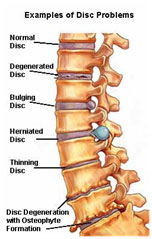
The articular disk (or disc) is a thin, oval plate of fibrocartilage
Fibrocartilage
White fibrocartilage consists of a mixture of white fibrous tissue and cartilaginous tissue in various proportions. It owes its inflexibility and toughness to the former of these constituents, and its elasticity to the latter. It is the only type of cartilage that contains type I collagen in addition to the normal type II.
Synovial joint
A synovial joint, also known as diarthrosis, joins bones with a fibrous joint capsule that is continuous with the periosteum of the joined bones, constitutes the outer boundary of a synovial cavity, and surrounds the bones' articulating surfaces. The synovial cavity/joint is filled with synovial fluid. The joint capsule is made up of an outer layer, the articular capsule, which keeps the bones together structur…
What is the function of articular discs?
Treatment may include:
- Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), such as ibuprofen, aspirin, and naproxen.
- Physical therapy, which can help a person regain some strength and movement in the spine through special exercises.
- Radiofrequency ablation.
- Anesthetic injections.
- Spine surgery.
What is an articular disk?
The articular disk (or disc) is a thin, oval plate of fibrocartilage present in several joints which separates synovial cavities. This separation of the cavity space allows for separate movements to occur in each space.
Can my TMJ cartilage be repaired?
Researchers from the Columbia University College of Dental Medicine have identified stem cells within the temporomandibular joint (TMJ) that can make new cartilage and repair damaged joints. The cells reside within the temporomandibular joint (TMJ), which articulates the jaw bone to the skull.
What is the function of the articular system?
Where Is Articular Cartilage Found
- Planar (Gliding) Joints. Planar joints do not rotate, but allow two, relatively flat bone surfaces to glide across one another.
- Hinge Joints. The two bone surfaces are of different shapes. ...
- Pivot Joints. ...
- Condyloid (Ellipsoidal) Joints. ...
- Saddle Joints. ...
- Ball and Socket Joints. ...
What is the function of articular disc?
The cartilaginous articular disc is situated between the condyle and the fossa and acts as a cushion that absorbs stress and allows the condyle to move easily when the mouth opens and closes.
What is meant by articular disc?
The articular disc is a somewhat oval body of fibrous tissue, which is convex on its upper surface to accommodate itself to the shape of the articular fossa and concave on its inferior surface to conform to the head of the mandible.
Which joint includes articular disc?
the temporomandibular jointThe fibers of which the disc is composed have a concentric arrangement, more apparent at the circumference than at the center. It divides the joint into two cavities, each of which is furnished with a synovial membrane....Articular disk of the temporomandibular jointFMA57059Anatomical terminology7 more rows
Is the articular disk a bone?
0:442:02Two Minutes of Anatomy: Articular Disc AKA Articular Disk - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipSpace an articular disc permits a more even distribution of forces between the articular surfaces ofMoreSpace an articular disc permits a more even distribution of forces between the articular surfaces of the bones increases the stability of the joint.
Where are articular discs found?
When complete they are called disks; when incomplete they are called menisci. Disks are found in the temporomandibular joint of the lower jaw, the sternoclavicular (breastbone and collarbone) joint, and the ulnocarpal (inner forearm bone and wrist) joint.
What is articular disc or meniscus?
The articular disk(meniscus) is a thin, oval plate of fibrocartilage present in several joints which separates synovial cavities. This separation of the cavity space allows for separate movements to occur in each space. Ex : meniscus of knee joint, articular disks of the temporomandibular or stenoclavicular joints.
What is an articular joint?
A joint or articulation (or articular surface) is the connection made between bones in the body which link the skeletal system into a functional whole.
What attaches to the articular disc?
Capsule - The capsule is a fibrous membrane that surrounds the joint and attaches to the articular eminence, the articular disc and the neck of the mandibular condyle.
Does the elbow have an articular disc?
The articular disc is attached to the ulnar styloid by its apex and by its base to the radius. The disc slides over the ulnar end during pronation and supination of the forearm.
How do you fix TMJ disc displacement?
Less frequently, the disk remains displaced and jaw opening is restricted. Diagnosis is based on history and physical examination. Treatment is with analgesics, jaw rest, muscle relaxation, physical therapy, and oral appliance therapy. If these methods fail, surgery may be necessary.
What causes TMJ disc displacement?
The most common cause is trauma to the lower jaw. Depending on the amount of trauma, there can be anterior disc displacement with or without reduction.
What is the TMJ made of?
Structure. The main components are the joint capsule, articular disc, mandibular condyles, articular surface of the temporal bone, temporomandibular ligament, stylomandibular ligament, sphenomandibular ligament, and lateral pterygoid muscle.
What is articular disc displacement without reduction?
Articular disc displacement without reduction is a progression of articular disc displacement with reduction. When the condition is acute, the opening is limited to less than 25 mm with an end-range deviation toward the affected joint, limited contralateral lateral excursion, and deviation of the mandible toward the affected side with protrusion. Because this pattern of limited mandibular AROM is the same as with capsular fibrosis, a history of joint sounds can help to distinguish the likelihood of a disc displacement without reduction. The disc displacement without reduction disorder typically has a history of an opening and closing joint sound, but the joint sounds disappear when the acute limitation in mandibular motion occurs. This condition occurs when the articular disc displaces anterior to the condyle and is unable to be reduced with movement of the mandible. The disc blocks further anterior transslation with opening, contralateral lateral excursion, and protrusion (Figure 7-12 ). Accessory motions of the affected joint are also limited. When the condition is chronic, the posterior ligament and capsular tissues can be stretched to allow full normal mandibular motion. Yatani et al. 46 reported that 80 of 138 patients (58%) who demonstrated MRI evidence of an anterior disc displacement without reduction presented with normal mandibular opening ROM on clinical examination.
What is the role of the articular disc in TMJ?
It fills the space between the condyle and the temporal bone, and acts as a stress absorber and distributors during the jaw activity.
Why is it important to place a needle as perpendicular to the articular disk?
It is important to place the needle as perpendicular as possible to the articular disk so that the needle perforates through the disk. If the needle is placed too horizontally, it potentially may shred through the articular disk, and the purchase of the suture will not be suitable.
Which nerve is retracted volarly?
The retinaculum of the extensor carpi ulnaris is then released along its radial side and is retracted volarly. Close attention is given to preserve the articular branch of the dorsal sensory branch of the ulnar nerve as it crosses the incision in an attempt to decrease the risk of sympathetic dystrophy.
What is the normal disc shape on MRI?
In a sagittal image slice, the normal biconcave disc appears as a “bow tie” shape.
What is disc displacement without reduction disorder?
The disc displacement without reduction disorder typically has a history of an opening and closing joint sound, but the joint sounds disappear when the acute limitation in mandibu lar motion occurs.
Can anterior disc displacement be reduced?
Patients with anterior disc displacement without reduction can make functional and symptomatic improvements with the use of joint mobilization and therapeutic exercise. Over time, the shape of the articular disc tends to change and the likelihood of reducing and maintaining a normal disc condyle relationship is minimal.
What is the plate attached to the joint capsule?
A plate or ring of fibrocartilage attached to the joint capsule and separating the articular surfaces of the bones for a varying distance, sometimes completely; it serves to adapt two articular surfaces that are not entirely congruent.
What is fibrocartilage attached to?
a plate or ring of fibrocartilage attached to the joint capsule and separating the articular surfaces of the bones for a varying distance, sometimes completely; it serves to adapt two articular surfaces that are not entirely congruent.
What is the articular disk?
The articular disk is a part of a joint which consists of fibrous cartilage and tight, parallely aligned connective tissue, which usually divides the articular cavity into two chambers. It serves to compensate incongruencies of the articular planes and to buffer respectively distribute the pressure which lasts on the joint .
Where are articular discs supplied?
They are supplied with nutrients via diffusion from the synovia. Typical examples for the articular discs are the menisci in between of femur and tibial plateau in the area of the knee joint; the disc in the area of the proximal hand joint; the disc of the sternoclavicular joint or the disc in the mandibular joint in between of the mandible and the temporal bone ( os temporale ).
What is the articular disc?
Articular disc: The articular disc is a thin piece of fibrocartilage in the TMJ that separates the condyle of the jaw from the mandibular fossa in the skull. It allows your jaw to open and close. Articular discs are also present in several other joints.
What is mensicus in knee?
If the cartilage comes loose and bend or moves as the knee is moving, then it can get caught in the joint between the bones, and will be pinched. This can cause pain, can cause a piece to be broken off and get loose in the knee and can cause problems for you. If you are concerned, see an orthopedist or your pcp. May need more diagnostics.
disk
a circular or rounded flat plate; often spelled disc in names of anatomic structures.
articular disk
The biconcave oval disk of fibrous connective tissue that separates the two joint cavities of the temporomandibular joint on each side.
What is the articular disc?
The articular disc is an important component of the temporomandibular joint, whose morphology has been studied on autopsy and biopsy materials. The normal posterior attachment of the disc is usually described as having two layers, one upper and one lower. The upper layer consists of elastic fibres, collagen fibres, fat deposits and blood vessels.
What is the role of elastic fibres in the posterior and anterior attachment regions?
In human TMJ, it is believed that elastic fibres in the posterior and anterior attachment regions may play an important role in the repositioning of the disc during jaw closure.
What are elastic fibres?
Elastic fibres are one of the main constituents of the extracellular matrix of many connective tissues, and they are believed to play a very important role in the normal functions of many tissues such as blood vessels, lungs and dermis.
What is the upper layer of the tympanic wall?
The upper layer consists of elastic fibres, collagen fibres, fat deposits and blood vessels. It is connected posteriorly to the anterior face of the post-glenoid tubercle, the tympanic wall of the temporal bone, the cartilaginous meatus and the parotid gland lining. The lower layer, on the other hand, consists of a compact lamina ...
Why does my anterior disc hurt?
Pain can result from an anteriorly displaced disc. However, it does not arise from the disc itself. Rather, it is caused by compression of the highly innervated tissue attached to the posterior aspect of the disc (retrodiscal tissue) that becomes located in the gliding area between the condyle and the skull when the disc becomes displaced ...
What is anterior displacement without reduction?
In later stages, when the disc becomes more anteriorly displaced, it acts as a barrier to condylar movement and limits mouth opening. This is referred to as “anterior displacement without reduction.”. It has also been referred to as “closed lock.”.
Do you need to treat a displaced disc?
A displaced disc does not necessarily need to be treated. If the disc restricts movement and causes pain, treatment may be required. However, if a displaced disc is present with no pain or limited mouth opening, no treatment is needed.
Can TMJ cause displaced discs?
Studies using MRI and arthroscopy have shown displaced discs in people who have symptoms of TMJ pain and dysfunction as well as those who have no symptoms. In other words, many people without TMJ problems have displaced discs.