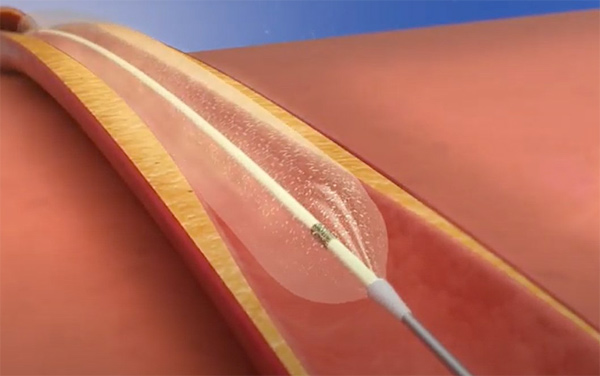
What is the purpose of PTCA?
MeSH terms
- Angioplasty, Balloon, Coronary*
- Coronary Angiography*
- Coronary Artery Bypass
- Female
- Humans
- Male
- Sex Characteristics
What does PTCA stand for in heart in medical category?
Percutaneous transluminal coronary angioplasty (PTCA) also called percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI) is a minimally invasive procedure to open blocked or stenosed coronary arteries allowing unobstructed blood flow to the myocardium. The blockages occur because of lipid-rich plaque within the arteries, diminishing blood flow to the myocardium.
What does PTCA stand for cardiology?
What does PTCA abbreviation stand for? List of 77 best PTCA meaning forms based on popularity. ... Percutaneous Transluminal Coronary Angioplasty + 1 variant. Medical, Cardiology, Diagnosis. Medical, Cardiology, Diagnosis. 1. P.T.C.A. Percutaneious Transluminal Coronary Angioplasty.
What does the acronym PTCA stand for?
Percutaneous Transhepatic Cholangiography. PTCA. Purple Throated Carib (Eulampis jugularis) PTCA. Power Thermal Control Adapter. showing only Science & Medicine definitions ( show all 8 definitions) Note: We have 80 other definitions for PTCA in our Acronym Attic. new search. suggest new definition.
What is the difference between PTCA and angioplasty?
Angioplasty is treatment designed to open blocked or narrowed arteries. An angioplasty can be used to treat problems in many areas of the body. An angioplasty is called a PTCA when used to treat a coronary artery obstruction and a PTA when treating other arteries.
Is PTCA same as stent?
The stent is left in place permanently to allow blood to flow more freely. Coronary angioplasty is sometimes known as percutaneous transluminal coronary angioplasty (PTCA). The combination of coronary angioplasty with stenting is usually referred to as percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI).
What is PTCA used to treat?
Percutaneous transluminal coronary angioplasty (PTCA) is performed to open blocked coronary arteries caused by coronary artery disease (CAD) and to restore arterial blood flow to the heart tissue without open-heart surgery.
What is difference between PCI and PTCA?
Percutaneous transluminal coronary angioplasty (PTCA) also called percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI) is a minimally invasive procedure to open blocked or stenosed coronary arteries allowing unobstructed blood flow to the myocardium.
Is PTCA open heart surgery?
To open up coronary (heart) arteries that are narrowed or blocked by plaque build-up (atherosclerosis). What is the procedure? Percutaneous transluminal coronary angioplasty is commonly called PTCA, or just angioplasty. A catheter is inserted into an artery—usually in the groin—but sometimes in the arm or wrist.
How many years a person can live after angioplasty?
Survival was 99.5% at 1 year and 97.4% after 5 years; "event free survival" was 84.6% at 1 year and 65.9% after 5 years; "ischemia free survival" was 84.6% at 1 year and 44.8% after 5 years.
What is the most serious complication of PTCA?
The most serious complication of percutaneous coronary intervention results when there is an abrupt closure of the dilated coronary artery within the first few hours after the procedure.
How serious is having a stent put in?
About 1% to 2% of people who have a stent may get a blood clot where the stent is placed. This can put you at risk for a heart attack or stroke. Your risk of getting a blood clot is highest during the first few months after the procedure.
Is PTCA a surgery?
Overview. PTCA, or percutaneous transluminal coronary angioplasty, is a minimally invasive procedure that opens blocked coronary arteries to improve blood flow to the heart muscle. First, a local anesthesia numbs the groin area. Then, the doctor puts a needle into the femoral artery, the artery that runs down the leg.
What is PTCA and CABG?
Background. Coronary-artery bypass grafting (CABG) and percutaneous transluminal coronary angioplasty (PTCA) are alternative methods of revascularization in patients with coronary artery disease.
Which is better CABG or angioplasty?
Bypass surgery is generally superior to angioplasty. When more than one heart artery is blocked, CABG may also offer better survival rates for people with heart failure.
When should PTCA be performed?
The recommendation states that PTCA can be an alternative “in patients who are within 36 hours of an acute ST-elevation/Q-wave or new left bundle branch block infarction who develop cardiogenic shock, are less than 75 years of age and in whom revascularization can be performed within 18 hours of shock.”
What is a PTCA catheter?
Percutaneous transluminal coronary angioplasty (PTCA) is a minimally invasive procedure to open up blocked coronary arteries, allowing blood to circulate unobstructed to the heart muscle. Next, a long narrow tube called a diagnostic catheter is advanced through the introducer over the guide wire, into the blood vessel.
Why do you need a PTCA?
Reasons for a Percutaneous Transluminal Coronary Angioplasty (PTCA) PTCA is performed to restore coronary artery blood flow when the narrowed artery is in a location that can be reached in this manner. Not all coronary artery disease can be treated with PTCA.
What is PTCA in medical terms?
Continuing Education Activity. Percutaneous transluminal coronary angioplasty (PTCA) also called percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI) is a minimally invasive procedure to open blocked or stenosed coronary arteries allowing unobstructed blood flow to the myocardium. The blockages occur because of lipid-rich plaque within the arteries, ...
What is PTCA in a cardiologist?
Introduction. Percutaneous transluminal coronary angioplasty (PTCA) also called percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI) is a minimally invasive procedure to open blocked or stenosed coronary arteries allowing unobstructed blood flow to the myocardium. The blockages occur because of lipid-rich plaque within the arteries, ...
What is a PCI procedure?
Percutaneous transluminal coronary angioplasty (PTCA) also called percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI) is a minimally invasive procedure to open blocked or stenosed coronary arteries allowing unobstructed blood flow to the myocardium.
How does a cardiologist control the direction of a PTCA guide wire?
The cardiologist controls the direction and movement of the PTCA guide wire, and balloon wire by twisting the part of guide wires that sit outside the patient. The balloon is then inflated and deflated repeatedly until the artery is patent. In most instances, a stent is required.
How long after PTCA should you use antiplatelet therapy?
The use of antiplatelet therapy is important during the first 12 months after PTCA, allowing appropriate duration for endothelial cell formation over the metallic stent to prevent stent thrombosis. Personnel. A team made up of an interventional cardiologist, nurse, and radiology technologist performs PTCA.
When was PCTA first performed?
Urgent PTCA is often required to limit myocardial damage. Andreas Gruentzig first developed PCTA in 1977, and the procedure was performed in Zurich, Switzerland that same year.[1] .
Is PTCA a CABG?
There is a long-term risk of re-stenosis of the stented vessel. Clinical Significance. PT CA is performed under local anesthesia and serves as an alternative to coronary artery bypass surgery (CABG). In comparison to CABG, PT CA is associated with lower morbidity and mortality, shorter convalescence and lower cost.
What is PTCA in medical terms?
PTCA short for percutaneous transluminal coronary angioplasty is also called coronary angioplasty, balloon angioplasty or percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI), is a minimally invasive procedure to open up blocked coronary arteries, allowing blood to circulate unobstructed to the heart muscle 1).
Why is PTCA not recommended?
Patients with left main coronary heart disease are poor candidates for the PTCA procedure due to the risk of acute obstruction or spasm of the left main coronary artery during the procedure. It is also not recommended for patients with hemodynamically insignificant (less than 70%) stenosis of the coronary arteries.
How long does a PTCA procedure last?
During the procedure, anticoagulation is administered to prevent the formation of clots. Most coronary angioplasty procedures last between 30 minutes to 3 hours depending upon the technical difficulties of the case.
What test is used to determine if a blockage is a PTCA?
How you prepare. Before a scheduled PTCA procedure, your doctor will review your medical history and do a physical exam. You’ll also have an imaging test called a coronary angiogram to see if your blockages can be treated with angioplasty.
Is PTCA a procedural procedure?
PTCA is widely practiced and has risks, but major procedural complications are rare. The mortality rate during angioplasty is 1.2% 13). People older than the age of 65, with kidney disease or diabetes, women and those with massive heart disease are at a higher risk for complications. Possible complications include hematoma at the femoral artery insertion site, pseudoaneurysm of the femoral artery, infection of skin over femoral artery, embolism, stroke, kidney injury from contrast dye, hypersensitivity to dye, vessel rupture, coronary artery dissection, bleeding, vasospasm, thrombus formation, and acute heart attack. There is a long-term risk of re-stenosis of the stented vessel.
Is PTCA a risk?
PTCA risks. Although percuta neous coronary angioplasty is a less invasive way to open clogged arteries than bypass surgery is, the procedure still carries some risks. The most common percutaneous coronary angioplasty risks include: Re-narrowing of your artery (restenosis).
Is PTCA a CABG?
PTCA is performed under local anesthesia and serves as an alternative to coronary artery bypass surgery (CABG). In comparison to coronary artery bypass grafting (CABG), PTCA is associated with lower morbidity and mortality, shorter convalescence and lower cost 3). It can significantly improve blood flow through the coronary arteries in about 90% of patients with relief of anginal symptoms and improvement in exercise capacity. It effectively eliminates arterial narrowing in most cases. Different modeling studies presented different conclusions regarding the cost-effectiveness of PTCA and CABG in patients of myocardial ischemia that do not respond to medical therapy 4).
What is PTCA in surgery?
PTCA is a minimally invasive surgical procedure for the treatment of coronary atherosclerosis. A balloon-tipped catheter is inserted percutaneously into the arterial circulation, advanced to the aortic root, and directed with a flexible guide wire to the site of coronary stenosis.
What is PCTA in cardiology?
PCTA Interventional cardiology A procedure in which an angioplasty balloon is inserted percutaneously into the arteries advanced to a stenosis, and inflated, reopening the lumen Indications Single and multivessel CAD, stable angina on exertion, unstable angina, acute MI–'primary' PCTA, stenosed renal arteries, arteries with fibromuscular hyperplasia, post-thrombolytic therapy Success rate 90%; re-stenosis in 30%; success is lower with stenoses that are chronic, long, eccentric, angulated, calcified, at branching, or with intraluminal thrombi, unstable angina, ↑ age, ♀. See Balloon angioplasty, Coronary artery bypass surgery, Excimer laser therapy. Cf Balloon valvoplasty.
What is a percutaneous transluminal angioplasty?
percutaneous transluminal angioplasty a type of balloon angioplasty in which the catheter is inserted through the skin and through the lumen of the vessel to the site of the narrowing.
What is a PTCA?
Percutaneous Transluminal Coronary Angioplasty (PTCA) and Percutaneous Coronary Intervention (PCI) both essentially mean the process of dilating a coronary artery stenosis using an inflatable balloon and a metallic stent introduced into the arterial circulation via the femoral, radial or the brachial artery. Nowadays it is the most commonly used intervention in the treatment of ischemic heart diseases. It should be stressed that there is no difference between PTCA and PCI. They are in fact synonyms. However, here, we will discuss PTCA or PCI procedure and complications in detail.
What is PTCA in a stent?
PTCA or Percutaneous Transluminal Coronary Angioplasty is the process of dilating a coronary artery stenosis using an inflatable balloon and a metallic stent introduced into the arterial circulation via the femoral, radial or the brachial artery. Percutaneous Coronary Intervention is another name given to this procedure. Therefore, there is no difference between PTCA and PCI.
When is PTCA not recommended?
PTCA is not recommended when the site of obstruction is within a calcified, long and tortuous artery which is bifurcating at an adjacent point.
Is PTCA the same as PCI?
There’s no difference between PTCA and PCI since Percutaneous Transluminal Coronary Angioplasty, or PTCA is also referred by the name Percutaneous Coronary Intervention or PCI.
What is a PTA?
Percutaneous transluminal angioplasty (PTA) is a procedure that can open up a blocked blood vessel using a small, flexible plastic tube, or catheter, with a "balloon" at the end of it. When the tube is in place, it inflates to open the blood vessel, or artery, so that normal blood flow is restored.
Why is it necessary?
Fatty deposits can build up in your blood vessels, reducing blood flow and in some cases, blocking it completely. The biggest danger from fat build up is that pieces may break off, form clots, and cause a heart attack or stroke. The PTA can open blocked arteries and reduce these risks.
How is it done?
The radiologist will insert a balloon-type catheter into an artery in your groin or arm. The doctor will inflate the balloon several times, for about one minute each time, in order to "push" the fatty deposits against the artery wall. The technologists working with the doctor will take X-ray pictures to make sure the blockage is opened.
What should you expect?
The procedure may be performed immediately after your diagnostic leg arteriogram, which was used to find the fatty build-up, or it may be done the following day.