siphon
- (General Physics) a tube placed with one end at a certain level in a vessel of liquid and the other end outside the vessel below this level, so that ...
- (Brewing) See soda siphon
- (Zoology) zoology any of various tubular organs in different aquatic animals, such as molluscs and elasmobranch fishes, through which a fluid, esp water, passes
What does the name siphon mean?
What does the word siphon means? 1 : a bent pipe or tube through which a liquid can be drawn by air pressure up and over the edge of a container. 2 : a tubelike part especially of a mollusk (as a clam) usually used to draw in or squirt out water. siphon. verb. siphoned; ]
What exactly does the siphon do?
- Have You Ever Emptied a Pool? ...
- How does it Work? ...
- The History of Siphon The usage of siphons goes back to ancient Egypt. ...
- It is all Science If you are using a siphon for the first time, you’d think it is no less than magic. ...
- A Mystery to Unravel If you are already confused, let’s put it in simpler words. ...
- What is Self-Siphon? ...
What does siphon mean?
v. 1. To draw off or convey something through or as if through a siphon: I used a tube to siphon off the excess water in the fish tank. The lawn mower ran out of gas, so we siphoned some off from the car's gas tank. 2.
What is a siphon used for?
This is used in the following cases:
- To carry water from one reservoir to another reservoir separated by a hill or ridge.
- To take out the liquid from the tank which is not having any outlet.
- To empty a channel not provided with any outlet sluice.
What does siphon mean in biology?
(Science: zoology) One of the tubes or folds of the mantle border of a bivalve or gastropod mollusk by which water is conducted into the gill cavity.
What does siphon mean in science?
siphon. [ sī′fən ] n. A tube bent into an inverted U shape of unequal lengths, used to remove fluid by means of atmospheric pressure from a cavity or reservoir at one end of the tube over a barrier and out the other end.
What is siphon in botany?
noun One of the tubes or folds of the mantle border of a bivalve or gastropod mollusk by which water is conducted into the gill cavity. See Illust. under Mya , and Lamellibranchiata . noun The anterior prolongation of the margin of any gastropod shell for the protection of the soft siphon.
What body system is the siphon?
Funnel or siphon The funnel, or siphon, is a muscular structure located on the ventral surface of the mantle. It has several functions, including respiration and discharge of wastes.
What is a siphon answer?
The definition of a siphon is a tube that is used to draw liquid from one container into another, lower container by atmospheric pressure and gravity. An example of a siphon is a tube where gas is forced out of a gas tank into a gas container on the ground. noun. 1.
What is siphon simple?
1 : a bent pipe or tube through which a liquid can be drawn by air pressure up and over the edge of a container. 2 : a tubelike part especially of a mollusk (as a clam) usually used to draw in or squirt out water. siphon. verb. siphoned; siphoning.
Why siphon is so called?
A siphon (from Ancient Greek: σίφων, romanized: síphōn, "pipe, tube", also spelled nonetymologically syphon) is any of a wide variety of devices that involve the flow of liquids through tubes.
What is a syphon Mcq?
A long bend pipe used to carry water from a reservoir at a lower level to another reservoir at a higher level with some work input when two reservoirs.
What is a siphon used for?
siphon, also spelled syphon, instrument, usually in the form of a tube bent to form two legs of unequal length, for conveying liquid over the edge of a vessel and delivering it at a lower level.
What is mosquito siphon?
The larvae require air to breathe and have a specialized body part called the “siphon” that they use to breathe air at the water's surface. The siphon uses the water's natural surface tension to attach for a breath. A few species have adapted their siphons to penetrate hollow aquatic plant stems.
Do fish have siphons?
Aquarium siphons use gravity to suck the water and debris out of your aquarium. To start the siphon, make sure the hose end of the siphon is inside the bucket.
Where is the siphon located on a mosquito?
The siphon is an air tube located on the abdomen of the larva. Because the larva hatches from the egg and lives in the water, the siphon allows the larva to breathe. Most species, including those in the genera Culex and Aedes, have a siphon and spend most of their time on the surface breathing.
Why is a siphon called a siphon?
The term "siphon" is used for a number of structures in human and animal anatomy, either because flowing liquids are involved or because the structure is shaped like a siphon, but in which no actual siphon effect is occurring: see Siphon (disambiguation) .
What is the siphon used for?
Egyptian reliefs from 1500 BC depict siphons used to extract liquids from large storage jars.
How does a siphon cause liquid to flow uphill?
There are two leading theories about how siphons cause liquid to flow uphill, against gravity, without being pumped, and powered only by gravity. The traditional theory for centuries was that gravity pulling the liquid down on the exit side of the siphon resulted in reduced pressure at the top of the siphon.
How does a siphon work?
A practical siphon, operating at typical atmospheric pressures and tube heights, works because gravity pulling down on the taller column of liquid leaves reduced pressure at the top of the siphon (formally, hydrostatic pressure when the liquid is not moving). This reduced pressure at the top means gravity pulling down on the shorter column of liquid is not sufficient to keep the liquid stationary against the atmospheric pressure pushing it up into the reduced-pressure zone at the top of the siphon. So the liquid flows from the higher-pressure area of the upper reservoir up to the lower-pressure zone at the top of the siphon, over the top, and then, with the help of gravity and a taller column of liquid, down to the higher-pressure zone at the exit.
What is the principle of a siphon?
Siphon principle. In the flying-droplet siphon, surface tension pulls the stream of liquid into separate droplets inside of a sealed air-filled chamber, preventing the liquid going down from having contact with the liquid going up, and thereby preventing liquid tensile strength from pulling the liquid up.
What happens when the bottom end of a siphon is pressurized?
While if both ends of a siphon are at atmospheric pressure, liquid flows from high to low, if the bottom end of a siphon is pressurized, liquid can flow from low to high. If pressure is removed from the bottom end, the liquid flow will reverse, illustrating that it is pressure driving the siphon.
What is a siphon rain gauge?
A siphon rain gauge is a rain gauge that can record rainfall over an extended period. A siphon is used to automatically empty the gauge. It is often simply called a "siphon gauge" and is not to be confused with a siphon pressure gauge.
In gastropods
File:Heron Island Giant balor S01.ogv In some (but not all) sea snails, marine gastropod molluscs, the animal has an anterior extension of the mantle called a siphon, or inhalant siphon, through which water is drawn into the mantle cavity and over the gill for respiration.
Paired siphons of bivalves
Drawing of the venerid Venus verrucosa showing paired siphons (upper inhalant and lower exhalant siphon), shell and foot.
Hyponome of cephalopods
Nautilus belauensis seen from the front, showing the opening of the hyponome.
Air Entrainment in Plunging Jet Flows
Hubert Chanson M.E., ENSHM Grenoble, INSTN (Saclay), Ph.D. (Cant.), Eur. Ing., MIEAust., MIAHR, in Air Bubble Entrainment in Free-Surface Turbulent Shear Flows, 1996
Family Culicidae
Jeane Marcelle Cavalcante do Nascimento, ... Neusa Hamada, in Thorp and Covich's Freshwater Invertebrates (Fourth Edition), 2018
Burnsville Cove, Virginia
Formerly known as Siphon Cave No. 1 (Douglas, 1964 ), Owl Cave opens as two entrances to a two-level maze cave exceeding 950 m. The Talus Cone Entrance, completed in December 2009, offers easy access to the rear of the cave and the ongoing Looking Glass dig.
Family Dytiscidae
Cesar J. Benetti, ... Mario Toledo, in Thorp and Covich's Freshwater Invertebrates (Fourth Edition), 2018
Measuring Precipitation and Windborne Drops
Recording instruments were necessary to determine the intensity of rainfall, or for delayed observations, and have the advantage of avoiding evaporation losses.
Monitoring for contamination caused by malevolent acts and unforeseen events
A backflow attack occurs when a pump or siphon is used to overcome the pressure gradient that is present in the distribution system’s pipes.
Rising Damp Treatment and Prevention
Other devices have been developed, inspired by Knapen siphons and the principle of ventilation within the damp wall, but better conceived to take advantage of wind and atmospheric turbulence around buildings.
What is a siphon?
The siphon basically an inverted U-tube or pipe filled with water. The filling of the pipe or tube is simple and many ways it can be done. It is the same as the priming of pumps.
What is the purpose of a siphon?
The purpose of Syphon are; If two tanks are kept in different elevations and there is a barrier between them, the siphon is used to transfer liquid from the tank at a higher elevation to the tank at a lower elevation. The net result is that the liquid passes from the reservoir to a lower level with a continuous flow.
What is the difference between a syphon and a leaky bucket?
It’s very simple! The main difference between a syphon and a leaky bucket: Liquid transfer happens without any hole in the tanks whether a leaky bucket means a lot of holes. Liquid transferred to a higher level tank before draining out to a lower level tank.
What is an inverted syphon?
When a siphon is used like U-tube or U-pipe, instead of an inverted U tube, it is called an inverted syphon. It’s used based on the requirements if liquid to be pass through a road. This inverted siphon installed below the road. Flow is due to the pressure instead of gravity flow.
What is the net result of a siphon syphon?
The net result is that the liquid passes from the reservoir to a lower level with a continuous flow. No external energy is required for liquid transfer. The flow continues unless and until the water level reaches the output end of the siphon tube. Siphon syphon basic.
What is the difference between liquid level in a tank and output siphon?
It’s all about gravitational potential difference. There will a gravitation potential difference between the liquid level in the tank and at the output siphon’s opening. This difference makes an unbalanced system and stores potential energy. As a result, the liquid flow will be continued.
What pulls a liquid down?
Normally gravity will pull the liquid down. Liquid column down means there will be a reduction of pressure at the top of the siphon. Reduction of pressure will create an unbalance in the small column. There will be a gravity force in the shorter column as well.
What is a siphon?
(Entry 1 of 2) 1 a : a tube bent to form two legs of unequal length by which a liquid can be transferred to a lower level over an intermediate elevation by the pressure of the atmosphere in forcing the liquid up the shorter branch of the tube immersed in it while the excess of weight of the liquid in ...
What does "siphon" mean?
Definition of siphon (Entry 2 of 2) transitive verb. : to convey, draw off, or empty by or as if by a siphon —often used with off. intransitive verb. : to pass by or as if by a siphon.
What is the purpose of siphon?
Purpose of Siphon. To transfer liquid from a higher elevation to a lower elevation without any external force or power. To get a continuous flow of liquids.
What is the siphon principle?
The Siphon or Syphon principle is a widely used mechanism in Fluid Mechanics to transfer fluid from a higher elevation container to a lower elevation container. Let us learn more about the Siphon working principle, the purpose of the siphon, advantages and disadvantages ...
What is the barrier between a siphon and a container?
Siphon. As you can see, the liquid flows from a higher elevation to a lower elevation, but there is a barrier ( Container Wall) between the flow. The liquid must climb a certain height against gravity before it flows down to the container kept at a lower elevation.
What is the role of gravity in siphon?
Gravity plays a big role in Siphon. The potential energy difference at different ends of the tube causes the flow of liquid. Of course, in this case, also, you need to create the initial pressure difference manually or using an alternate method.
How many ends does a siphon have?
It has two ends, one is the long end, and the other is the short end. The long end is submerged into the container at the lower elevation. The short end is dipped into the container that is at a higher elevation. Siphon.
Can siphon transfer fluid?
We already learned that Siphon could transfer fluid from a higher elevation to a lower elevation. Many of you may think that water can easily flow from a higher to a lower elevation due to gravity. Then what’s the big deal in Siphon?
What is a siphon?
Siphon (noun) A soda siphon. Siphon (noun) A tubelike organ found in animals or elongated cell found in plants.
What does "siphon" mean?
Siphon (verb) convey, draw off, or empty by or as if by a siphon. Siphon (verb) move a liquid from one container into another by means of a siphon or a siphoning action; "siphon gas into the tank".
What is a siphon bottle?
A siphon bottle. To convey, or draw off, by means of a siphon, as a liquid from one vessel to another at a lower level. Show More ... a tube running from the liquid in a vessel to a lower level outside the vessel so that atmospheric pressure forces the liquid through the tube.
How does a siphon cause liquid to flow uphill?
There are two leading theories about how siphons cause liquid to flow uphill, against gravity, without being pumped, and powered only by gravity. The traditional theory for centuries was that gravity pulling the liquid down on the exit side of the siphon resulted in reduced pressure at the top of the siphon.
What is the name of the device that allows liquid to flow through a tube?
Siphon. The word siphon (from Ancient Greek: σίφων, "pipe, tube", also spelled syphon) is used to refer to a wide variety of devices that involve the flow of liquids through tubes. In a narrower sense, the word refers particularly to a tube in an inverted "U" shape, which causes a liquid to flow upward, above the surface of a reservoir, ...
Can gravity and atmospheric pressure explain siphons?
It need not be one theory or the other that is correct, but rather both theories may be correct in different circumstances of ambient pressure. The atmospheric pressure with gravity theory obviously cannot explain siphons in vacuum, where there is no significant atmospheric pressure.
Does gravity explain CO2 siphons?
But the cohesion tension with gravity theory cannot explain CO2 gas siphons, siphons working despite bubbles, and the flying droplet siphon, where gases do not exert significant pulling forces, and liquids not in contact cannot exert a cohesive tension force.
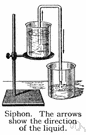
Overview
A siphon (from Ancient Greek: σίφων, romanized: síphōn, "pipe, tube", also spelled nonetymologically syphon) is any of a wide variety of devices that involve the flow of liquids through tubes. In a narrower sense, the word refers particularly to a tube in an inverted "U" shape, which causes a liquid to flow upward, above the surface of a reservoir, with no pump, but powered by the fall of the liquid as it flows down the tube under the pull of gravity, then discharging at a le…
History
Egyptian reliefs from 1500 BC depict siphons used to extract liquids from large storage jars.
Physical evidence for the use of siphons by Greeks are the Justice cup of Pythagoras in Samos in the 6th century BC and usage by Greek engineers in the 3rd century BC at Pergamon.
Theory
A practical siphon, operating at typical atmospheric pressures and tube heights, works because gravity pulling down on the taller column of liquid leaves reduced pressure at the top of the siphon (formally, hydrostatic pressure when the liquid is not moving). This reduced pressure at the top means gravity pulling down on the shorter column of liquid is not sufficient to keep the liquid station…
Modern research into the operation of the siphon
In 1948, Malcolm Nokes investigated siphons working in both air pressure and in a partial vacuum, for siphons in vacuum he concluded that: "The gravitational force on the column of liquid in the downtake tube less the gravitational force in the uptake tube causes the liquid to move. The liquid is therefore in tension and sustains a longitudinal strain which, in the absence of disturbing factors, is insufficient to break the column of liquid". But for siphons of small uptake height work…
Practical requirements
A plain tube can be used as a siphon. An external pump has to be applied to start the liquid flowing and prime the siphon (in home use this is often done by a person inhaling through the tube until enough of it has filled with liquid; this may pose danger to the user, depending on the liquid that is being siphoned). This is sometimes done with any leak-free hose to siphon gasoline from a motor vehicle's gasoline tank to an external tank. (Siphoning gasoline by mouth often results in the acc…
Applications and terminology
When certain liquids needs to be purified, siphoning can help prevent either the bottom (dregs) or the top (foam and floaties) from being transferred out of one container into a new container. Siphoning is thus useful in the fermentation of wine and beer for this reason, since it can keep unwanted impurities out of the new container.
Devices that are not true siphons
While if both ends of a siphon are at atmospheric pressure, liquid flows from high to low, if the bottom end of a siphon is pressurized, liquid can flow from low to high. If pressure is removed from the bottom end, the liquid flow will reverse, illustrating that it is pressure driving the siphon. An everyday illustration of this is the siphon coffee brewer, which works as follows (designs vary; this i…
In nature
The term "siphon" is used for a number of structures in human and animal anatomy, either because flowing liquids are involved or because the structure is shaped like a siphon, but in which no actual siphon effect is occurring: see Siphon (disambiguation).
There has been a debate if whether the siphon mechanism plays a role in blood circulation. However, in the 'closed loop' of circulation this was discounted; "In contrast, in 'closed' systems, l…
in Gastropods
Paired Siphons of Bivalves
- Those bivalves that have siphons, have two of them. Not all bivalves have siphons however: those that live on or above the substrate, as is the case in scallops, oysters, etc., do not need them. Only those bivalves that burrow in sediment, and live buried in the sediment, need to use these tube-like structures. The function of these siphons is to reach up to the surface of the sediment, so that t…
Hyponome of Cephalopods
- The hyponome or siphon is the organ used by cephalopods to expel water, a function that produces a locomotive force. The hyponome developed from the foot of the molluscan ancestor. Water enters the mantle cavity around the sides of the funnel, and subsequent contraction of the hyponome expands and then contracts, expelling a jet of water. In most c...
External Links