What type of circulatory system does a grasshopper have?
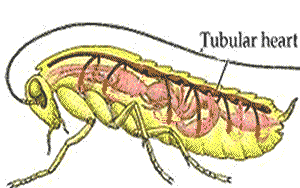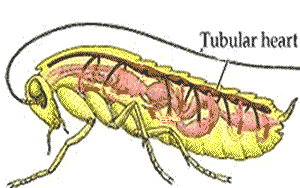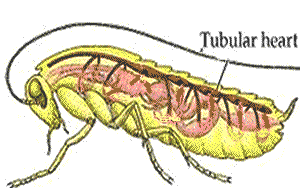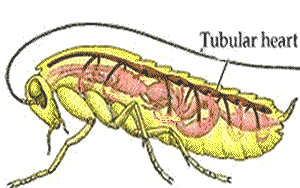
Like other insects, grasshoppers have an open circulatory system and their body cavities are filled with haemolymph. A heart-like structure in the upper part of the abdomen pumps the fluid to the head from where it percolates past the tissues and organs on its way back to the abdomen.
What is the digestive system of a grasshopper?
Grasshoppers are heterotrophic organisms and like many other heterotrophs they have a digestive system beginning with a mouth where food is ingested and ending in an anus where food is expelled. After the food is sufficiently masticated it travels to the stomach where it is met with a variety of digestive enzymes.
How to make circulatory system model?
the first part of our heart model is ready take a big balloon cover it with balloon dual part of our heart model is ready fix the drip chamber on the small valves fix it with the hot glue gun cut the nose tip of the drip chamber like this connect two more drip pipe on the drip chamber attach the parts of our heart join with tape
What are the 4 main parts of the circulatory system?
- The vascular system: a system of tube, or vessels, through which blood or lymph flows
- The pumping organ, or heart, which pumps blood through the blood vessels
- Blood
- Lymph
Is grasshopper closed circulatory system?
They don't have closed circulatory systems that restrict fluid flow to certain parts of the body. Researchers discovered how insects adjust their cardiovascular and respiratory activity in response to gravity.
Why circulatory system of the grasshopper is an open one?
An open circulatory system is beneficial because animals don't have a blood pressure, so they can live at great ocean depths. In the case of insects with a tracheal system, there are reduced oxygen demands because they bring oxygen into their body through a series of tubes.
What is the circulatory system of insects?
Insects, like all other arthropods, have an open circulatory system which differs in both structure and function from the closed circulatory system found in humans and other vertebrates. In a closed system, blood is always contained within vessels (arteries, veins, capillaries, or the heart itself).
Do grasshoppers have blood vessels?
The constituent components of grasshopper circulatory system consist of blood vessels, heart, and aorta. The blood of grasshopper does not contain haemoglobin that is not red.
What is open circulatory system?
Open circulation happens when there are no vessels to contain the blood and it flows freely through the cavities of the body. Also Read: Human Circulatory System.
What is open and closed circulatory system?
In open circulatory system, the blood vessels open into spaces and not into capillaries, so that blood comes in direct contact with tissues. Whereas in closed circulatory system, blood flows through capillaries connected by arteries and veins.
How many hearts do grasshoppers have?
The number of chambers in an insect heart varies with grasshoppers having eight, for instance, and cockroaches a whopping thirteen. Each chamber of the heart has two holes called ostia. These have valves so that blood only flows one way: from the pool of haemolymph in the body into the heart.
Which organ does a grasshopper breathe through?
Respiration is performed using tracheae, air-filled tubes, which open at the surfaces of the thorax and abdomen through pairs of valved spiracles.
What type of circulatory system do arthropods have?
open circulatory systemArthropods possess an open circulatory system consisting of a dorsal heart and a system of arteries that may be very limited (as in insects) or extensive (as in crabs). The arteries deliver blood into tissue spaces (hemocoels), from which it eventually drains back to a large pericardial sinus surrounding the heart.
Why the circulatory system of worm is different with grasshopper?
Worms also carry oxygen around with a pigment. Grasshoppers, on the other hand, have an open circulatory system, meaning that blood flows into open spaces (sinuses), rather than through blood vessels.
How does a grasshoppers heart Work?
The abdomen section of the dorsal vessel is considered the insect's heart because it has muscles and ostia, openings that allow hemolymph to enter and exit. Hemolymph enters the heart when it's relaxed. The heart then contracts and pumps the hemolymph through the vessel toward the insect's head.
Where does the exchange of oxygen and carbon dioxide occur in the grasshopper?
In the grasshopper, exchange of oxygen and carbon dioxide occurs in the tracheal system. Hemolymph plays no part in the process. There is not even an oxygen-carrying pigment in insect hemolymph.
What is an open circulatory system?
An "Open" Circulatory System: The Grasshopper. The circulatory system of insects differs from that of vertebrates and many other invertebrates in being "open". In insects, "blood" is confined to vessels during only a portion of its circuit through the body. The remainder of its journey takes place within the body cavity (called the hemocoel).
Where does hemolymph go in the heart?
The hearts pump hemolymph into the sinuses of the hemocoel where exchanges of materials take place. Coordinated movements of the body muscles gradually bring the hemolymph back to the dorsal sinussurrounding the hearts. Between contractions, tiny valves in the wall of the hearts open and allow hemolymph to enter.
Which system is responsible for transporting oxygen to all tissues and removing carbon dioxide from them?
In vertebrates, the circulatory system is responsible for transporting oxygento all the tissues and removing carbon dioxidefrom them. It is this requirement that establishes the level of performance demanded of the system.
What is the body cavity of an insect called?
The remainder of its journey takes place within the body cavity (called the hemocoel ). For this reason, insect "blood" is called hemolymph. The volume of hemolymph needed for such a system is kept to a minimum by a reduction in the size of the body cavity. The hemocoel is divided into chambers called sinuses.
What are the two types of circulatory system?
There are two types of circulatory system; closed and open circulatory system . Grasshoppers have an open circulatory system, which is different from that of vertebrates and other invertebrates. The constituent components of grasshopper circulatory system consist of blood vessels, heart, and aorta.
Do frogs have a heart?
Frogs are amphibians and have a closed circulatory system. Unless there is an abnormal mutation present, frogs only have one heart to pump blood throughout the body.
Does a crayfish have a closed circulatory system?
Additionally, does a crayfish have an open or closed circulatory system? Crayfish has open circulatory system. No veins or arteries are present in the open circulatory system, but instead, blood like fluid is circulated through the blood vessels, throughout the heart, also in the hemolymph.
What is the respiratory system of a grasshopper?
The respiratory system of a grasshopper, showing spiracles in the thorax and abdomen. Although movements of oxygen and carbon dioxide occur solely by gaseous diffusion in sedentary insects, the system is ventilated mechanically in active species.
What is the circulatory system?
The circulatory system is an open one, with most of the body fluid, or hemolymph, occupying cavities of the body and its appendages. The one closed organ, called the dorsal vessel, extends from the hind end through the thorax to the head; it is a continuous tube with two regions, the heart or pumping organ, which is restricted to the abdomen, and the aorta, or conducting vessel, which extends forward through the thorax to the head. Hemolymph, pumped forward from the hind end and the sides of the body along the dorsal vessel, passes through a series of valved chambers, each containing a pair of lateral openings called ostia, to the aorta and is discharged in the front of the head. Accessory pumps carry the hemolymph through the wings and along the antennae and legs before it flows backward again to the abdomen.
What is the function of the hemolymph?
It contains free cells called hemocytes, most of which are phagocytes that help to protect the insect by devouring microorganisms. An important tissue bathed by the hemolymph is the fat body, the main organ of intermediary metabolism. It serves for the storage of fat, glycogen, and protein, particularly during metamorphosis.
Where do accessory pumps carry hemolymph?
Accessory pumps carry the hemolymph through the wings and along the antennae and legs before it flows backward again to the abdomen. circulatory system of a generalized insect.
Which system is a continuous system of air filled tubes?
Respiratory system. The respiratory system consists of air-filled tubes or tracheae, which open at the surface of the thorax and abdomen through paired spiracles. The muscular valves of the spiracles, closed most of the time, open only to allow the uptake of oxygen and the escape of carbon dioxide. The tracheal tubes are continuous with ...
What is the reproductive system of grasshoppers?
Control of Grasshopper. 1. Habit, Habitat and External Features of Grasshopper: Grasshoppers have worldwide distribution and are found where there are open grasslands and abundant leafy vegetation. They feed on leafy vegetation.
What are the sense organs of grasshoppers?
The sense organs of the grasshopper are adapted for receiving stimuli from the air and other environment in which it lives and to make adjustment to the external changes by the movement or other responses.
Why can grasshoppers hear?
It is supposed that grasshopper can hear because it creates particular sound with the stridulating apparatus. The pair of auditory organs are located on the sides of the tergite of the first abdominal segment. Each auditory organ consists of a tympanum or tympanic membrane stretched within an almost circular chitinous ring.
How do grasshoppers pump air?
There are also several thin-walled air sacs in the abdomen which pump air in and out of the tracheal system by the alternate contraction and expansion of the abdomen. In the grasshopper the action of spiracles is so synchronized that the first four pairs of spiracles are open at inspiration and closed at expiration, while the other six pairs are closed at inspiration and open at expiration.
What are grasshoppers controlled by?
The grasshoppers are controlled by natural as well as artificial or chemical means. The grasshopper eggs are eaten by some beetles, bee flies, moles, skunks, and mice, the nymphs by robber flies and digger wasps and both nymphs and adults by large predatory insects and by frogs, reptiles, birds and mammals.
How to tell if a grasshopper is male or female?
The sexes are separate and the distinction between male and female grasshopper can be determined by the posterior ends of abdomen. In the male it is round; in the female it is pointed because of ovipositor.
What are the parts of a grasshopper's mouth called?
The mouth parts of grasshopper are chewing or mandibulate type. ADVERTISEMENTS: The mouth parts include the labrum, mandibles, maxillae, labium and hypo pharynx. There is a labrum or upper lip attached to the ventral edge of the clypeus. Beneath this is a membranous tongue-like organ, the hypo pharynx.
What is grasshopper?
For other uses, see Grasshopper (disambiguation). Grasshoppers are a group of insects belonging to the suborder Caelifera. They are among what is probably the most ancient living group of chewing herbivorous insects, dating back to the early Triassic around 250 million years ago.
How do grasshoppers jump?
Grasshoppers jump by extending their large back legs and pushing against the substrate (the ground, a twig, a blade of grass or whatever else they are standing on); the reaction force propels them into the air. They jump for several reasons; to escape from a predator, to launch themselves into flight, or simply to move from place to place. For the escape jump in particular there is strong selective pressure to maximize take-off velocity, since this determines the range. This means that the legs must thrust against the ground with both high force and a high velocity of movement. A fundamental property of muscle is that it cannot contract with high force and high velocity at the same time. Grasshoppers overcome this by using a catapult mechanism to amplify the mechanical power produced by their muscles.
What suborder are grasshoppers in?
Grasshoppers belong to the suborder Caelifera. Although "grasshopper" is sometimes used as a common name for the suborder in general, some sources restrict it to the more "advanced" groups. They may be placed in the infraorder Acrididea and have been referred-to as "short-horned grasshoppers" in older texts to distinguish them from the also-obsolete term "long-horned grasshoppers" (now bush-crickets or katydids) with their much longer antennae. The phylogeny of the Caelifera, based on mitochondrial ribosomal RNA of thirty-two taxa in six out of seven superfamilies, is shown as a cladogram. The Ensifera (crickets, etc. ), Caelifera and all the superfamilies of grasshoppers except Pamphagoidea appear to be monophyletic.
What are the diseases that grasshoppers are affected by?
Grasshoppers are affected by diseases caused by bacteria, viruses, fungi and protozoa. The bacteria Serratia marcescens and Pseudomonas aeruginosa have both been implicated in causing disease in grasshoppers, as has the entomopathogenic fungus Beauveria bassiana. This widespread fungus has been used to control various pest insects around the world, but although it infects grasshoppers, the infection is not usually lethal because basking in the sun has the result of raising the insect's temperature above a threshold tolerated by the fungus. The fungal pathogen Entomophaga grylli is able to influence the behaviour of its grasshopper host, causing it to climb to the top of a plant and cling to the stem as it dies. This ensures wide dispersal of the fungal spores liberated from the corpse.
How do grasshoppers flex their legs?
First, the grasshopper fully flexes the lower part of the leg (tibia) against the upper part (femur) by activating the flexor tibiae muscle (the back legs of the grasshopper in the top photograph are in this preparatory position).
How many segments are there in a grasshopper?
The abdomen has eleven segments, the first of which is fused to the thorax and contains the tympanal organ and hearing system. Segments two to eight are ring-shaped and joined by flexible membranes. Segments nine to eleven are reduced in size; segment nine bears a pair of cerci and segments ten and eleven have the reproductive organs. Female grasshoppers are normally larger than males, with short ovipositors. The name of the suborder "Caelifera" comes from the Latin and means chisel-bearing, referring to the shape of the ovipositor.
What is the name of the worm that infects grasshoppers?
The grasshopper nematode ( Mermis nigrescens) is a long slender worm that infects grasshoppers, living in the insect's hemocoel. Adult worms lay eggs on plants and the host becomes infected when the foliage is eaten. Spinochordodes tellinii and Paragordius tricuspidatus are parasitic worms that infect grasshoppers and alter the behaviour of their hosts. When the worms are sufficiently developed, the grasshopper is persuaded to leap into a nearby body of water where it drowns, thus enabling the parasite to continue with the next stage of its life cycle, which takes place in water.