The angiosperms are part of the kingdom Plantae and make up 80% of the plant population on the earth. They are the most commonly found plants because they can grow in various habitats in the ecosystem.
What is the process of producing seeds?
Plants that have reproductive tissues end up producing seeds, they are phanerogams. The reproduction process leads to the formation of seeds. They have embryos with food for the process of germination. The phonograms are further classified in angiosperms and gymnosperms based on seed covering.
What is the life cycle of a gametophyte?
The sporophytes are dominant in this cycle. They are both haploid and diploid. The life phase of a gametophyte is very short and the cones act as reproductive organs.
Why do plants have endosperms?
The seeds of these plants have endosperms to store food for the future.
What is the process of pollination?
The pollination is by wind where the pollen grain releases sperm and fuses with female gametophyte to create a zygote. This process is called fertilization.
How many times can a flower fusion occur?
The flowers can have fusion 2-3 times and form a diploid zygote and triploid endosperm.
Diversity
Anatomical Differences
- Since gymnosperms and angiosperms are both vascular plants, they have a sporophyte-dominant life-cycle. Tissue formation in angiosperms exceeds the amount and complexity found in gymnosperms. Angiosperms have a triploid vascular tissue, flat leaves in numerous shapes and hardwoodstems. Because of the innumerable varieties of the fruit and/or flower...
Reproduction
- Reproduction in angiosperms can be unisexual or bisexual. The gametes are spread by wind and by insect and animal pollinatorsattracted by their flowers. Flowers often have both female and male gametes inside them, and after fertilization, the ovules develop into a fruit. The gametes of gymnosperms are found in cones. Fertilization is described as single; the pollen grains fall and g…
Uses
- Angiosperms provide virtually all plant-based food, as well as most livestock feed. Grains, fruit, legumes, nightshades (including potatoes and tomatoes), gourds, and cabbages are all angiosperms. Other angiosperms like cotton and flax provide paper and textiles. The hardwood of angiosperms is used to make hardwood floors. Gymnosperms from the conifer group like pine, …
References