What are the 6 research methods?
- Research Methods
- Research Methods Chapter 6. ...
- MIdterm CJ research Methods. ...
- Chapter 4 Research Methods. ...
- Social Research Methods. ...
- Research Methods Chapter 10. ...
- Research Methods Chapter 8. ...
- Chapter 3 Research Methods. ...
- Research Methods Chapter 11. ...
- Chapter Research Methods. ...
How to use sequential statistical methods?
Sequential Analysis
- Evidence-Based Medicine and Systematic Reviews. ...
- Survival and Time-Series Analysis. ...
- Sequential Analysis and Time Series. ...
- Computerized Test Construction. ...
- Sample size estimation. ...
- Sample Size Estimation and Meta-Analysis. ...
- Sequence Analysis and Transition Models. ...
- Eisenmenger Syndrome. ...
What is a sequential study in psychology?
Strengths & Weakness of Sequential Study
- Strength: Mitigated Cultural Variations. By consistently studying the same group of people, researchers are able to eliminate cultural or demographic factors from their findings.
- Weakness: Participant “Mortality”. ...
- Strength: Observing Changes. ...
- Weakness: Poor Causational Analysis. ...
What is a sequential study?
Sequential, or longitudinal, studies test a single variable on the same individual or group of individuals consistently over a period of time. Other ways of constructing a research study include surveys, experiments and cross-sectional studies. Each of these methods has advantages and disadvantages.
What is an example of sequential research?
For example, an investigator using a cross-sequential design to evaluate children's mathematical skills might measure a group of 5-year-olds and a group of 10-year-olds at the beginning of the research and then subsequently reassess the same children every 6 months for the next 5 years.
Why research is sequential?
Sequential designs have the advantages of both. They offer information in a short amount of time in that you have several groups being studied. You also have individual differences recorded over the long term so that a researcher can look at larger effects and trends.Sep 24, 2021
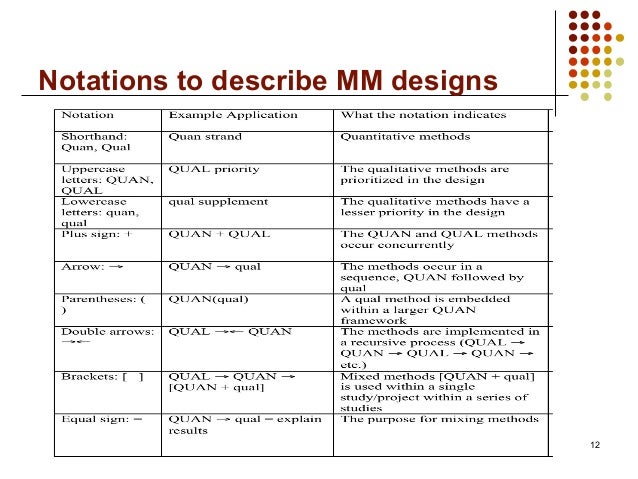
What is sequential mixed method research?
Exploratory sequential mixed methods is an approach to combining qualitative and quantitative data collection and analysis in a sequence of phases (Creswell & Plano Clark, 2018).
What are the advantages and disadvantages of sequential studies?
Strengths & Weakness of Sequential StudyStrength: Mitigated Cultural Variations. By consistently studying the same group of people, researchers are able to eliminate cultural or demographic factors from their findings. ... Weakness: Participant “Mortality” ... Strength: Observing Changes. ... Weakness: Poor Causational Analysis.
What is a basic idea of sequential designs?
Sequential designs are developmental research designs that include elements of both cross-sectional and longitudinal studies; they are configured in ways to address confounds between age, cohort, and time of measurement.
What is longitudinal research?
In a longitudinal study, researchers repeatedly examine the same individuals to detect any changes that might occur over a period of time. Longitudinal studies are a type of correlational research in which researchers observe and collect data on a number of variables without trying to influence those variables.May 8, 2020
What is sequential mixed methods sampling?
A sequential design utilizing identical samples was used to classify mixed methods studies via a two- dimensional model, wherein sampling designs were grouped according to the time orientation of each study's components and the relationship of the qualitative and quantitative samples.Jul 3, 2007
What is qualitative sequential analysis?
In the context of social science research, sequential analysis refers to ways of organizing and analyzing behavioral data in an attempt to reveal sequential patterns or regularities in the observed behavior.Jan 1, 2011
What is a triangulation method?
Triangulation in research means using multiple datasets, methods, theories and/or investigators to address a research question. It's a research strategy that can help you enhance the validity and credibility of your findings.Jan 3, 2022
What are the advantages of a sequential approach?
The sequential approach is held to have several advantages. The distinct stages make the process easy to manage and control since each stage is predetermined and can be reviewed. Uncertainty is reduced before the next phase begins, since the information received 'downstream' is complete and 'signed off'.
What is a longitudinal study example?
Longitudinal case studies are studies that gather copious amounts of data on a single person or small group of people. Other longitudinal studies may use cohorts to compare data over time. For example, a five-year study of children learning to read would be a cohort longitudinal study.Aug 11, 2015
What is sequential experimental design?
Sequential experimentation is the application of statistical experimental design methods to improving processes when many experimental factors must be studied.
What is sequential study?
A sequential study is one of many ways to construct research studies. Sequential, or longitudinal, studies test a single variable on the same individual or group of individuals consistently over a period of time. Other ways of constructing a research study include surveys, experiments and cross-sectional studies.
Why is it important to study the same group of people?
By consistently studying the same group of people, researchers are able to eliminate cultural or demographic factors from their findings. While variations may exist within the study group, these variations will persist from one measurement to the next.
What is the weakness of longitudinal studies?
One weakness that plagues longitudinal studies is the steady decrease in participation over time, referred to as “participant mortality.” The number of subjects able to participate decreases with each survey, particularly when studies occur over years or decades. As a result, many critics contend that the survey results toward the end of a sequential study may be measurably different than the overall group that began the study.
What is sequence sampling?
Sequential sampling is a non-probability sampling technique wherein the researcher picks a single or a group of subjects in a given time interval, conducts his study, analyzes the results then picks another group of subjects if needed and so on.
Why is sampling schedule dependent on the researcher?
Sampling schedule is also completely dependent to the researcher since a second group of samples can only be obtained after conducting the experiment to the initial group of samples. As mentioned above, this sampling technique enables the researcher to fine-tune his research methods and results analysis.
Is sampling randomized?
The sampling technique is also hardly randomized. This contributes to the very little degree representativeness of the sampling technique. Due to the aforementioned disadvantages, results from this sampling technique cannot be used to create conclusions and interpretations pertaining to the entire population .
Can a researcher accept a null hypothesis?
The researcher can accept the null hypothesis, accept his alternative hypothesis, or select another pool of subjects and conduct the experiment once again. This entails that the researcher can obtain limitless number of subjects before finally making a decision whether to accept his null or alternative hypothesis.
Difference of Sequential Sampling from All Other Sampling Techniques
Advantages of Sequential Sampling
- The researcher has a limitless option when it comes to sample size and sampling schedule. The sample size can be relatively small of excessively large depending on the decision making of the resear...
- As mentioned above, this sampling technique enables the researcher to fine-tune his research methods and results analysis. Due to the repetitive nature of this sampling method, minor ch…
- The researcher has a limitless option when it comes to sample size and sampling schedule. The sample size can be relatively small of excessively large depending on the decision making of the resear...
- As mentioned above, this sampling technique enables the researcher to fine-tune his research methods and results analysis. Due to the repetitive nature of this sampling method, minor changes and ad...
- There is very little effort in the part of the researcher when performing this sampling technique. It is not expensive, not time consuming and not workforce extensive.
Disadvantages of Sequential Sampling
- This sampling method is hardly representative of the entire population. Its only hope of approaching representativeness is when the researcher chose to use a very large sample size significant enou...
- The sampling technique is also hardly randomized. This contributes to the very little degree representativeness of the sampling technique.
- This sampling method is hardly representative of the entire population. Its only hope of approaching representativeness is when the researcher chose to use a very large sample size significant enou...
- The sampling technique is also hardly randomized. This contributes to the very little degree representativeness of the sampling technique.
- Due to the aforementioned disadvantages, results from this sampling technique cannot be used to create conclusions and interpretations pertaining to the entire population.