Definition Mottling (spots or blotches with different shades) of the retinal pigment epithelium, i.e., localized or generalized fundal pigment granularity associated with processes at the level of the retinal pigment epithelium. [from HPO] Term Hierarchy
What is mottling of the retinal pigment?
Definition: Mottling (spots or blotches with different shades) of the retinal pigment epithelium, i.e., localized or generalized fundal pigment granularity associated with processes at the level of the retinal pigment epithelium. Click to see full answer. Besides, what causes retinal pigmentation?
What does mottling of the eye mean?
What is pigment mottling? Definition: Mottling (spots or blotches with different shades) of the retinal pigment epithelium, i.e., localized or generalized fundal pigment granularity associated with processes at the level of the retinal pigment epithelium. Click to see full answer.
What is mottled skin?
Medically reviewed by Cynthia Cobb, APRN on October 31, 2017 — Written by Lana Bandoim. Mottled skin, also called livedo reticularis, is skin that has patchy and irregular colors. The skin may have red and purple marks, streaks, or spots.
What is the pathophysiology of macular mottling?
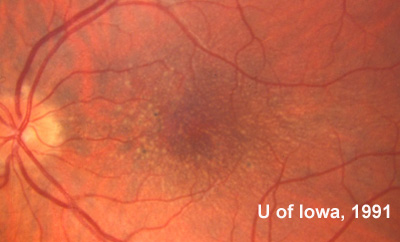
Macular mottling is evident at an early age with attenuation and narrowing of the retinal arterioles. The pigmentary changes are salt-and-pepper in appearance but there are also areas of RPE atrophy with relative sparing of the fovea.
What causes mottling of the retina?
Your eye doctor will put drops in your eyes to dilate them and use a special instrument to examine the back of your eye. He or she will look for a mottled appearance that's caused by drusen – yellow deposits that form under the retina. People with macular degeneration often have many drusen.
What does pigment changes in the eye mean?
While most people develop some very small drusen as a normal part of aging, the presence of medium-to-large drusen may indicate that you have macular degeneration. Another sign of macular degeneration is the appearance of pigment changes in the retina.Feb 5, 2018
What is pigment clumping?
Pigment clumping is a characteristic feature of macular telangiectasia which progresses over time, is associated with decreased visual function, and may reflect a reaction to underlying neurodegeneration.
What is retinal pigment epithelial changes?
As the retinal pigment epithelium (RPE) ages, a number of structural changes occur, including loss of melanin granules, increase in the density of residual bodies, accumulation of lipofuscin, accumulation of basal deposits on or within Bruch's membrane, formation of drusen (between the basal lamina of the RPE and the ...
What is a mottled macula?
Macular mottling is evident at an early age with attenuation and narrowing of the retinal arterioles. The pigmentary changes are salt-and-pepper in appearance but there are also areas of RPE atrophy with relative sparing of the fovea. Pigment clumping in the shape of bone spicules has been observed in the periphery.
What does pigment on the retina mean?
The pigmented layer of retina or retinal pigment epithelium (RPE) is the pigmented cell layer just outside the neurosensory retina that nourishes retinal visual cells, and is firmly attached to the underlying choroid and overlying retinal visual cells.
What is a pigment epithelial detachment?
Pigment epithelial detachment (PED) is a pathological process in which the retinal pigment epithelium separates from the underlying Bruch's membrane due to the presence of blood, serous exudate, drusen, or a neovascular membrane.Nov 1, 2012
What is macular pigment deposit?
In macular degeneration, clumps of yellowish material gradually accumulate within and beneath the retinal pigment epithelium. These deposits are visible to a doctor who looks inside the eye. The clumps appear as small yellow spots known as drusen (singular: druse).
What is pigmentary retinal degeneration?
Pigmentary retinopathy (PR) is a term used to describe a group of inherited, degenerative disorders of the retina, characterized by progressive photoreceptor damage, leading to atrophy, and cell death of the photoreceptors and adjacent layers of the retina.
What does Photopsia mean?
Photopsia definition Photopsias are defined as an effect on the vision that causes appearances of anomalies in the vision. Photopsias usually appear as: flickering lights. shimmering lights. floating shapes.Nov 9, 2018
What is macular RPE mottling?
Definition. Mottling (spots or blotches with different shades) of the retinal pigment epithelium, i.e., localized or generalized fundal pigment granularity associated with processes at the level of the retinal pigment epithelium. [
Why is my skin mottled?
Causes of mottled skin. Many conditions can cause mottled skin. Blood circulation problems and blood vessel spasms are two common causes. Causes also include:
What are the symptoms of mottled skin?
Symptoms of mottled skin. The main symptom of mottled skin is a blotchy appearance with red or purple spots. The irregular skin color can appear on any part of the body. You may see a lacy network of patches on the skin. Accompanying symptoms that are concerning and require medical treatment include: painful nodules. ulcers on the skin.
What medications cause mottled skin?
Drugs that are known to cause mottled skin include: amantadine. catecholamines. minocycline (Minocin) gemcitabine (Gemzar)
What is a marbled skin?
Mottled skin, also called livedo reticularis, is skin that has patchy and irregular colors. The skin may have red and purple marks, streaks, or spots. It may also have a marbled appearance with different colors.
What to do if your skin is mottling from a medication?
For skin mottling caused by a medication, talk to your doctor about your options. They may decide to reduce your dosage or change to a different medication.
Why does my newborn have mottled skin?
Some newborn babies have mottled skin. Usually, this benign condition goes away on its own. Exposure to cold temperatures frequently causes it. Treatment includes keeping the baby warm and avoiding the cold. There is usually no need to have additional medical treatment.
Is there a treatment for mottled skin?
There is no one specific treatment for all mottled skin cases. Treatment depends on the cause of this condition and other symptoms that appear along with the skin mottling. Shock requires immediate medical attention.
Prognosis
INTRAVITREOUS CHEMOTHERAPY FOR ACTIVE VITREOUS SEEDING FROM RETINOBLASTOMA: Outcomes After 192 Consecutive Injections. The 2015 Howard Naquin Lecture.
Clinical prediction guides
VISION LOSS IN A PATIENT WITH PRIMARY PULMONARY HYPERTENSION AND LONG-TERM USE OF SILDENAFIL.
What is a symptoma?
Symptoma is a Digital Health Assistant & Symptom Checker. Patients and doctors enter symptoms, answer questions, and find a list of matching causes – sorted by probability. Symptoma empowers users to uncover even ultra-rare diseases.
What is the congenital form of blindness?
Clarification and classification of the congenital form of blindness known as Leber congenital amaurosis (LCA) continues to provide its challenges and dilemmas. Until recently, seven genes have been identified that cause LCA. Clarifying the relation between LCA and associated neurological abnormalities such as autism, ] [ncbi.nlm.nih.gov]
What is the mottling of the retina at an early age?
Macular mottling is evident at an early age with attenuation and narrowing of the retinal arterioles. The pigmentary changes are salt-and-pepper in appearance but there are also areas of RPE atrophy with relative sparing of the fovea. Pigment clumping in the shape of bone spicules has been observed in the periphery.
What are the early childhood psychomotor delays?
Early childhood psychomotor delays are evident in early childhood by the lack of fine motor and coordination skills along with learning difficulties. Patients have facial dysmorphism with hypoplasia of the ala nasae, upslanting palpebral fissures, and malar hypoplasia.
What happens to the sensory retina after chronic retinal detachment?
The chronic retinal detachment resulted in depigmentation of the RPE and degeneration of the photoreceptor elements. As the photoreceptors degenerate, the sensory retina becomes very thin, and RPE cells migrate into the sensory retina to form the bone spicules.
What eye is bone spicules in?
Our patients left eye shows bone spicules in the inferior retina. Note the shape and distribution of the pigment within the retina.
Is bone spicules in the peripheral retina pathognomonic?
Bone spicules in the peripheral retina are pathognomonic in patients with retinitis pigmentosa (RP). However, given that the bone spicules are present only in this patients left eye and are localized to one area in the retina, you should suspect other causes.
Does central serous choroidopathy cause degeneration?
Chronic central serous choroidopathy can also result in the migration of these bone spicules into the sensory retina. A similar phenomenon occurs in RP, because the disease results in degeneration of the photoreceptor elements and subsequent collapse of the sensory retina onto the RPE.
Is a dilated fundus exam normal?
The dilated fundus exam of both eyes showed small cups with good rim coloration and perfusion. The right eye was completely normal. In the left eye, there was some mild mottling of the retinal pigment epithelium (RPE) in the macula. There was no subretinal fluid, but a foveal light reflex was present. Also, there were bone spicules in the inferior ...
Can pigment migrate forward?
From there, pigment can easily migrate forward. I recommended that this patient wear protective eyewear to guard against further trauma to the eyes. If something were to happen to his good eye, then he would be left with an eye that had a significantly reduced visual field.