What does OAC medical abbreviation stand for?
OAC Medical Abbreviation. 6. OAC. Obesity Action Coalition. Bariatric Surgery, Weight Loss Surgery, Obesity. Bariatric Surgery, Weight Loss Surgery, Obesity. 5. OAC. Oral Anticoagulation + 1 variant.
What is the most common cause of OAC?
Four upper last maxillary teeth are the main cause of OAC but the tooth most often related varies depending on sample consulted. Other factors such as a history of coronary artery disease or cigarette smoking may also influence your physicians decision to use OAC.
What is oesophagogastric adenocarcinoma (OAC)?
Oesophagogastric adenocarcinoma ( OAC) includes adenocarcinomas of the stomach (gastric cancer), of the distal oesophagus, and of the gastrooesophageal junction.
What does OA stand for in occupational therapy?
Abbreviation: OA. A practice model used by the occupational therapist to provide strategies for interpreting and enhancing observed patient performance and for facilitating mastery for the patient over performance challenges.
What is OTs in medical terms?
For the most part, occupational therapy consists of two primary roles: occupational therapists (also referred to as OTs) and occupational therapy assistants (OTAs).
What does ROC stand for in medical terms?
Receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve for medical researchers.
What is ROC in nursing?
A Resumption of Care (ROC) assessment is required any time the patient is admitted as an inpatient for 24 hours or more for other than diagnostic tests and returns to home care. A ROC must follow a transfer if the patient returns to the agency within the episode.
What is the abbreviation for oncology?
Abbreviation for Oncology:3OncolOncology Medical2OncOncology + 1 Medical, Hospital, Hospital Ward1O nc NCOncology Medical, Pathology1OOncology Hematology, Medical
What is the NOAC concept?
NOAC Concept. The term “novel” was initially applied to dabigatran (Pradaxa) when it was introduced to the US market in 2010. 1 Instead of reducing clotting factor production (like warfarin) or binding to antithrombin III to induce anticoagulation (like heparin and heparin derivatives), dabigatran directly binds to clotting factor IIa (thrombin).
What does DOAC stand for?
The most popular competing term is “DOAC,” which stands for direct oral anticoagulant. This terminology reflects the novel mechanism of the newer anticoagulants (directly binding to specific clotting factors), which may even reflect future oral anticoagulants that haven’t been developed, like those directly binding to other clotting factors (aside from Xa or IIa) within the clotting cascade.
How long has NOAC been approved?
Initially, terms like “novel oral anticoagulant” (NOAC) were used extensively. But now, more than 6 years have passed and 3 additional NOACs have been approved by the FDA. The recognition that these drugs are no longer novel has led guidelines and international societies to reassess their nomenclature.
When was the first anticoagulant approved?
The first oral anticoagulant, warfarin, was approved by the FDA in 1954. 1 For more than 60 years, warfarin was the only mainstream oral anticoagulant used in the United States.
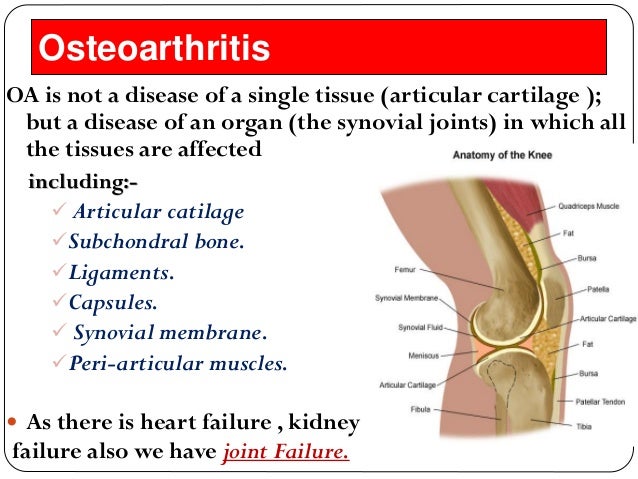
What is OA in sports?
OA. A type of arthritis marked by progressive cartilage deterioration in synovial joints and vertebrae. Risk factors include aging, obesity, overuse or abuse of joints (repetitive motions, bending, lifting), as in sports or strenuous occupations, instability of joints, excessive mobility, immobilization, and trauma.
What is the meaning of "adjusting"?
1. Adjustment of an organism to a change in internal or external conditions or circumstances. 2. Adjustment of the eye to various intensities of light, accomplished by changing the size of the pupil and accompanied by chemical changes occurring in the rods. 3.