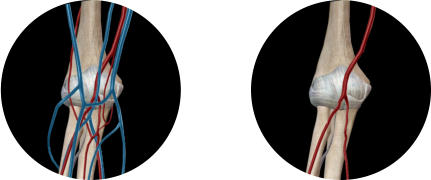
What is the anterior elbow called?
What is the anterior elbow called? The cubital fossa is an area of transition between the anatomical arm and the forearm. It is located in a depression on the anterior surface of the elbow joint. It is also called the antecubital fossa because it lies anteriorly to the elbow (Latin cubitus) when in standard anatomical position.
What is posterior elbow?
- Elbow stiffness is associated with arthritis or trauma. Stiffness restricting flexion is more disabling then restriction of extension.
- Neurological symptoms like numbness and tingling should be assessed. ...
- Referred pain from neck or shoulder can present as elbow pain. ...
What muscles are near the elbow?
Top 4 Reasons for Elbow Twitching and What To Do About It
- Elbow Injury It is important that you first look into the chance that you actually have some sort of elbow injury. ...
- Excessive Use of Your Elbow This is a no brainer! ...
- Muscle Disorders Muscle disorders can also cause your elbow to tweak and twitch. These are hard to detect but not difficult to treat. ...
- Excessive Consumption of Caffeine
What is the anterior aspect of the elbow?
This is the anterior joint line of the elbow: the articular cartilage and the cortical bone is present. Mark continues to scan down the arm until the brachial artery is present. The bicep tendon goes dark and begins to turn onto its side.
What are the parts of your elbow called?
The elbow is where the two bones of the forearm – the radius on the thumb side of the arm and the ulna on the pinky finger side – meet the bone of the upper arm -- the humerus. The lower end of the humerus flares out into two rounded protrusions called epicondyles, where muscles attach.
Is the elbow posterior or anterior?
Elbow joint, posterior view. The humerus contributes the humeral condyle, composed of the trochlea medially from anterior to posterior and the capitulum laterally on the anterior aspect, to the articular surface of the elbow joint.
What are the parts of your arm called?
Each arm consists of four main parts: upper arm. forearm. wrist.
What body part is Antecubital?
The Cubital Fossa is a triangular-shaped depression, located between the forearm and the arm on the anterior surface of the elbow, with the apex of the triangle pointing distally. It is also known as the “antecubital” because it lies anteriorly to the elbow.
What is the anatomy of the elbow?
The Anatomy of the Elbow. The elbow is a hinged joint made up of three bones, the humerus, ulna, and radius. The ends of the bones are covered with cartilage. Cartilage has a rubbery consistency that allows the joints to slide easily against one another and absorb shock. The bones are held together with ligaments that form the joint capsule.
What is the capsule of the elbow?
The joint capsule is a fluid filled sac that surrounds and lubricates the joint. The important ligaments of the elbow are the medial collateral ligament (on the inside of the elbow) and the lateral collateral ligament (on the outside of the elbow.)
What are the tendons that attach to the biceps?
There are tendons in your elbow that attach muscle to bone. The important tendons of the elbow are the biceps tendon, which is attached the biceps muscle on the front of your arm, and the triceps tendon, which attaches the triceps muscle on the back of your arm.
Which ligaments are responsible for the stability of the humerus and ulna?
Together these ligaments provide the main source of stability for the elbow, holding the humerus and the ulna tightly together. A third ligament, the annular ligament, holds the radial head tight against the ulna. There are tendons in your elbow that attach muscle to bone.
Where do the muscles on the inside of the arm attach?
Most of the muscles that straighten the fingers and wrist come together and attach to the medial epicondyle, or the bump on the inside of your arm just above the elbow. These two tendons are important to understand because they are common locations of tendonitis.
What nerves are involved in shoulder arthroscopy?
Three main nerves begin together at the shoulder the radial nerve, the ulnar nerve and the medial nerve. These nerves are responsible for signaling your muscles to work and to also relay sensations such as touch, pain and temperature. NEXT TOPIC: Common Conditions that Require Elbow Arthroscopy.