The distinction between active and passive margins refers to whether a crustal boundary between oceanic lithosphere and continental lithosphere A lithosphere is the rigid, outermost shell of a terrestrial-type planet or natural satellite that is defined by its rigid mechanical properties. On Earth, it comprises the crust and the portion of the upper mantle that behaves elastically on time scales of thousands of years or greater. The oute…Lithosphere
What is the difference between active and passive margin?
Modern Passive Continental Margin
- Continental Rift. ...
- New Ocean Basin. ...
- Mature Ocean Basin. ...
- Tectonic Development of the Atlantic Ocean and Gulf of Mexico. ...
- NPS Sites along Atlantic and Gulf Coasts. ...
- Source of Sediment in NPS Sites along Atlantic and Gulf Coasts. ...
- Topography of a Passive Continental Margin. ...
- Changing Coastline as Sea Level Rises and Falls. ...
- Migration of Barrier Island. ...
What are passive margins?
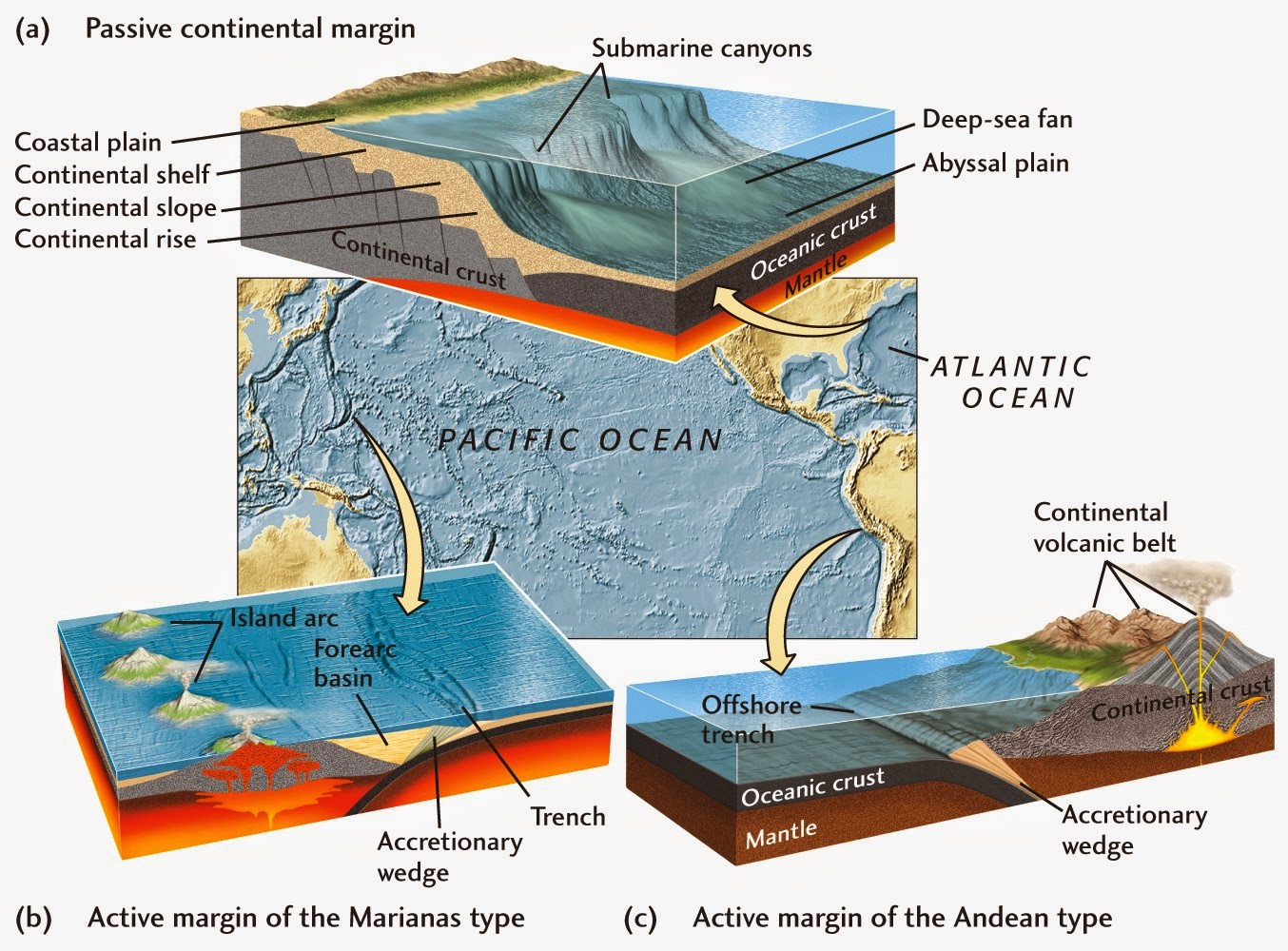
The term passive margin is a synonym for the bulkier Atlantic-type margin, trailing-edge margin, rifted margin, or divergent margin. A passive margin is one formed by rifting followed by seafloor spreading, so that the resulting plate consists of both continental and oceanic lithosphere, welded across an igneous contact.
What is active margin?
what is an active margin
- Vodcast 9.3: Passive & Active Continental Margins
- 23.2 The Continental Margin
- Passive vs. Active Margins
- Continental Rifting, New Oceans, and Passive Continental Margins for Beginners
What are passive and active continental margins?
Passive margins are where the flooded extensions of the continent merge into the oceanic crust, and there is active deposition. Active continental margins are located along converging plate boundaries where the oceanic lithosphere is submerged below the leading edge of a continent (all the way around the ring of fire).
What makes a margin active or passive?
The distinction between active and passive margins refers to whether a crustal boundary between oceanic lithosphere and continental lithosphere is a plate boundary. Active margins are found on the edge of a continent where subduction occurs.
What happens active margin?
Active margins are marked by earthquakes, volcanoes, and mountain belts. Unlike passive margins, they lack a continental rise and abyssal plain. Instead, the continental slope ends in an oceanic trench, and beyond the trench, the topography is hilly and irregular, often dotted with rugged volcanic seamounts.
What is an example of a passive margin?
Examples of passive margins are the Atlantic and Gulf coastal regions which represent setting where thick accumulations of sedimentary materials have buried ancient rifted continental boundaries formed by the opening of the Atlantic Ocean basin.Feb 14, 2021
What is meant by active margin?
An active margin refers to a continental margin above an oceanic subduction zone, with typical examples located along the western coast of South America.
What are three major features of a passive continental margin?
Passive continental margins are low in tectonic and seismic activity. This means that the inland coast and the sea floor are gradually sloped throu...
Is Antarctica a passive or active continental margin?
The continent of Antarctica is bounded by a passive continental margin. As a result, there is little tectonic or seismic activity.
What is the meaning of a continental margin?
A continental margin is the area where tectonic plates meet. This may result in the process of subduction, in which the denser oceanic plate is pus...
Where are two locations of active continental margins?
Active continental margins can be found throughout the world. The western coasts of North and South America are one example of active continental m...
Where is the active margin located?
An active continental margin is found on the leading edge of the continent where it is crashing into an oceanic plate. An excellent example is the west coast of South America. Active margins are commonly the sites of tectonic activity: earthquakes, volcanoes, mountain building, and the formation of new igneous rock.
Where are passive continental margins found?
Passive continental margins are found along the remaining coastlines. Because there is no collision or subduction taking place, tectonic activity is minimal and the earth's weathering and erosional processes are winning.
What are the two types of plates?
The earth's crust is broken into sections, called plates. There are two (2) basic types: oceanic plates which are composed of basalt, and continental plates, which are mostly granite. The continental plates are in motion, and literally bounce around on the surface like giant air hockey pucks.
Is the West Coast active or passive?
The west coast is the active margin, and is the location of earthquakes, volcanoes, and mountains. The Eastern Seaboard is a passive margin, as is the Gulf Coast.
Continental Margins
Continental margins are the areas along the edges of tectonic plates where the rocks which make up the continents, meet the types of rocks which make up the ocean floor.
Active Continental Margins
At areas where a continental plate converges with an oceanic plate, the tectonic and seismic activities, associated with an active margin, take place.
Passive Continental Margins
At areas of the lithosphere where continental and oceanic plates are not meeting, passive margins are found. These areas have low levels of tectonic and seismic activity, as no friction or stress is created by tectonic movements. These passive continental margins can share a number of characteristics.
What is the difference between active and passive margins?
The distinction between active and passive margins refers to whether a crustal boundary between oceanic lithosphere and continental lithosphere is a plate boundary. Active margins are found on the edge of a continent where subduction occurs. These are often marked by uplift and volcanic mountain belts on the continental plate.
Where are passive margins found?
Passive margins are found at every ocean and continent boundary that is not marked by a strike-slip fault or a subduction zone. Passive margins define the region around the Atlantic Ocean, Arctic Ocean, and western Indian Ocean, and define the entire coasts of Africa, Greenland, India and Australia. They are also found on the east coast of North ...
What are the stages of passive margins?
There are three main stages in the formation of passive margins: In the first stage a continental rift is established due to stretching and thinning of the crust and lithosphere by plate movement. This is the beginning of the continental crust subsidence. Drainage is generally away from the rift at this stage.
What is the transitional crust?
Transitional crust, separating true oceanic and continental crusts, is the foundation of any passive margin. This forms during the rifting stage and consists of two endmembers: volcanic and non-volcanic. This classification scheme only applies to rifted and transtensional margin; transitional crust of sheared margins is very poorly known.
How does heat flow at passive margins change over its lifespan?
Heat flow at passive margins changes significantly over its lifespan, high at the beginning and decreasing with age . In the initial stage, the continental crust and lithosphere is stretched and thinned due to plate movement ( plate tectonics) and associated igneous activity.
What are volcanic margins?
Volcanic margins form part of large igneous provinces, which are characterised by massive emplacements of mafic extrusives and intrusive rocks over very short time periods. Volcanic margins form when rifting is accompanied by significant mantle melting, with volcanism occurring before and/or during continental breakup. The transitional crust of volcanic margins is composed of basaltic igneous rocks, including lava flows, sills, dykes, and gabbro .
What is constructional margin?
Constructional margins are the "classic" mode of passive margin sedimentation. Normal sedimentation results from the transport and deposition of sand, silt, and clay by rivers via deltas and redistribution of these sediments by longshore currents.