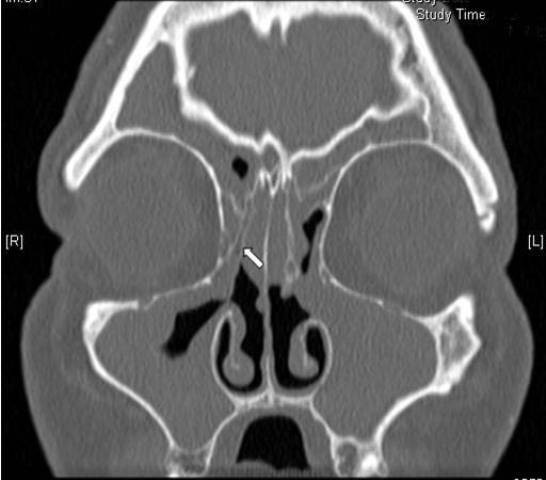
2) while partial opacification was defined as at least one-third of the maxillary sinus being opacified without clear distinct boundaries (Fig. 3). Complete opacification was a completely opacified maxilla in all axial and coronal slices (Fig. Click to see full answer.
What is the difference between partial and complete opacification?
2) while partial opacification was defined as at least one-third of the maxillary sinus being opacified without clear distinct boundaries (Fig. 3). Complete opacification was a completely opacified maxilla in all axial and coronal slices (Fig.
What is partial opacification of the sinuses?
2) while partial opacification was defined as at least one-third of the maxillary sinus being opacified without clear distinct boundaries (Fig. 3). Complete opacification was a completely opacified maxilla in all axial and coronal slices (Fig. Click to see full answer. In this manner, what is opacification of the sinuses? Inflammation.
What does opacification mean in medical terms?
Medical Definition of opacification : an act or the process of becoming or rendering opaque opacification of the cornea opacification of the bile passages for radiographic examination. What is opacification of the sphenoid sinus?
What is complete opacification of the maxilla?
Complete opacification was a completely opacified maxilla in all axial and coronal slices (Fig. Click to see full answer. In this manner, what is opacification of the sinuses? Inflammation. Sinonasal inflammatory disease with sinus ostial obstruction is a very common cause of an opacified paranasal sinus.
What is opacification of the sinuses?
The polyp opacifies and slightly enlarges the sinus cavity with no bone destruction. The enlarged antral polyp protrudes through the maxillary infundibulum or accessory ostium into the middle meatus and then the posterior choana, with possible extension into the posterior nasopharynx.
Is sinus opacification serious?
Isolated sphenoid sinus opacifications (ISSOs) are clinically important because they can lead to serious complications. However, some patients with ISSOs are asymptomatic, and not all patients are properly referred to the otolaryngology department.
What is MRI opacification?
On MRI, opacifications as mucosal thickening, polyps/retention cysts and fluid in the five paired sinuses were measured and recorded if ≥1 mm. For each participant, opacification thickness was summed for each sinus and, in addition, a total sum of all sinuses was calculated.
What is maxillary opacification?
INTRODUCTION. Unilateral maxillary sinus opacification is a rela- tively common finding on radiographic studies of the para- nasal sinuses. There are many disease processes that can lead to solitary maxillary sinus opacification.
What does opacification mean on CT scan?
Pulmonary opacification represents the result of a decrease in the ratio of gas to soft tissue (blood, lung parenchyma and stroma) in the lung. When reviewing an area of increased attenuation (opacification) on a chest radiograph or CT it is vital to determine where the opacification is.
What does completely Opacified mean?
Medical Definition of opacify transitive verb. : to cause (as the cornea or internal organs) to become opaque or radiopaque. intransitive verb. : to become opaque or radiopaque.
What causes opacification?
The opacification is caused by fluid or solid material within the airways that causes a difference in the relative attenuation of the lung: transudate, e.g. pulmonary edema secondary to heart failure. pus, e.g. bacterial pneumonia. blood, e.g. pulmonary hemorrhage.
What is soft tissue opacification?
Soft tissue opacity in xray means an opacity which almost equal to opacity produced by soft tissues. Can be due to pneumonia and others. Any opacity in xray is corroberated with complains ,clinical assessment and other investigation.
What is opacification of the left sphenoid sinus?
Unilateral sphenoid sinus opacification (SSO) on imaging is a common incidental radiologic finding. Inflammatory sinus disease is rarely isolated to one sinus cavity therefore SSO raises the potential for neoplastic etiology.
How do you fix sinus opacification?
TreatmentNasal corticosteroids. ... Saline nasal irrigation, with nasal sprays or solutions, reduces drainage and rinses away irritants and allergies.Oral or injected corticosteroids. ... Allergy medications. ... Aspirin desensitization treatment, if you have reactions to aspirin that cause sinusitis and nasal polyps.More items...•
What is opacity in maxillary sinus?
Conclusion: Although unilateral maxillary sinus opacity is usually inflammatory in origin, fungal sinusitis and neoplastic disorder are also likely. A careful history-taking, a thorough head and neck examination including nasal endoscopy, and CT evaluation are all imperative for reaching a correct diagnosis.
What is the treatment for maxillary sinusitis?
Rather, treatment is based on topical nasal decongestants and saline irrigation of the nasal cavity. Topical decongestants such as ephedrine or xylometazoline constrict the nasal lining, widening the paranasal sinus ostia, facilitating drainage by ciliary activity.
What is PCO?
Posterior capsular opacification (PCO) is the clouding of the posterior lens capsule in which an IOL is implanted. It is the most common complication of cataract surgery. About one in five people develop PCO within one year after cataract surgery. About one-third develop PCO after five years.
How is a PCO different from a cataract?
A cataract occurs when the natural lens of the eye becomes cloudy. When the cataract begins to interfere with activities of daily life, cataract surgery is performed.
What are the symptoms of PCO?
The symptoms of PCO and cataracts are similar. This is because both conditions make it difficult for light to pass through the lens to the retina.
Why is PCO called a "secondary cataract"?
Although this condition is sometimes called a " secondary cataract, " it is not a cataract.
What is the treatment for PCO?
PCO usually develops slowly, much like a cataract. If the decrease in vision starts affecting your daily life, your eye doctor may recommend a procedure called YAG laser capsulotomy.
How do I know if I need treatment for PCO?
PCO usually develops slowly, much like a cataract. If your vision begins to decrease after cataract surgery, let your doctor know. Your cataract surgeon can determine if YAG laser capsulotomy is the appropriate treatment for you.
Notes and References
Posterior capsule opacification. Experimental Eye Research. February 2009.
Causes
There are several possible causes for a CT scan to reveal the maxillary sinus as opaque 1. Polyps can appear opaque, as can tumors. Inflamed tissue, which is common with chronic sinus infections, and thick mucus also can cause opaqueness.
Polyps
Polyps can form in the sinus cavities, which can cause poor drainage. This in turn can lead to chronic sinusitis (infection) 2. These combined factors can cause total opacification.
Tumors
Since tumors in the maxillary sinus are often large and appear opaque, they can cause total opacification of the sinus 1.
Inflammation
If your scan was done during a sinus infection or if you have chronic sinus infections, your maxillary sinus was likely inflamed 1. This can cause the area to be opaque on a CT scan.
Mucous
If you had sinusitis, you might have had thick mucus lining or even filling the sinus, which will make it appear opaque on a CT scan.
I need to understand what it means if a ct scan of head shows opacification of the left mastoid air cells with most of these air cells sclerosed over?
Mastoiditis: These findings signify prior infection/inflammation of the mastoid which is part of the skull. This is almost always a result of old middle ear infect... Read More
Ct: "nonspecific focal opacification of a left mastoid air cell" but "no findings to explain hearing loss". what is this & what else could be wrong?
Mastoid air cells: are part of the sinus cavity and previous sinus issues can result in opacification on a CT scan. This does not usually cause hearing loss unless it is... Read More
Mri: mild opacification of the inferior left maxillary & right sphenoid sinuses. a mild opacification is seen in the inferior right mastoid air cells?
If no symptoms....: Probably nothing to worry about. Many patients have some mucosal thickening or a small amount of fluid in 1 or more of the sinuses or mastoid air cel... Read More
Mri shows extensive opacification of the mastoid cells on the left. what does that mean?
Infection: This could be a mastoid infection. There can be other diagnoses and this will depend on your physician and your infectious disease consultants
What does near complete opacification of the right mastoid air cell. with soft tissue fullness of the epitympanum, mesotympanum, and hypotympanum incl?
Tympanomastoiditis: These are the findings of a CT scan of the mastoid bone. The radiologist is detecting inflammation in the mastoid and the middle ear. Inflammation mea... Read More
Partial opacification of the bilateral mastoid air cells, middle ear, ethmoid air cells. meaning?
Inflammation: May be due to allergy, a viral or bacterial infection or its residual. Need more history to better define. Speak to your doctor who ordered the test a... Read More
Hi i recently had an contrast mri hoping someone can help me to understand a few findings. - 8x10mm in diameter septated pineal cyst, thin walled minor peripheral enhancement which may in part be vascular, minor patchy opacification left mastoid?
This topic needs to be addressed by the doctor who ordered the study and the radiologist who interpreted the films. Clinical symptoms and signs can b... Read More
What does opacity in the lungs mean?
The opacities may represent areas of lung infection or tumors.
What are the three common patterns of lung opacities?
Lung opacities may be classified by their patterns, explains Radiopaedia.org. The three common patterns seen are patchy or airspace opacities; linear opacities; and nodular or dot opacities. Airspace or patchy opacities may represent consolidation, atelectasis or mucoid impaction.
What is the term for a solid or liquid occupying the normally gaseous areas in the lungs?
Consolidation indicates solid or liquid occupying the normally gaseous areas in the lungs and may be due to accumulation of fluid, pus, blood, cells, gastric contents, protein or even fat in the lungs. Atelectasis is an incomplete expansion of the lungs.
What is the term for an incomplete expansion of the lungs?
Atelectasis is an incomplete expansion of the lungs. Ground-glass opacities may represent opportunistic infections such as with pneumocystis or cytomegalovirus or chronic interstitial disease. Linear opacities indicate an interstitial pattern of lung infection or lung disease.