Condensation Polymerization
- In addition polymerization monomers only join at the active site of the chain. ...
- In addition polymerization, there are three distinct steps. ...
- Addition polymerization results in homo-chain polymers whereas condensation polymerization results in hetro-chain polymers.
- The most significant difference is that in addition polymers there is no loss of atom. ...
What is the difference between addition and condensation?
this chain reaction can be of three types:
- Dedication
- Spreading
- Termination
What is the process of addition polymerization?
Addition polymerisation is a process involving many small, unsaturated monomers combining to form one large polymer molecule. The alkenes ethene and propene are two important feedstocks in the petrochemical industry which can also be used to make addition polymers.
What does addition polymerization mean?
addition polymerization noun A form of polymerization in which copies of a monomer are repeatedly added to one end of an existing polymer How to pronounce addition polymerization?
What is an example of an addition polymer?
What Are Some Examples of Polymers?
- Natural Polymers. Polymers are both found in nature and manufactured in laboratories. ...
- Synthetic Polymers. Polymers were first manufactured by people seeking substitutes for natural ones, in particular, rubber and silk.
- Non-Polymers. ...
What is the difference between addition polymerization and polymerization?
The addition polymerization definition is that this is the process of repeated addition of monomers. These monomers possess double or triple bonds to form polymers. On the other hand, condensation polymerization is a process that involves repeated condensation reactions between tri-functional or bi-functional monomers.
What are addition polymers and condensation polymers with example?
Addition polymers include polystyrene, polyethylene, polyacrylates, and methacrylates. Condensation polymers are formed by the reaction of bi- or polyfunctional molecules, with the elimination of some small molecule (such as water) as a by-product. Examples include polyester, polyamide, polyurethane, and polysiloxane.
What is the difference between a condensation polymer and copolymer?
Summary – Copolymer vs Condensation Polymer Copolymers are polymer material containing at least two types of monomers. On the other hand, condensation polymers are polymer materials that form via condensation reactions while removing a small molecule as a byproduct.
What is addition polymerization with example?
Addition polymerization is when the monomer molecules bond to each other without the loss of any other atoms. Examples of addition polymers include polyethylene, polypropylene, polystyrene, polyvinylchloride, polytetrafluoroethylene, etc.
What is condensation polymerization examples?
Examples of natural condensation polymers include cellulose, starch, and polypeptide chains of proteins. Several synthetic condensation polymers discussed include nylon, kevlar, polyester, Bakelite, Melamine, polycarbonates, polyurethanes, epoxies.
What is addition polymerization reaction?
In addition polymerization (sometimes called chain-growth polymerization), a chain reaction adds new monomer units to the growing polymer molecule one at a time through double or triple bonds in the monomer.
What is condensation polymerization and name the different type of polymerization?
Condensation polymerization is a form of step-growth polymerization. Linear polymers are produced from bifunctional monomers, i.e. compounds with two reactive end-groups. Common condensation polymers include polyamides, polyacetals, and proteins.
1. Mention the reaction that is accompanied by the removal of by-products during the formation of po...
The reaction that results in the elimination of by-products while forming polymers is condensation polymerization. In this process, the molecules t...
2. What are Linear Polymers ?
A linear polymer is defined as a long continuous chain of carbon-carbon bonds along with two valence bonds attached primarily to hydrogen or anothe...
3. Is the chain growth process usually much slower than the step-growth process? If not, then why?
In truth, the chain growth process is usually much slower than the addition reaction. This is because the chain growth process is usually followed...
4. Mention the process in which the molecular weight of polymers almost remains unchanged while the ...
In the addition polymerization process the total molecular weight of the polymers remains almost unchanged with the increasing conversion. Further,...
5. In the process of addition polymerization, what does the entire reaction contain at any point in ...
At any point in time, the process of addition polymerization contains free radical chains and initiators, full-grown polymer molecules, and unreact...
What is the difference between addition and condensation polymerization?
The difference between addition and condensation polymerization is that for addition polymerization, monomer should be an unsaturated molecule whereas for condensation polymerization, monomers are saturated molecules.
What is an example of condensation polymer?
For example, if the joining ends of two molecules have a –OH group and a –COOH group, a water molecule will release and an ester bond forms. Polyester is an example for a condensation polymer. In the synthesis of polypeptides, nucleic acids or polysaccharides, condensation polymerization takes place within biological systems.
What is the process of synthesizing polymers?
The process of synthesizing addition polymers is addition polymerization. Any condensation process, which results in the formation of polymers, is the condensation polymerization. Therefore, addition polymerization is the reaction between monomers with multiple bonds, where they join together to form saturated polymers.
What happens when two monomers combine?
In some of the polymerization reactions, when two monomers combine, a small molecule releases, i.e. water. Such polymers are condensation polymers. Polymers have very different physical and chemical properties than their monomers.
What is the process of condensation?
Any condensation process that results in the formation of polymers, is the condensation polymerization. A small molecule like water or HCl releases as a by-product during the condensation polymerization. The monomer should have functional groups in ends, which can react together to continue the polymerization.
What is the monomer of polyethylene?
The monomer for polyethylene is ethene (CH 2 =CH 2 ). Its repeating unit is –CH 2 -. In the initiation step, a peroxide radical generates. This radical attacks the monomer to activate it and produce a monomer radical. During the propagation phase, the chain grows.
How many atoms are in a polymer?
They have a high molecular weight and consist over 10,000 atoms. In the synthesis process (polymerization), longer polymer chains form. There are two main types of polymers depending on their synthesis methods. If the monomers have double bonds between carbons, addition polymers form via addition polymerization.
What is condensation polymerization?
It is important for readers to remember that condensation polymerization is a type of step-growth polymerization. This means that linear polymers are produced from bifunctional monomers, which refers to compounds with two reactive end groups.
How is addition polymer formed?
According to experts, an addition polymer is a polymer that is formed by simply linking monomers. This is done without the co-generation of other by-products. Further, it is important to note that addition polymers can be formed through chain polymerization.
How are polymers formed in a chain reaction?
In condensative chain polymerization, the polymers are formed by sequential addition or the condensation reaction of the monomers to an active site in a chain reaction. The other important and alternative forms of polymerization are polyaddition and chain polymerization.
What is polyaddition in biology?
Polyaddition refers to the process in which polymers are formed by carrying out an addition reaction between species of all degrees of polymerization. It is also important to note that, usually, almost all polymers are unsaturated compounds - some examples of this include alkalines and alkenes.
What is the process of combining a large number of small molecules to form a single macromolecule?
Polymerization is defined as the process of combining a large number of small molecules to form a single macromolecule. There are integral steps and products used in this process. One such important product is called a monomer. Monomers are small molecules that act as building blocks of polymers.
Why are addition polymers non-biodegradable?
On the other hand, condensation polymers tend to be more biodegradable. This is because the backbone of those molecules contains weaker bonds.
What are the two groups of polymerization?
These two groups are addition polymerization and condensation polymerization. The addition polymerization definition is that this is the process of repeated addition of monomers.
What is the difference between addition polymerisation and condensation polymerisation?
Based on the nature of the chemical reaction involved in the formation of a polymer, there are two types of polymerisation reactions: addition polymerisation and condensation polymerisation. Addition polymerisation produces addition polymers through the addition of olefinic monomers without the formation of any by-product. In contrast, condensation polymerisation produces condensation polymers through the intermolecular condensation of two different monomers with the formation of small molecules such as HCl, water, ammonia, etc. , as by-products. This is the main difference between addition polymerisation and condensation polymerisation. In addition to this main difference, there are many more differences between these two polymerisation reactions.
What is the process of condensation polymerisation?
Condensation polymerisation is the process of intermolecular condensation of two different monomers to form a large chain of polymer molecules. In this process, linking of every two monomer molecules will result in a simple molecule such as HCl, ammonia, water, etc., as a by-product. Hence, the molecular weight of the polymer will be the product ...
What is addition polymerization?
What is Addition Polymerisation. Addition polymerisation is the addition of one monomer to another monomer to form long chain polymers. This process does not produce any by-products. Hence, the molecular weight of the polymer will be an integral multiple of monomer’s molecular weight.
What is the nature of a monomer?
Nature of the Monomer. Addition polymerisation: Monomer must have at least a double or triple bond. Condensation polymerisation: Monomer must have at least two similar or different functional groups.
Is a polymer an integral multiple of a monomer?
Condensation polymerisation: Molecular weight of the resulting polymer is not an integral multiple of monomer’s molecular weight.
What is the difference between addition and condensation polymerization?
Addition polymerisation is the process in which the unsaturation in monomers is essential, whereas the condensation polymerisation is the process in which the presence of the functional group is essential. Addition polymerisation is a very fast process, whereas the condensation process is a very slow process.
What is condensation polymerisation?
Condensation polymerisation is the step-growth process in which monomers of a different kind undergo condensation and produces the condensed polymers. It is a type of reaction of formation of by-polymers.
What happens to the thermoplastics in addition polymerization?
Addition polymerisation always produces the thermoplastics. In this process, monomers add to one another to form longer chains. In this process, the multiple bonds break off and form covalent bonds with the adjacent monomers. In addition polymerisation, it always involves alkenes and alkynes monomers.
How does addition polymerisation produce the addition polymers?
Addition polymerisation produces the addition polymers by the addition of olefinic monomers, whereas the condensation produces the condensed polymers by the condensation of two different monomers. ADVERTISEMENT. CONTINUE READING BELOW.
Why is the longer time of reaction in condensation polymerisation important?
The longer time of reaction in condensation polymerisation is very crucial for the production of high yields. It produces condensed polymers. Condensation polymerisation produces the thermosets. In this process, adjacent makes covalent bonds with each other.
What type of bond does polymerization have?
In addition polymerisation, monomers have multiple bonds such as double bond and triple bonds. The polymers have a molecular weight whose integral multiple of molecular weight of monomers. Addition polymerisation also produces homo-chain.
What are the processes involved in addition polymerisation?
There are many processes involve in addition polymerisation such as free radicle mechanism, ionic mechanism, and coordination mechanism. In these reactions, monomers must have the unsaturation. In this process, longer the reaction time it will produce the higher yields.
What is the difference between condensation and polymerization?
Additional polymerization involves polymers which are formed by the combination of alkene monomers to produce a single huge molecule only. Condensation polymerization involves polymers which are formed by the combination of monomers with the elimination of simple molecules like water (H 2 O) or ammonia (NH 3 ).
What is condensation polymerization?
A condensation polymerization is a form of step-growth polymerization. Small molecules react with each other to form larger structural units while releasing smaller molecules as a byproduct, such as water, HCl or methanol. A good example of polymerization reaction is the esterification of carboxylic acids with alcohols.
What happens to the molecular weight of a monomer in condensation polymerization?
Condensation polymerization reaction results in lower molecular weight polymer in the beginning, however, molecular weight of the polymer increases steadily as the reaction progresses.
What is polymerization reaction?
Polymerization describes the formation of large molecules (Polymers) with repeating structure from small molecules (monomers). There are two types of polymerization reactions, additional and condensation.
What are some examples of condensation polymers?
A condensation polymer consists of two different kinds of monomers. Typical examples of condensation polymers are Polyesters, nylon, Bakelite and Polyamides. Mineral acids and bases are normally employed as catalysts in this process. In condensation polymerization, HCl, CH 3 OH, NH 3 are usually produced as by-products.
What is the process of linking monomers with double bonds?
It involves the linking of monomers with double bonds. The double bond of one monomer breaks and links onto the neighboring monomer. This process continues to form polymers, some of which can be many thousands of monomers long. Additional polymers.
What is additional polymer?
Additional polymer is made of only one kind of monomer. Typical examples of additional polymerization are the formation of PolyVinyl Chloride (PVC) from Vinyl Chloride or formation of Polyethylene from Ethylene. Radical initiators, Lewis acid or bases are used as catalysts in this process.
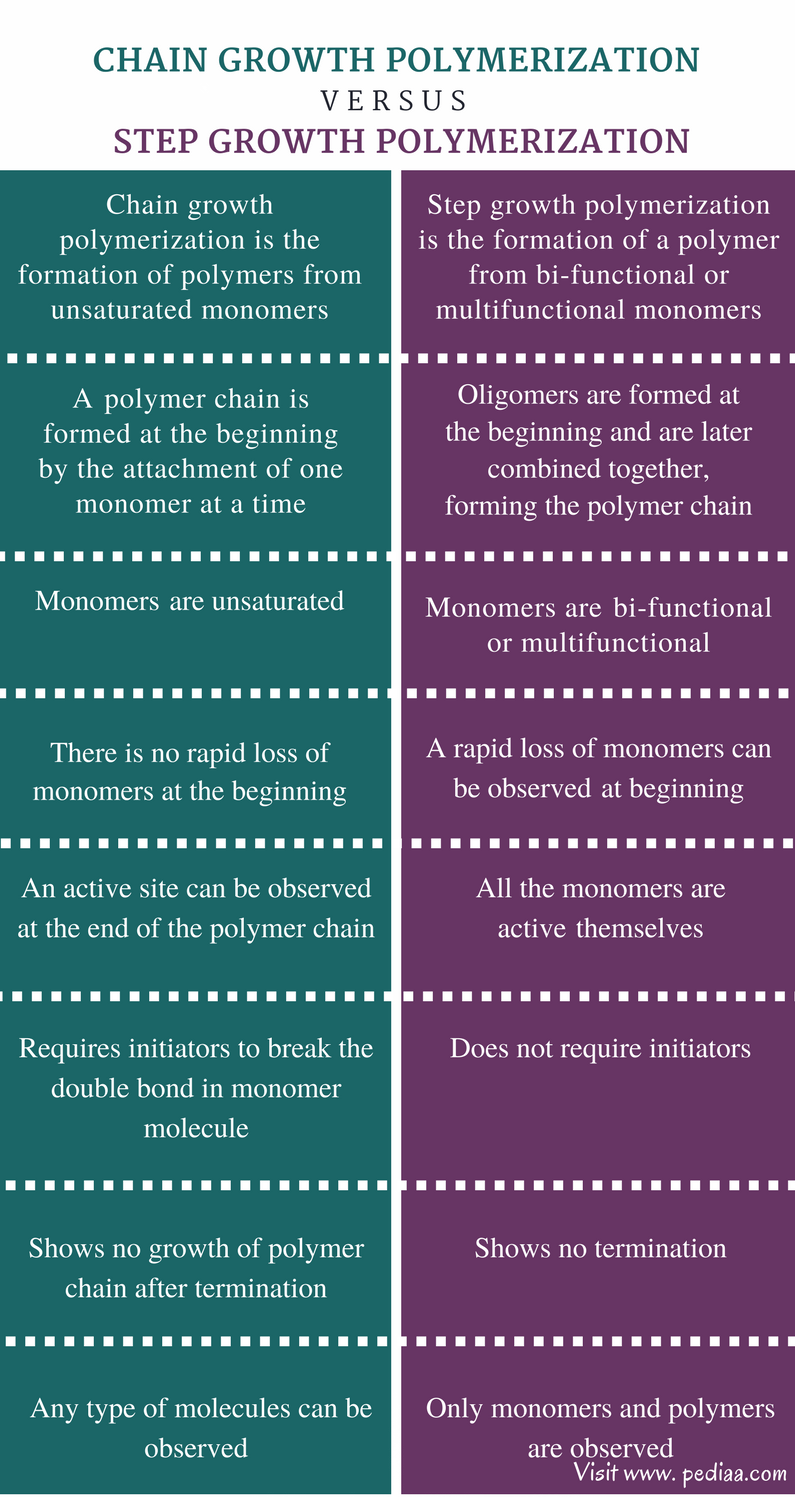
Main Difference – Addition Polymerisation vs Condensation Polymerisation
What Is Addition Polymerisation
- Addition polymerisation is the addition of one monomer to another monomer to form long chain polymers. This process does not produce any by-products. Hence, the molecular weight of the polymer will be an integral multiple of monomer’s molecular weight. The monomers involved in these reactions must be unsaturated (double or triple bonds must be present). During the reacti…
What Is Condensation Polymerisation
- Condensation polymerisation is the process of intermolecular condensation of two different monomers to form a large chain of polymer molecules. In this process, linking of every two monomer molecules will result in a simple molecule such as HCl, ammonia, water, etc., as a by-product. Hence, the molecular weight of the polymer will be the product of the degree of polyme…
Difference Between Addition Polymerisation and Condensation Polymerisation
- Nature of the Monomer
Addition polymerisation: Monomer must have at least a double or triple bond. Condensation polymerisation: Monomer must have at least two similar or different functional groups. - Nature of Polymer Formation
Addition polymerisation: Addition of monomer results in a polymer. Condensation polymerisation: Monomers condense to give a polymer.