What Is the Principle of Parsimony in Biology?
- Definition. The principle of parsimony argues that the simplest of competing explanations is the most likely to be correct.
- Examples. The simplest example involves a physical characteristic like feathers. ...
- Computer Algorithms. ...
- Assumptions. ...
Why would a scientist want to be parsimonious?
Parsimony is an important principle of the scientific method for two reasons. First and most fundamentally, parsimony is important because the entire scientific enterprise has never produced, and never will produce, a single conclusion without invoking parsimony. Parsimony is absolutely essential and pervasive.
How to use "parsimonious" in a sentence?
the quality of being careful with money or resources To save money, the parsimonious old man always bought used clothes. My mother is parsimonious and never tips more than five percent.
What is the principle of parsimony?
- The lights went out because you pressed the switch.
- The lights went out because at the exact second you pressed the light switch, there was a power outage.
- The lights haven’t actually gone out since the light switch doesn’t work, but at the exact second you pressed the switch you developed a special type of vision impairment, which ...
What does parsimonious mean in research?
- Marketing
- Operations & SCM
- Human Resources
What is parsimony in biology example?
The Principle of Parsimony in Phylogeny It states that the tree with the fewest common ancestors is the most likely. An example would be hypothesizing that if two species both have prominent incisor teeth they also share a single ancestor, rather than that they evolved the trait independently.
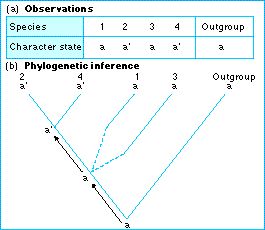
Which tree is most parsimonious?
Leftmost tree is preferred because it requires the fewest evolutionary changes to explain the available data. It's easy to see how complex this process could become with a large number of taxa and characters. Biologists often use data matrices with tens or hundreds of taxa and thousands of characters.
Which is the most parsimonious explanation?
The most parsimonious explanation is usually the first port of call, and regular, continuous and low-magnitude processes usually provide the most satisfactory explanation for environmental condition and change.
How can you tell if a tree is parsimonious?
1:465:45Find the most parsimonious tree - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipWould be to assume. That either a or g. Was the ancestral site or the ancestral sequence rather forMoreWould be to assume. That either a or g. Was the ancestral site or the ancestral sequence rather for site number two and then there was a change in either group one two or group three four.
How many equally parsimonious trees are there?
In the case of phylogenetic analysis, the most parsimonious hypothesis of evolutionary relationships (or phylogenetic tree) is considered to have the fewest character changes. Sometimes the data suggest two phylogenetic trees are equally likely. Under these circumstances we say there are two MOST PARSIMONIOUS trees.
How do you draw a parsimonious phylogenetic tree?
3:268:51Creating a Phylogenetic Tree - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipWe'll start by combining a and C this group to do this will take the average difference that a and CMoreWe'll start by combining a and C this group to do this will take the average difference that a and C show to each of the other sequences. Let's start with the differences they show to be.
What is parsimonious theory?
Parsimony is a guiding principle that suggests that all things being equal, you should prefer the simplest possible explanation for a phenomenon or the simplest possible solution to a problem.
What is parsimonious research?
The principle of parsimony reflects the notion that researchers should strive for simple measurement models that use the minimum number of parameters needed to explain a given phenomenon (Raykov & Marcoulides, 1999).
What is an example of parsimonious?
Excessively sparing or frugal. The definition of parsimonious is people who are cheap, frugal or unwilling to spend money. An example of someone who is parsimonious is someone who obsessively watches every dime of his money.
Is the most parsimonious tree always the correct tree?
Because the most-parsimonious tree is always the shortest possible tree, this means that—in comparison to the "true" tree that actually describes the evolutionary history of the organisms under study—the "best" tree according to the maximum-parsimony criterion will often underestimate the actual evolutionary change ...
What does it mean to say that one phylogenetic tree is more parsimonious than another quizlet?
What does it mean to say that one phylogenetic tree is more parsimonious than another? Fewer changes have to occur to make the origin of traits fit on the tree.
What is parsimony in science?
Science. By Andrea Becker. Parsimony is the idea that, given a set of possible explanations, the simplest explanation is the most likely to be correct. The principle of parsimony in the sciences is used to select from competing models that describe a phenomenon. In biology, it is most often used in the study of phylogeny.
How does parsimonious approach work?
Starting with a set of species and a set of genetic traits, the parsimonious approach would be to look at which traits are shared between species. The tree is constructed by working through the possible relationships for each trait and selecting the option that has the fewest number of state changes.
What is the principle of parsimony in phylogeny?
The Principle of Parsimony in Phylogeny. Humans weren’t around when most species diverged, so biologists trying to recreate phylogenetic trees must work from genetics, models and fossil records to determine relationships.
What is the principle of maximum parsimony?
In phylogeny, the principle of maximum parsimony is one method used to infer relationships between species. It states that the tree with the fewest common ancestors is the most likely.
What is phylogeny in biology?
What is Phylogeny? Phylogeny is a way of thinking about how organisms are related through evolutionary time. It is like a family tree, but it shows how species are related to each other. You start with species existing today and determine how closely related they are by looking at the overlap in their genetic material.
What is parsimonious society?
A society that is parsimonious in its personal charity (in terms of both time and money) will require more government welfare. — William J. Bennett, The Death of Outrage, 1998 Their merchant princes were supposed to be parsimonious and austere: fustian in apparel and coarse in diet.
What is the difference between "stingy" and "penurious"?
Stingy, close, penurious, and miserly are a few terms that, like parsimonious, suggest an unwillingness to share with others. Stingy implies a marked lack of generosity, whereas close suggests keeping a tight grip on one's money and possessions. Penurious implies frugality that gives an appearance of actual poverty, and miserly suggests avariciousness and a morbid pleasure in hoarding. Parsimonious usually suggests an extreme frugality that borders on stinginess.
Principle of parsimony Definition
The principle of parsimony or Ockham’s razor is the scientific principle that ‘entities should not be multiplied without necessity.’ and reduces the effect of homoplasy in the phylogenetic tree for better understanding of the evolutionary relationship among taxa.
Overview of Principle Of Parsimony
Parsimony is the universal scientific principle and is a conflation that has befuddled some phylogenetic thinking. The principle of parsimony is a general epistemological one that is used in scientific research for explanations of phenomena.
Historical Perspective on Parsimony
The parsimony has two distinct, but related meanings. One, parsimony has been considered a feature of nature that nature chooses the simplest course, and second, the parsimony has been deemed a feature of good theories that the simplest theory that fits the facts is best. Humans choose the simplest explanation.
Varieties of Parsimony
E.C Barnes differentiates anti-quantity from the anti-superfluity principle of parsimony. An anti-superfluity principle urges to avoid elements that are superfluous by the lights of the theories they feature in and an anti-quantity principle urges to minimize the number of elements in our theories.
Tree evaluation
Decay analysis determines the number of steps that are required to collapse nodes. The tree length is increased by successive steps to perform a decay analysis. This represents how many trees exist that re one or more steps longer than the parsimonious tree (MPT). Many phylogeny trees of similar length to the MPT, but have different topologies.
Why is parsimonious explanation important?
Overall, this example illustrates the importance of choosing parsimonious explanations, which accurately capture the phenomenon at hand in a generalizable manner. Such explanations are contrasted with non-parsimonious explanations, which are overfitted to particular data and therefore fail to accurately capture the underlying phenomenon, and with overly-parsimonious explanations, which are so simplified that they also fail to properly capture the underlying phenomenon.
Why is parsimonious explanation better than less parsimonious explanation?
This means that a parsimonious explanation will generally be better able to explain a wider range of phenomena than a less parsimonious one, since a parsimonious explanation doesn’t rely on as many assumptions that are specific to the situation at hand.
Why is parsimony important?
This is why parsimony is so important: because it forces you to stick to the simplest and most reasonable explanation, unless you have compelling evidence which suggests that this explanation is wrong.
What is complexity based on?
The complexity of a given explanation or solution can be defined in many ways, based on the context and on the factors involved. In general, however, complexity is based on the number of assumptions that are required for a given explanation to make sense, with the simplest explanation (i.e. the most parsimonious one) being the one ...
What is the meaning of parsimony?
Outside the philosophical and scientific uses of the word, ‘parsimony’ is defined as the quality of being reluctant to spend resources.
When looking for the best explanation or solution, should you select the simplest one?
Specifically, according to the principle of parsimony, when looking for the best explanation or solution, you should select the simplest one, as long as no other criterion can be used in order to choose between the available options. The complexity of a given explanation or solution can be defined in many ways, ...
Who said parsimony shouldn't be overapplied?
The most famous of these formulations was proposed by Walter of Chatton, a philosopher who proposed the Chatton Principle, which is the adage that: