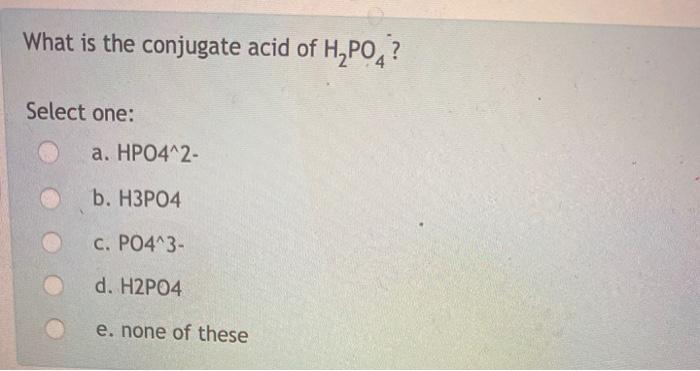What is the conjugate base of hpo42 -?
| Acid | Conjugate base |
| H 2 S Hydrosulfuric acid | HS − Hydrogen sulfide ion |
| H 2 PO − 4 Dihydrogen phosphate ion | HPO 2− 4 Hydrogen phosphate ion |
| NH + 4 Ammonium ion | NH 3 Ammonia |
| H 2 O Water (pH=7) | OH − Hydroxide ion |
What is the conjugate base of HPO42 -?
20/10/2021 · Part a. The conjugate acid of will from after accept one proton by as follows: After donate one proton from an acid conjugate base will form and after accepts one proton by a base conjugate acid will form. The pair of Acid-Base which is differs by a proton is called conjugated Acid-Base pair. The acid of conjugated acid-base pair has one more ...
What is the conjugate acid of HP O2-4?
Therefore, the base hydrogen phosphate ion reacts with a proton to form a conjugate acid. The reaction of hydrogen phosphate ion with a proton to form its conjugate acid is given below: HP O 4 2 − + H + → H 2 P O 4 −. Therefore, the conjugate acid that is formed is H 2 P O 4 −, which is dihydrogen phosphate ion.
What is the conjugate acid of H2PO4-?
The conjugate acid of H P O 4 2 − is H 2 P O 4 − H 2 P O 4 − → H + + H P O 4 2 − The base and its conjugate acid differ by one proton only.
What is a conjugate acid?
When a base accepts a proton in a solution, it forms a conjugate acid. Explore the history of acid theory, learn more about the definition and formation of conjugate acids, and check out common ...
class 5
The Fish Tale Across the Wall Tenths and HundredthsParts and Whole Can you see the Pattern?
class 9
Circles Coordinate Geometry What is Democracy? Why Democracy?Nazism and the Rise of Hitler Socialism in Europe and the Russian Revolution
Properties of Phosphoric Acid
Phosphoric acid contains three removable protons and exhibits three different acid dissociation equilibrium. It appears a viscous liquid at normal temperature and pressure.
Answer and Explanation: 1
The conjugate acid contains an extra hydrogen (H) atom and one less negative charge compared to the corresponding base.