1 Piaget's stages are:
- Sensorimotor stage: birth to 2 years
- Preoperational stage: ages 2 to 7
- Concrete operational stage: ages 7 to 11
- Formal operational stage: ages 12 and up
What are the 5 stages of cognitive development?
There are four stages in all:
- sensorimotor stage
- preoperational stage
- concrete operational stage
- formal operational stage
What are Piaget's four stages of intellectual development?
Piaget's four stages of intellectual (or cognitive) development are:
- Sensorimotor. Birth through ages 18-24 months
- Preoperational. Toddlerhood (18-24 months) through early childhood (age 7)
- Concrete operational. Ages 7 to 11
- Formal operational. Adolescence through adulthood
What are the Piaget stages of development?
Piaget concluded that there were four different stages in the cognitive development of children. The first was the Sensory Motor Stage, which occurs in children from birth to approximately two years. The Pre-operational Stage is next, and this occurs in children aged around two to seven years old. Children aged around seven to eleven or twelve go through the Concrete Operational stage, and adolescents go through
What is the first stage of cognitive development?
Stages of Cognitive Development
- Sensorimotor Stage. The sensorimotor stage is the first stage of cognitive development and lasts from birth to two years of age.
- Preoperational Stage. The preoperational stage ranges from two years to approximately six or seven years of age. ...
- Concrete Operational Stage. ...
- Formal Operational Period. ...
See more
What is the correct sequencing of Piaget stages of cognitive development?
The correct sequence is letter D. sensorimotor, pre-operational, concrete operational, formal operational.
What is the correct order of Piaget's stages quizlet?
What is the correct order of Piaget's stages of development? a) sensorimotor, concrete, operational, preoperational, formal operational.
What are the 4 stages of Piaget's theory?
Piaget's four stagesStageAgeGoalSensorimotorBirth to 18–24 months oldObject permanencePreoperational2 to 7 years oldSymbolic thoughtConcrete operational7 to 11 years oldOperational thoughtFormal operationalAdolescence to adulthoodAbstract conceptsMar 29, 2018
What are Piaget's stages of development quizlet?
Terms in this set (4)Sensorimotor (stage 1) experiencing the world through senses and actions (looking, hearing, touching, mouthing, and grasping). ... Preoperational (stage 2) ... concrete operational (stage 3) ... Formal operational (stage 4)
What is Piaget's theory of moral development?
Piaget's Theory of Moral Development Basically, children accept that authority figures have godlike powers, and are able to make rules that last forever, do not change, and must be followed.
What are the four stages of growth and development?
In these lessons, students become familiar with the four key periods of growth and human development: infancy (birth to 2 years old), early childhood (3 to 8 years old), middle childhood (9 to 11 years old), and adolescence (12 to 18 years old).
What are the main influences of Piaget's theory on cognitive development of child?
Piaget believed that our thinking processes change from birth to maturity because we are always trying to make sense of our world. These changes are radical but slow and four factors influence them: biological maturation, activity, social experiences, and equilibration.
What does Piaget's theory focus on?
Jean Piaget's theory of cognitive development suggests that children move through four different stages of mental development. His theory focuses not only on understanding how children acquire knowledge, but also on understanding the nature of intelligence.1? Piaget's stages are: Sensorimotor stage: birth to 2 years.
What are the 5 stages of child development?
Children develop skills in five main areas of development: Cognitive Development. This is the child's ability to learn and solve problems. Social and Emotional Development. Speech and Language Development. Fine Motor Skill Development. Gross Motor Skill Development.
What is Piaget's first stage of moral development?
Piaget's first stage of moral development encapsulates up to the child's fourth year or so. It could be considered “pre-moral” in a sense because the child does not truly interact socially with others. On one end of the spectrum, the child is still attempting to master basic motor skills necessary to play.
What are the main stages of child development?
There are three broad stages of development: early childhood, middle childhood, and adolescence. The definitions of these stages are organized around the primary tasks of development in each stage, though the boundaries of these stages are malleable.
What is the effect of Piaget's work on children's cognitive abilities?
When tasks were altered, performance (and therefore competence) was affected. Therefore, Piaget might have underestimated children’s cognitive abilities. For example, a child might have object permanence (competence) but still not be able to search for objects (performance).
Where did Piaget develop the theory of logical thinking?
How Piaget Developed the Theory. Piaget was employed at the Binet Institute in the 1920s, where his job was to develop French versions of questions on English intelligence tests. He became intrigued with the reasons children gave for their wrong answers to the questions that required logical thinking.
What is the basic building block of cognitive models?
According to Piaget, children are born with a very basic mental structure (genetically inherited and evolved) on which all subsequent learning and knowledge are based. Schemas are the basic building blocks of such cognitive models, and enable us to form a mental representation of the world. Piaget (1952, p.
What is the basic building block of intelligent behavior?
In more simple terms Piaget called the schema the basic building block of intelligent behavior – a way of organizing knowledge. Indeed, it is useful to think of schemas as “units” of knowledge, each relating to one aspect of the world, including objects, actions, and abstract (i.e., theoretical) concepts.
What did Piaget believe?
Piaget believed that all human thought seeks order and is uncomfortable with contradictions and inconsistencies in knowledge structures. In other words, we seek 'equilibrium' in our cognitive structures.
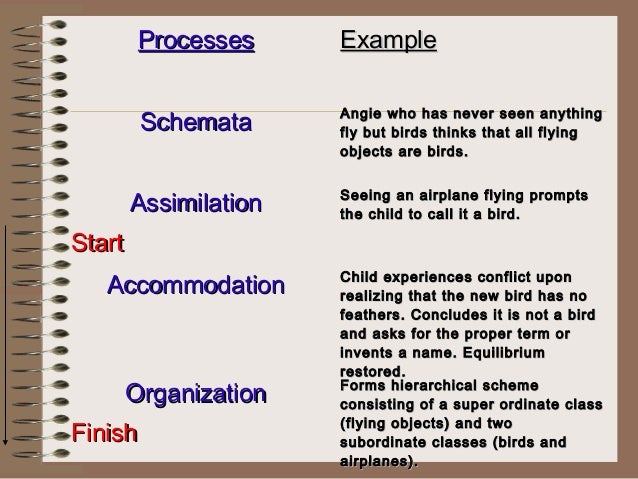
What is the process of fitting new information into existing cognitive schemas, perceptions, and understanding?
Assimilation. Piaget defined assimilation as the cognitive process of fitting new information into existing cognitive schemas, perceptions, and understanding. Overall beliefs and understanding of the world do not change as a result of the new information.
How did Piaget change the world?
He was an inspiration to many who came after and took up his ideas. Piaget's ideas have generated a huge amount of research which has increased our understanding of cognitive development.
What are Piaget's stages of cognitive development?
Piaget’s four stages of cognitive development are: Sensorimotor. Preoperational. Concrete operational. Formal operational. Each of the stages of cognitive development reflect the increasing sophistication of a child's thoughts, and all children go through the stages in the same order. Piaget also believed that:
What is the final stage of Piaget's theory?
The final stage of Piaget's theory involves an increase in logic, the ability to use deductive reasoning, and an understanding of abstract ideas. At this stage, the adolescent or young adult begins to think abstractly and reason on hypothetical problems.
What is the theory of cognitive development?
Jean Piaget's theory of cognitive development suggests that as children grow, they move through four different stages of mental development. The theory focuses not only on understanding how children acquire knowledge but also on the nature of the child’s intelligence. Piaget studied his children from infancy to adolescence.
What did Piaget study?
Piaget studied his children from infancy to adolescence. Based on his observations, he determined that a child’s cognitive development is not just about acquiring knowledge, but about constructing a mental model of the world. Piaget’s four stages of cognitive development are: Each of the stages of cognitive development reflect ...
What did Piaget believe about the development of children?
Piaget also believed that: Child development is determined by biological maturation and environmental interaction. At each stage of development, the child’s thought process is qualitatively different from the other stages. Each stage involves a different type of intelligence.
What are the characteristics of a developmental child?
During this stage, a range of cognitive abilities develop: object permanence, self-recognition, deferred imitation, and representational play.
What is the stage 2 of language development?
Stage 2: Preoperational (2-7 years) Major characteristics and developmental changes: The emergence of language is one of the major hallmarks of this stage. During this stage, children begin to think symbolically and learn to use words and pictures to represent objects.
What is the cognitive process of Piaget?
Piaget's Cognitive Learning Process. 1. all thinking begins at balanced mental state of equilibrium. 2. child receives new info. 3. child adapts new info assimilation/ accommodation. 4. new thought (schema) is formed.
Who is the father of cognitive development?
Jean Piaget is the father of cognitive development, he noticed that children around the same age tend to make the same mistakes. Jean Piaget then observed children and he proposed a sequence of development that all normal children follow. He believed there are 4 STAGES of cognitive development.
What is the term for the ability to recognize that objects can be transformed in some way, visually or physically, yet still
Conservation. A conceptual tool - Ability to recognize that objects can be transformed in some way, visually or physically, yet still be the same in numbers, volumes, weight, liquid, or matter. Assimilation. The way children incorporate (take in) new information with existing schemes to form new cognitive structures.
History of Piaget's Theory of Cognitive Development
The Preoperational Stage
- The foundations of language development may have been laid during the previous stage, but the emergence of language is one of the major hallmarks of the preoperational stage of development.3 At this stage, kids learn through pretend play but still struggle with logic and taking the point of view of other people. They also often struggle with understanding the idea of consta…
The Concrete Operational Stage
- While children are still very concrete and literal in their thinking at this point in development, they become much more adept at using logic.2 The egocentrism of the previous stage begins to disappear as kids become better at thinking about how other people might view a situation. While thinking becomes much more logical during the concrete operational state, it can also be very ri…
The Formal Operational Stage
- The final stage of Piaget's theory involves an increase in logic, the ability to use deductive reasoning, and an understanding of abstract ideas.3At this point, adolescents and young adults become capable of seeing multiple potential solutions to problems and think more scientifically about the world around them. The ability to thinking about abstract ideas and situations is the k…
Important Concepts
- It is important to note that Piaget did not view children's intellectual development as a quantitative process. That is, kids do not just add more information and knowledge to their existing knowledge as they get older. Instead, Piaget suggested that there is a qualitative change in how children think as they gradually process through these four stages.4 At age 7, children don't just have more inf…
A Word from Verywell
- One of the main points of Piaget's theory is that creating knowledge and intelligence is an inherently activeprocess. "I find myself opposed to the view of knowledge as a passive copy of reality," Piaget wrote. "I believe that knowing an object means acting upon it, constructing systems of transformations that can be carried out on or with this object. Knowing reality means constru…
How Piaget Developed The Theory
Stages of Cognitive Development
- Piaget’s Four Stages
Although no stage can be missed out, there are individual differences in the rate at which children progress through stages, and some individuals may never attain the later stages. Piaget did not claim that a particular stage was reached at a certain age - although descriptions of the stages … - Piaget's Theory Differs From Others In Several Ways:
Piaget's (1936, 1950) theory of cognitive development explains how a child constructs a mental model of the world. He disagreed with the idea that intelligence was a fixed trait, and regarded cognitive development as a process which occurs due to biological maturation and interaction …
Schemas
- Piaget claimed that knowledge cannot simplyemerge from sensory experience; some initial structure is necessary to make sense of the world. Schemas are the basic building blocks of such cognitive models, and enable us to form a mental representation of the world. In more simple terms Piaget called the schema the basic building block of intelligent behavior – a way of organi…
Educational Implications
- Piaget (1952) did not explicitly relate his theory to education, although later researchers have explained how features of Piaget's theory can be applied to teaching and learning. Piaget has been extremely influential in developing educational policy and teaching practice. For example, a review of primary education by the UK government in 1966 was based strongly on Piaget’s theor…
Piaget vs Vygotsky
- Piaget maintains that cognitive development stems largely from independent explorations in which children construct knowledge of their own. Whereas Vygotsky argues that children learn through social interactions, building knowledge by learning from more knowledgeable others such as peers and adults. In other words, Vygotsky believed that culture affects cognitive developme…