What are the principles of principlism in healthcare?
Using this principle, the healthcare providers have a responsibility to consider the pain experienced by the patients in their decisions. The theory replaces the moral theory and rules with principles that are one of the greatest weaknesses of the principlism theory.
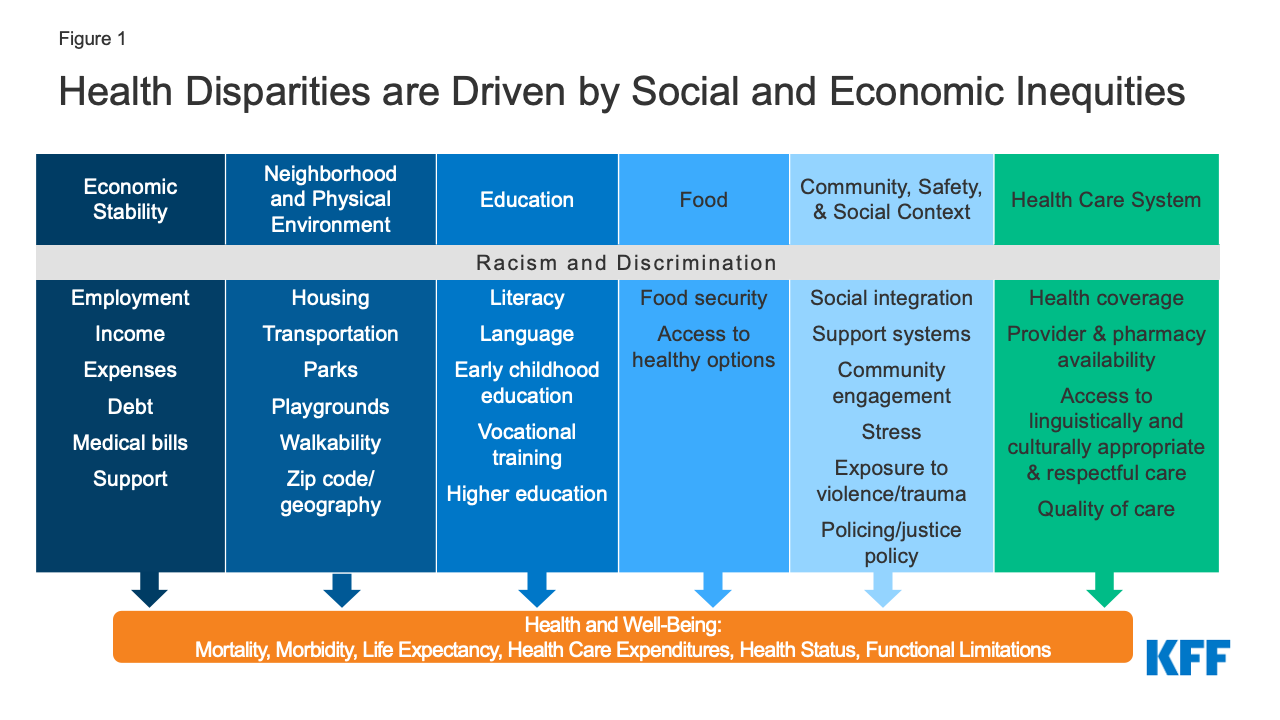
What are the principles of Health and social care?
Empowerment, safety a, confidentiality, social justice are all principles that apply to providing health and social care in practice. In addition, Beneficence and non-maleficence are principles that apply to health and social care providers in their clinical practice.
What is principlism?
The authors use the term "principlism" to refer to the practice of using "principles" to replace both moral theory and particular moral rules and ideals in dealing with the moral problems that arise in medical practice. The authors argue that these "principles" do not function as claimed, and that t … A critique of principlism
Why does principlism reign in medicine?
The current situation has become one in which principlism reigns because it suits the needs and purposes of teachers, journals, and institutions while offering little succor to actual patients, family members, and clinicians.
What is meant by principlism?
The term “principlism” designates an approach to biomedical ethics that uses a framework of four universal and basic ethical principles: respect for autonomy, nonmaleficence, beneficence, and justice. It is presented and defended in Beauchamp and Childress' Principles of Biomedical Ethics.
How is principlism used?
As a form of practical ethics, principlism assists clinicians to make ethical decisions relating to their practice, providing a common language for discussion, debate and response to ethical conflicts that arise in practice.
What are the 4 principles of principlism?
Principlism, the bioethical theory championed by Tom Beauchamp and James Childress, is centered on the four moral principles of beneficence, non-maleficence, respect for autonomy, and justice.
What is principlism in psychology?
Principlism is an applied ethics approach to the examination of moral dilemmas that is based upon the application of certain ethical principles.
What is principlism in nursing?
Principlism is a commonly used ethical approach in healthcare and biomedical sciences. It emphasises four key ethical principles of autonomy, beneficence, non-maleficence, and justice, which are shared by most ethical theories, and blends these with virtues and practical wisdom.
Which of the following is true regarding principlism?
Which of the following is true about Principlism? -Principlism is consistent with a multitude of ethical, theological and social approaches towards moral decision-making. -Principlism can be derived from a multitude of ethical, theological and social approaches towards moral decision-making.
What is a disadvantage of principlism?
The "principles" lack any systematic relationship to each other, and they often conflict with each other. These conflicts are unresolvable, since there is no unified moral theory from which they are all derived. For comparison the authors sketch the advantages of using a unified moral theory.
What are the 4 main ethical principles in nursing?
There are four main principles of ethics: autonomy, beneficence, justice, and non-maleficence. Each patient has the right to make their own decisions based on their own beliefs and values. [4].
Why are the 4 ethical principles important?
These principles are autonomy, beneficence, non-maleficence, and justice. Each of these principles has a unique objective, but the four come together to empower you as a health care professional and ensure that patients are receiving high quality and ethical health care.
Why was Principlism created?
Principlism is a normative ethical framework that was designed for practical decision making in health care. Its basic approach is an attempt to bypass intractable disagreements at the level of normative ethical theory and the resulting lack of agreement about how to proceed.
What are the 5 psychological principles?
The principles are organized into five areas of psychological functioning: cognition and learning; motivation; social and emotional dimensions; context and learning; and assessment.
What is Nonmaleficence in healthcare?
Non-maleficence This means that nurses must do no harm intentionally. Nurses must provide a standard of care which avoiding risk or minimizing it, as it relates to medical competence. An example of nurses demonstrating this principle includes avoiding negligent care of a patient.
What is organizational policy?
Organization policy – law, practice policies, rules, regulations, and codes are important present. Providing guidelines it says that Policy and law, institutions will have to practice. Without reference to the law and the law of the organization, legal, health and social care center for which it is really difficult to formulate policy. Any violation of the rights of the individual, organizational policy, Law and practice in an organized, competent and ethical work environment, service users and staff will be made. The organizing principle of the organization without any serious conflict, it is very easy to use. It is the employee to work in accordance with the law to respect the law and acclimate employee’s helps. An employee fines or even anyone who breaks the law and regulations, will not leave him in his work. An employee is an employee of any laws and regulations to be confused about, then you can ask his superiors, and they will help him to get out of the dilemma. Both employers and employees and the respective authority is obliged to obey and follow the rules and regulation and correct them or even anyone to take immediate steps to punish those who break the law.
What is the Maslow hierarchy of needs?
Service users, physical, spiritual, social, emotional, and mental fitness to promote healthy lifestyles and to achieve a high level, the theory helps to develop a plan. Maslow hierarchy of needs state that theory of health and social care. his theory, human needs are classified into different levels, and basic needs are put first. According to his theory, the bottom level is not met, a man to go to the next level. Physiological or physical demands of this theory are considered to be the most basic needs. Safety and security, love and belonging, self-esteem and self actualization is the next level. While planning for the care and services to a service user of this theory is applied. Other well-known theory of human growth and development, Help and Care is needed in a variety of different levels. Age, growth and development, the care and services is changing.
Why is the organizing principle important?
Employees need to follow to ensure the smooth running of the system , the organizing principle of the organization is important. To reduce misunderstanding and misinterpretation , it is necessary to organizational policies are clear and blunt.
How to promote and uphold privacy, dignity, rights, health and wellbeing?
2. Promote and uphold the privacy, dignity, rights, health and wellbeing of people who use health and care services and their carers at all times . 3. Work in collaboration with colleagues to ensure the delivery of high quality, safe and compassionate healthcare, care and support.
What is person centered care?
Person-centred care is a way of thinking and doing things that sees the people using health and social services as equal partners in planning, developing and monitoring care to make sure it meets their needs. This means putting people and their families at the centre of decisions and seeing them as experts, working alongside professionals to get the best outcome. Person-centred care is not just about giving people whatever they want or providing information. It is about considering people’s desires, values, family situations, social circumstances and lifestyles; seeing the person as an individual, and working together to develop appropriate solutions. Being compassionate, thinking about things from the person’s point of view and being respectful are all important. This might be shown through sharing decisions with patients andhelping people manage their health, but person-centred care is not just about activities. It is as much about the way professionals and patients think about care and their relationships as the actual services available.
Why is interprofessional work important?
Inter-professional working is crucial to meet the needed of service users in health and social care setting. Health care practitioner work in collaboration and compliment each other skills to provide effective health care to the society. Doctors, health care assistant, nurses, midwives, psychologists or physical therapists sometimes work together to effectively meet the needs of patients. This approach is essential in health care because it help to provide fast service to the patients and also healthcare practitioners to improve on the services rendered to service users. Inter-professional working foster positive and trustworthy working relationship among health care employee and service users. In addition, the approach facilitates and promote holistic methods to health.
What is the definition of social care?
2.1 The implementation of policies, legislation, regulations and codes of practice that are relevant to own work in health and social care. 3.1 The theories that underpin health & social care practice. 3.2 Analysis of how social processes impact on users of health and social care services.
Why is it important for care workers to maintain the organisational policy and procedures of their provider?
However, it is important that the care employees maintain the organisational policy and procedures of their provider in order to avoid unnecessary legal challenge. People have different beliefs, culture, values and orientation and these factors are sometimes what form their opinion or decisions. In most cases, conflict may arise in the values belief or culture between care workers and service users. For instance, some patients may decide not to take their medication because it against their culture or religion, and it is important that the sick patients take their drugs to get better, Likewise, the service users have the right to make their own decisions but sometimes they make worthless decisions that can even hamper their recovery, thus care worker is faced with a dilemma.
What are the principles of support in health care?
The principles of supports in health care helps care workers to understand the treatment procedure individual patients, how to maintain their privacy and how service users right are protected and informed decisions made.
What is the responsibility of health and social care?
The responsibility and duty of health and social practice is to provide support for the service users. In health care setting, the providers of health and social care must ensure that service users wellbeing and right are not violated. Worker must ensure that the service user received appropriate medical care as well as respecting the personality, belief or culture of the patients. In other word, the worker must understand how Equality Act 2010 applies to their work and how non-implementation can lead to severe consequences. People have different beliefs and culture; care employees have to respect service user culture and beliefs even if they do not agree with their faith or religion. In addition, service user has the right to make their own decisions, this is their statutory right that must not be violated by care worker. hence, balancing these factors with organisational policy can be complex sometimes. Confidentiality is paramount for health and social care worker because patients and care provider develops over time and many these will be known to the care worker. Keeping to the principles of health and social, the worker must keep all information relevant to the service user private, any information that may violated users’ privacy will need the consent of the service user. Care worker must have empathy and make ensured that decisions about patients are informed choice of the user. Empowerment, safety a, confidentiality, social justice are all principles that apply to providing health and social care in practice. In addition, Beneficence and non-maleficence are principles that apply to health and social care providers in their clinical practice.
What is NCCHPP in Canada?
The NCCHPP is one of six centres financed by the Public Health Agency of Canada. The six centres form a network across Canada, each hosted by a different institution and each focusing on a specific topic linked to public health. The National Collaborating Centre for Healthy Public Policy is hosted by the Institut national de santé publique du Québec (INSPQ), a leading centre in public health in Canada.
Why do clinicians start with mid level principles?
Starting with mid-level principles allows clinicians to “get straight to work” on ethical deliberation without becoming enmeshed in theoretical debates and without the need to specialize in theories and their justificatory mechanisms, their nuances, etc.
What are the tools used in public health?
In public health, the tools used for applying ethics in practice generally take the form of ethical frameworks. Since about 2001, numerous frameworks have been developed to guide ethical decision making in diverse areas of practice, with early influential examples including Kass (2001), Upshur (2002) and Childress et al. (2002), and with more recent examples including Willison et al. (2012), ten Have, van der Heide, Mackenbach, & de Beaufort (2012), and Marckmann et al. (2015). To date, the field of public health ethics has produced a diversity of frameworks for various purposes, which is a dramatically different landscape from the more monolithic terrain of medical ethics in which principlism dominates.
What is Principlism in philosophy?
Approaching the work from a strongly theory-based perspective, the authors claim that principlism lacks a sufficient theoretical foundation . For them, since principlism lacks a “moral theory that ties the ‘principles’ together, there is no unified guide to action which generates clear, coherent, comprehensive and specific rules for action nor any justification of those rules” (Clouser & Gert, 1990, p. 227). Others point out that these authors have different expectations of moral “theory” and that they cannot but arrive at incompatible conclusions about what works or about what is acceptable (e.g., Davis, 1995), whether in terms of foundations, methodologies, justification, etc. Proponents of a principlist approach do not expect or wait for general agreement upon something that could satisfy these theoretical aspirations. Instead of debating those issues, they focus (and depend) on the mid-level principles where a certain degree of agreement is said to exist already.
What is the normative framework for health care?
Principlism is a normative ethical framework designed for decision making in health care. It is a common-morality approach relying on four mid-level principles: respect for autonomy, nonmaleficence, beneficence, and justice. The normative force of the principles arises from a
What is Principlism in health care?
Principlism is a normative ethical framework that was designed for practical decision making in health care . Its basic approach is an attempt to bypass intractable disagreements at the level of normative ethical theory and the resulting lack of agreement about how to proceed. Instead, the authors focus on what people generally do agree upon, in the form of general, mid-level principles. They observe that “often little is lost in practical moral decision making by dispensing with general moral theories. The rules and principles shared across these theories typically serve practical judgment more adequately (as starting points) than the theories” (Beauchamp & Childress, 1994, p. 17). They say that this is because “theories are rivals over matters of justification, rationality and method but they often converge on mid-level principles” (Beauchamp & Childress, 1994, p. 102). Due to this general convergence on principles, they call principlism a common-morality approach.
What is the ethical paradigm of medicine?
The ethical paradigm in medicine that immediately precedes principlism is now often referred to as benevolent paternalism, a term usually with negative connotations. Principlism has supplanted paternalism and now is the primary method that is currently taught at professional schools for health care clinicians.
What is principle based ethics?
Principlism (synonym: principle-based ethics) is an approach to applied et hics based on (1) a framework of prima-facie (i.e., nonabsolute) moral principles, (2) specification as a method for bringing moral norms to bear on concrete cases and issues, (3) analyzing problems of applied ethics in terms of their underlying conflicts of norms , (4) additional specification and balancing as methods for solving moral conflicts, and (5) a theory of justification. Principlism is most prominently represented in the four-principle approach to biomedical ethics by Tom L. Beauchamp and James F. Childress, based on beneficence, nonmaleficence, respect for autonomy, and justice.
What are the elements of autonomy?
There are three basic elements to autonomy: agency (awareness of oneself, desires, and intentions), independence (absence of influences), and rationality (capacity for reflection on desires). Respect for a patient's autonomy is the fundamental principle underlying privacy, confidentiality, valid consent, and refusal of treatment.
What are the guidelines for medical practice?
Guidelines for the professional behavior of medical practitioners have been promulgated for at least 4000 years, according to writings from ancient Egypt and Mesopotamia. The comparatively recent Oath attributed to Hippocrates (460-380 b.c.) is among the most famous, but other prominent medical writers such as Galen and Maimonides offered advice on privacy, duty to patients, and end-of-life issues. 1 Such guidelines express values common to medical practitioners, but they also serve to elevate the standing of medicine as a profession and not a mere vocation. For example, the American Medical Association was founded in 1847 in part to restrain unseemly competition among medical practitioners; that same year, the association's leadership disseminated a code of appropriate behavior for medical practitioners that included rules for referrals and fee splitting. 2
What is the human capacity to generate judgments of value?
At its origin, ethics is the human capacity to generate judgments of value, based on the ability of a self-reflective being to take a stance towards his or her thoughts and actions. All the diverse approaches to ethics presuppose this foundational faculty, although they explicate it in different terms.
What is Gilligan's ethical perspective?
Gilligan’s work led to an ethical perspective based on relationships and caring for others. Some have argued that “caring” is essentially another word for “beneficence,” but the emphasis on the primacy of relationships distinguishes these two concepts.
Why was the American Medical Association founded?
For example, the American Medical Association was founded in 1847 in part to restrain unseemly competition among medical practitioners; that same year, the association's leadership disseminated a code of appropriate behavior for medical practitioners that included rules for referrals and fee splitting. 2.
Abstract
The term “principlism” designates an approach to biomedical ethics that uses a framework of four universal and basic ethical principles: respect for autonomy, nonmaleficence, beneficence, and justice. It is presented and defended in Beauchamp and Childress’ Principles of Biomedical Ethics.
Further Readings
Beauchamp, T. L. (2010). Standing on principles: collected essays. New York: Oxford University Press. Google Scholar
What is beneficence in nursing?
At its core, beneficence is an essential principle of health care ethics and ethical selfishness. The principle encourages health care workers to consciously invest the time ...
Why is maleficence considered maleficence?
Such a case is considered maleficence, because the physician had other better options. Additionally, each the health care professionals must inform the patient of any potential good or bad effects from any treatment, so the patient can make the best decision for themselves if able to.
Why is autonomy important in healthcare?
The practice of autonomy prevents health care professionals from potentially coercing or persuading the patient to take a specific action or treatment plan that might not be in their best interest.
What is the act of kindness or mercy?
Beneficence is the act of showing kindness or mercy. The actions of any health care provider should always bring positivity. Beneficence should not be confused with the closely related ethical principle of non-maleficence, which states that one should do no harm to patients.
What is non-maleficence principle?
Keep in mind that the non-maleficence principle does not only apply to patients but also to fellow health care professional colleagues. Every health care provider should provide a comfortable working environment for other employees. Actions intended to harm other employees are considered maleficence.
What are the four principles of ethics in healthcare?
These principles are autonomy, beneficence, non-maleficence, and justice. Each of these principles has a unique objective, but the four come together to empower you as a health care ...
What is considered maleficence?
Actions intended to harm other employees are considered maleficence. Even verbal abuse at work is treated as maleficence. The non-maleficence principle was developed to protect health care workers and patients.
What is the principle of healthcare?
Principlism is also a consequential theory widely applied in the healthcare sector. The theory is based on four principles that include autonomy. The second principle is the non-maleficence, the third principle is beneficence, and the fourth principle is justice. Principles provided by the principles theory are less general several other theories in making ethical decisions but can be applied in the rules, cases, and virtues in the healthcare profession.
What are the different types of ethical theories?
Ethical theories can be categorized as consequentialism, non-consequentialism, and age centered theories. Consequentialism theories focus on the consequences of the ethical decisions made while non-consequentialism theories focus on ...
Why are ethical theories important in healthcare?
Ethical theories are a significant part of the healthcare profession. They help healthcare providers overcome challenges and conflicts that arise in the profession. These difficulties and conflicts stem from competing personal, organizational, professional and societal values through which healthcare professionals are required to make critical ...
What is utilitarianism in healthcare?
When applied in the healthcare setting, the theory gives a medical professional the power to decide what is best depending on the circumstance. The utilitarianism approach provides a solution when one is faced with a situation where a decision has to make on choosing one option of the other especially when the best alternative available is morally wrong. According to Mack (2004), the theory lays a strong emphasis on impartiality and unselfishness as it does not require one to refer to the precedent actions on if they worked for the decision or not
How can the theory of ethics be applied to healthcare?
In the healthcare sector, the theory can be applied in making ethical decisions in situations that require minimizing pain and maximizing pleasure even when the decision is morally wrong. It focuses on benefiting the majority while agrees with common sense making its principles fair and widely accepted.
What are the weaknesses of the Principlism Theory?
Weaknesses. The theory replaces the moral theory and rules with principles that are one of the greatest we aknesses of the principlism theory. Hence, The theory misses several moral problems that are common in the healthcare environment. This makes the theory either misleading or impractical in such situations.
How does the theory of ethics work in real life?
It dictates the ethical decisions made by an individual must behold his point of view and interests to promote the happiness of others, making the theory very practical in real life. The strengths of the theory have been very applicable in balancing the costs and benefits in health care.