Monosaccharide
- Monosaccharide Definition. A monosaccharide is the most basic form of carbohydrates. ...
- Function of Monosaccharide. Monosaccharides have many functions within cells. ...
- Monosaccharide Structure. ...
- Examples of Monosaccharide. ...
- Related Biology Terms. ...
- Quiz. ...
What does monosaccharide mean biology?
Monosaccharides are carbohydrate molecules that cannot be broken down by hydrolysis 2 into simpler (smaller) carbohydrate molecules. Hence, monosaccharides are at times referred to as “simple sugars” or just :sugars," which infers that they are the simplest (smallest) of the carbohydrates.
What are five examples of monosaccharides?
Types of monosaccharides are as follows :
- Neutral monosaccharides
- Osamines
- Uronic acids
- Sialic acids
What are the three types of monosaccharides?
- glucose (dextrose)
- fructose (levulose)
- galactose
- ribose
- xylose
What are the 4 monosaccharides?
What are the 4 monosaccharides?
- Glucose or dextrose.
- Fructose.
- Galactose.
- Mannose.
- Ribose and deoxyribose.
What is monosaccharide classified as in biology?
In biology and biochemistry, a monosaccharide is a simple sugar that constitutes the building blocks of a more complex form of sugars such as oligosaccharides and polysaccharides. Examples are fructose, glucose, and ribose. The term monosaccharide etymologically means “single saccharide”.
What is monosaccharide and its function?
The monosaccharide consists of single unit which contains carbon chain of three to six carbon. They can combine through glycosidic bonds to form larger carbohydrates. The main function of monosaccharide is to produce and store energy. Glucose and fructose are the most available monosaccharide in nature.
What are monosaccharides in science?
Monosaccharides are the most simple sugars, containing three to seven carbon atoms in each molecule, and are the only form of sugar that can be fermented by starter cultures directly into lactic acid.
What are 5 examples of monosaccharides?
Examples of monosaccharides include glucose (dextrose), fructose, galactose, xylose and ribose.
What is monosaccharide answer?
monosaccharide, also called simple sugar, any of the basic compounds that serve as the building blocks of carbohydrates.
What is monosaccharides and example?
Examples of monosaccharides include glucose (dextrose), fructose (levulose), and galactose. Monosaccharides are the building blocks of disaccharides (such as sucrose and lactose) and polysaccharides (such as cellulose and starch).
What are monosaccharides and disaccharides?
Monosaccharides are comprised of a single simple sugar unit, glucose, fructose, or galactose, and they cannot be broken down into simple sugar units. These three monosaccharides are combined in various ways to make more complex carbohydrates. Disaccharides are comprised of two monosaccharides bonded together.
What is monosaccharide and polysaccharide?
Monosaccharides are simple sugar unit molecules, whereas polysaccharides are enormous, linking thousands of sugar units. Monosaccharides provide cells with short-term energy. Polysaccharides provide long-term energy storage and rigid structure to cell walls and exoskeletons of animals.
What is monosaccharide structure?
Structure of Monosaccharides All the monosaccharides have the formula as (CH2O) n. Here, the two hydrogen atoms and one oxygen atom associate itself to the central carbon molecule. A hydroxyl group is formed when oxygen will bond with hydrogen. Several carbon molecules bond together because 4 bonds can form on carbon.
What are the 4 types of monosaccharides?
The pentoses, ribose, deoxyribose, and ribitol are also monosaccharides but are not thought of as major sources of dietary energy. They are called “pentoses” because, unlike glucose, fructose, and galactose, they are comprised of a five-carbon backbone rather than a six-carbon backbone.
What are the 3 monosaccharides?
Simple Carbohydrates (Sugars) Glucose, fructose and galactose are the three monosaccharides important in nutrition. These single sugar molecules contain 6 carbon atoms, 12 hydrogen atoms and 6 oxygen atoms (i.e. chemical formula as C6H12O6).
Where are monosaccharides found?
The most common monosaccharides provided by foods are glucose, fructose and galactose. Sweet foods such as honey and cane sugar are rich in monosaccharides, but a wide variety of other foods, such as dairy products, beans and fruit, also contain these simple sugars.
What is a monosaccharide?
: a sugar that is not decomposable into simpler sugars by hydrolysis, is classed as either an aldose or ketose, and contains one or more hydroxyl groups per molecule. — called also simple sugar.
What is the unit of a carbohydrate?
The simplest, most fundamental unit of a carbohydrate is a monosaccharide —a single sugar molecule—made of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen atoms. — Carolyn L. Todd, SELF, 23 May 2019 Your body responds by secreting digestive enzymes to break down the disaccharide molecule sucrose (or table sugar) into the monosaccharide glucose.
Is fructose a monosaccharide?
Recent Examples on the Web But there’s no science to say that fructose is a worse monosaccharide for the body than any other, Tewksbury says. — Carolyn L. Todd, SELF, 24 June 2019 The first is monosaccharides, or single sugar molecules, which include fructose, galactose, and glucose. — Carolyn L. Todd, SELF, 24 June 2019.
What is monosaccharide sugar?
Anne Marie Helmenstine, Ph.D. Updated January 13, 2020. A monosaccharide or simple sugar is a carbohydrate that cannot be hydrolyzed into smaller carbohydrates. Like all carbohydrates, a monosaccharide consists of three chemical elements: carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen.
How are monosaccharides classified?
Monosaccharides are classified based on how many carbon atoms they contain, the placement of the carbonyl group, and their stereochemistry.
What are the ring sugars made of?
Rings made of five atoms are called furanose sugars, while those consisting of six atoms are the pyranose form. In nature, the straight-chain, furanose, and pyranose forms exist in equilibrium. Calling a molecule "glucose" could refer to straight-chain glucose, glucofuranose, glucopyranose, or a mixture of the forms.
Which monosaccharide has more than one hydroxyl group?
These include glucose, fructose, mannose, and galactose. Sedoheptulose and mannoheptulose are examples of heptose monosaccharides. Aldoses have more than one hydroxyl group (-OH) and a carbonyl group (C=O) at the terminal carbon, while ketoses have the hydroxyl group and carbonyl group attached to the second carbon atom.
Why do monosaccharides have a sweet flavor?
Monosaccharides have a sweet flavor because the orientation of the OH group interacts with the taste receptor on the tongue that detects sweetness. Via a dehydration reaction, two monosaccharides can form a disaccharide, three to ten can form an oligosaccharide, and more than ten can form a polysaccharide .
What are the three most common forms of monosaccharides?
Examples of monosaccharides include the three most common forms: glucose (dextrose), fructose (levulose), and galactose.
What are some examples of monosaccharides?
Examples of monosaccharides include glucose, fructose, ribose, xylose, and mannose. The two main functions of monosaccharides in the body are energy storage and as the building blocks of more complex sugars that are used as structural elements. Monosaccharides are crystalline solids that are soluble in water and usually have a sweet taste.
How are monosaccharides classified?
Monosaccharides are classified as well based on their functional groups. A functional group is categorized by atoms or bonds that are responsible for the chemical reactivity within a molecule. If a monosaccharide contains a ketone group in an inner atom, then the monosaccharide is classified as a ketose.
Which monosaccharide contains a ketone group?
Ketose - a monosaccharide which contains a ketone group in an inner atom. Ketone group - a carbon atom forming a double bond with oxygen and single bonds with two hydrocarbon groups. Hydrocarbon group - a group that contains carbon bonded with hydrogen.
How to find the number of carbon atoms in a mirror image of glucose?
Step 1: Number the carbon atoms starting from the top. Step 2: Find the second highest number of carbon atoms for the mirror images of glucose. In this case, we'll be looking at carbon number 5. If the -OH group (also known as the hydroxyl group) is on the right side, then it is D-glucose.
What is the formula for carbohydrate?
Carbohydrates have this general formula: The possible values for n are positive integers equal or greater than 3. If, for instance, n = 3, that means that there are three carbon atoms, and these monosaccharides are called trioses. If n = 4, there are four carbon atoms, so these monosaccharides are called tetroses.
What is a hydrocarbon group?
A hydrocarbon group is a group that contains carbon bonded with hydrogen. If a monosaccharide contains an aldehyde group at an end carbon, meaning a carbon at the end of the chain in the Fischer projection, then the monosaccharide is classified as an aldose.
What are carbohydrates made of?
We mentioned earlier that carbohydrates are composed of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen atoms. Since monosaccharides are the simplest units of carbohydrates, then they are also made up of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen atoms. Carbohydrates have this general formula:
Why are carbohydrates important?
Carbohydrates are very important because they provide energy and fuel for our bodies so that our brains can function properly and so that our muscles can work. Carbohydrates are our preferred source of energy.
Structure of monosaccharides
As explained in the article on carbohydrates, monosaccharides are organic molecules composed of carbon, hydrogen and oxygen atoms. They can be shown in their linear or ring structure. Have a look at figures 1 and 2, which show the two structures of the same molecule.
Types of monosaccharides
Monosaccharides are categorised according to how many atoms of carbon they contain. These are the three most common types:
Examples of monosaccharides
You will come across three monosaccharides classed as the most important in nutrition: glucose, galactose, and fructose. However, these are not the only ones. Deoxyribose and ribose are of great importance too, being the bases of DNA and RNA.
Monosaccharides form disaccharides and polysaccharides
Monosaccharides are joined together in a process called condensation. The condensation reaction of certain monosaccharides results in the formation of disaccharides and polysaccharides. In disaccharides, two monosaccharides are bonded, while in polysaccharides, there are many (poly- stands for ‘many’).
Monosaccharides
A monosaccharide is a simple carbohydrate. It is an organic biological molecule composed of one molecule of sugar. Monosaccharides are building blocks (monomers) of larger molecules of carbohydrates (polymers).
What is monosaccharide?
monosaccharide. Any of a class of carbohydrates that cannot be broken down to simpler sugars by hydrolysis and that constitute the building blocks of oligosaccharides and polysaccharides.
How many carbon atoms are in monosaccharides?
Monosaccharides consist of at least three carbon atoms, one of which is attached to an oxygen atom to form an aldehyde group (CHO) or a ketone, and the others of which are each attached to a hydroxyl group (OH). Monosaccharides can occur as chains or rings. Fructose, glucose, and ribose are monosaccharides.
What is a carbohydrate that does not hydrolyze?
noun Chemistry. a carbohydrate that does not hydrolyze, as glucose, fructose, or ribose, occurring naturally or obtained by the hydrolysis of glycosides or polysaccharides.
What does "simple sugar" mean?
n. A carbohydrate that cannot be decomposed to a simpler carbohydrate by hydrolysis, especially one of the hexoses.simple sugar. The American Heritage® Stedman's Medical Dictionary Copyright © 2002, 2001, 1995 by Houghton Mifflin Company. Published by Houghton Mifflin Company.
What is the simplest form of sugar?
The simplest form of sugar. Monosaccharides are classified by the number of carbon atoms in the molecule. They may thus be trioses, tetroses, pentoses, hexoses, etc. The commonest monosaccharide in the body is GLUCOSE, which is a hexose, with six carbons.
What is the name of the sugar that is soluble in water?
a carbohydrate MONOMER, a simple sugar with the formula (CH2O)n, e.g. C6H12 O6 glucose and fructose. See Fig. 224 . Such carbohydrates are generally white, crystalline solids, with a sweet taste, and are usually soluble in water. The carbon chain forming the backbone of such sugars can be of varying lengths. Some monosaccharides contain only three carbons (‘triose’ types such as glyceraldehyde) others contain five carbons (‘pentose’ types such as the deoxyribose sugar of DNA ), but those with six carbons (‘hexose’ types such as glucose) are the most important since they can be joined together by CONDENSATION REACTIONS (loss of water) to form DISACCHARIDES and POLYSACCHARIDES.
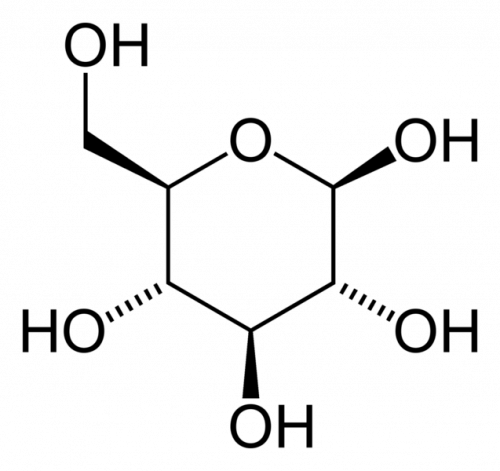
Properties
Functions
- Monosaccharides serve two main functions within a cell. They are used to store and produce energy. Glucose is a particularly important energy molecule. Energy is released when its chemical bonds are broken. Monosaccharides are also used as building blocks to form more complex sugars, which are important structural elements.
Structure and Nomenclature
- The chemical formula (CH2O)nindicates a monosaccharide is a carbon hydrate. However, the chemical formula doesn't indicate the placement of the carbon atom within the molecule or the chirality of the sugar. Monosaccharides are classified based on how many carbon atoms they contain, the placement of the carbonyl group, and their stereochemistry. The...
Linear vs. Cyclic
- Monosaccharides may exist as straight-chain (acyclic) molecules or as rings (cyclic). The ketone or aldehyde group of a straight molecule can reversibly react with a hydroxyl group on another carbon to form a heterocyclic ring. In the ring, an oxygen atom bridges two carbon atoms. Rings made of five atoms are called furanose sugars, while those consisting of six atoms are the pyra…
Stereochemistry
- Monosaccharides exhibit stereochemistry. Each simple sugar can be in either D- (dextro) or L- (levo) form. The D- and L- forms are mirror images of each other. Natural monosaccharides are in the D- form, while synthetically produced monosaccharides are usually in the L-form. Cyclic monosaccharides also display stereochemistry. The -OH group replacing oxygen from the carbo…
Sources
- Fearon, W.F. (1949). Introduction to Biochemistry(2nd ed.). London: Heinemann. ISBN 9781483225395.
- IUPAC (1997) Compendium of Chemical Terminology (2nd ed.). Compiled by A. D. McNaught and A. Wilkinson. Blackwell Scientific Publications. Oxford. doi:10.1351/goldbook.M04021ISBN 0-9678550-9-8.
- Fearon, W.F. (1949). Introduction to Biochemistry(2nd ed.). London: Heinemann. ISBN 9781483225395.
- IUPAC (1997) Compendium of Chemical Terminology (2nd ed.). Compiled by A. D. McNaught and A. Wilkinson. Blackwell Scientific Publications. Oxford. doi:10.1351/goldbook.M04021ISBN 0-9678550-9-8.
- McMurry, John. (2008). Organic Chemistry(7th ed.). Belmont, CA: Thomson Brooks/Cole.
- Pigman, W.; Horton, D. (1972). "Chapter 1: Stereochemistry of the Monosaccharides". In Pigman and Horton (ed.). The Carbohydrates: Chemistry and Biochemistry Vol 1A(2nd ed.). San Diego: Academic Pr...