What is density gradient in human geography? Density Gradient. Definition: The change in density in an urban area from the center to the periphery.
What does density gradient mean?
Here are all the possible meanings and translations of the word density gradient. Density gradient is a spatial variation in density over an area. The term is used in the natural sciences to describe varying density of matter, but can apply to any quantity whose density can be measured.
How do find a gradient?
The Gradient and Directional Derivative
- Examples. For the function z=f (x,y)=4x^2+y^2.
- Geometric Description of the Gradient Vector. There is a nice way to describe the gradient geometrically. Consider z=f (x,y)=4x^2+y^2. The surface defined by this function is an elliptical paraboloid.
- Directional Derivatives. For a function z=f (x,y), the partial derivative with respect to x gives the rate of change of f in the x direction and the partial derivative with ...
What is the difference between gradient and imgradient?
The gradient of a pixel is the difference between diagonally adjacent pixels. For gradients in one direction, the weights are: In the orthogonal direction, the weights are flipped along the vertical axis. Horizontal gradient, specified as a numeric matrix. The horizontal ( x) axis points in the direction of increasing column subscripts.
How does gradient determine the size of sediment?
particles sediment through the fluid according to Stokes' Law. The required steepness of the density gradient depends upon the net density of the sample to be measured. A sample with higher net density (higher particle concentration and/or higher particle density) requires a steeper density gradient than a sample with lower net density.
What is density gradient geography?
Density gradient is a spatial variation in density over an area. The term is used in the natural sciences to describe varying density of matter, but can apply to any quantity whose density can be measured.
What is an example of density AP Human Geography?
An example of density can be measured by the amount of cars per square mile. The total number of people divided by the total land area. For example, The Netherlands have a higher density of people than China. The number of people per unit of area of arable land which is suitable for agriculture.
What does density mean AP Human Geography?
Ap Human Geography : Example Question #1 Population density refers to the number of people who live in a defined land area (usually square miles or square kilometers). So, if two million people live in ten square miles, the population density is two hundred thousand people per square mile.
What is an example of filtering in human geography?
Definition. Def: A process of change in the use of a house, from single-family owner to abandonment. Ex: Inner-city homes were/are strongly affected by filtering.
What are the three types of density in geography?
The three methods for calculating population density are arithmetic, physiological and agricultural. The method used to calculate population density reveals different information about the pressure the population exerts on the land.
What are the 3 types of density?
There is arithmetic density, physiological density, and agricultural density.
What is density of population explain with example?
It is calculated by dividing the population by the area. For example, France has a population of 60,561,200, and an area of 551,695 square kilometres, so its population density is about 109.8 persons per square kilometre. A number of factors can affect population density. For example, the climate.
What is the difference between density and concentration in geography?
Concentration is the spread of objects in a given area, density is the frequency of objects in a given area,and pattern is the arrangement of objects in a given area.
What are the 4 different types of diffusion?
Expansion DiffusionContagious Diffusion.Hierarchical Diffusion.Stimulus Diffusion.
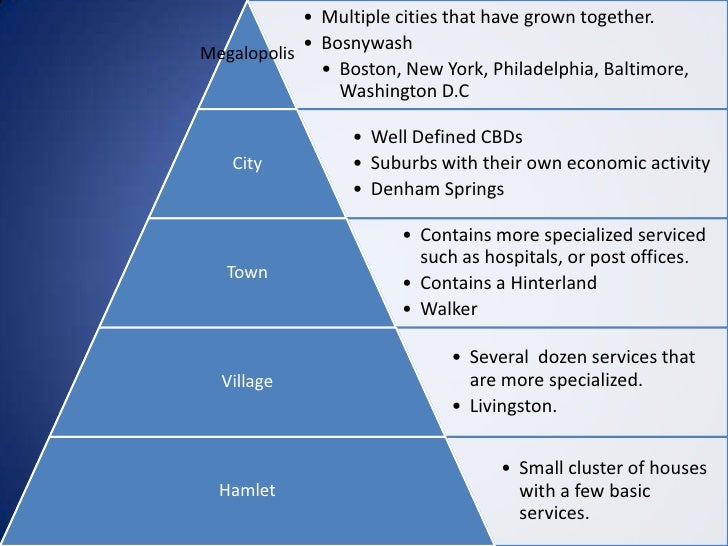
What is an example of density gradient in AP Human Geography?
Density Gradient. Definition: The change in density in an urban area from the center to the periphery. Example: Model. Application:Very Important because Density Gradient affects urban areas. Edge City.
In what two ways has the density gradient changed in recent years?
Two changes have impacted the density gradient in recent years: fewer people living in the center, and fewer differences in density within urban areas. These two changes flatten the density gradient and reduce the extremes of density between inner and outer areas traditionally found within cities.
What does filtering mean in AP Human Geography?
Filtering is the process of subdivision of houses and occupancy by succesive waves of lower-income. Landlords stop maintaining houses when the rent they collect becomes less than the maintenance costs. The building soon deteriorates and grows unfit for occupancy.
How to find density gradient?
A density gradient is simply established by placing sugar crystals at the bottom of a test tube (Fisher and Cline, 1963). The sugar dissolves in the solution and diffuses slowly toward the top which is a time-consuming process and not very reproducible. A more practical approach is to place layer after layer of sucrose solutions of decreasing concentrations in a test tube, resulting in the heaviest layer at the bottom and the lightest layer on top. Finally, the cell fraction is placed on top of the sucrose layers. If the density of a given particle is higher than that of the surrounding solution it will sink until the density of the surrounding solution is exactly the same as that of the particle. Using a centrifuge will accelerate this process. Unlike the differential centrifugation technique described above, centrifugation time does not matter, as long as the whole system is allowed to come to quasiequilibrium.
Why are density gradients undesirable?
As a general rule, density gradients are undesirable because they contribute to differential sintering and shape distortion (Ewsuk 1993 ).
What happens to the gradient after centrifugation?
After centrifugation the gradients are fractionated by upwards displacement. The very low-density lipoprotein is found at the top of the gradient, low-density lipoprotein between 10 ml and 15 ml from the top, and the high-density lipoprotein at the original sample position along with other serum proteins.
What should a gradient be?
1. The materials should be sufficiently soluble in water to produce the range of densities needed. 2. Solutions of the gradient materials should be adjustable to a pH and ionic strength that are not harmful to proteins in the sample. 3. The materials should not interfere with methods of analysis of the target protein.
Is sucrose a gradient material?
Sucrose has most often been used as a gradient material. Sucrose is inexpensive and extremely soluble in aqueous media and can be used to produce density gradients ranging up to 1.35 g mL −1. Thus, it is suitable for separation of almost all proteins in cells.
Numerical simulation of internal cooling in turbine blades by using two-layer turbulence model
G.J. Hwang Professor, Frank K.T. Lin Ph.D. student, in Parallel Computational Fluid Dynamics 1998, 1999
Plasma Science and Engineering
J.L. Shohet, in Encyclopedia of Physical Science and Technology (Third Edition), 2003
Recent Developments and Applications of Modern Density Functional Theory
K.M. Neyman, ... N. Rösch, in Theoretical and Computational Chemistry, 1996
Environmental Observation and Forecasting Systems
António M. Baptista, in Encyclopedia of Physical Science and Technology (Third Edition), 2003
Cryogenic Process Engineering
Klaus D. Timmerhaus, in Encyclopedia of Physical Science and Technology (Third Edition), 2003
Advances in techniques for diagnosing fusion plasmas
Although microwave reflectometry is a well-known technique in atmospheric physics, where it is used to probe the density of the ionosphere and it was applied in several early tokamaks, it did not develop as a front line fusion diagnostic until quite recently.
Vehicular Traffic IV: Non-CA Approaches
Andreas Schadschneider, ... Katsuhiro Nishinari, in Stochastic Transport in Complex Systems, 2011
How to find density?
To calculate density, you divide the number of objects by the measurement of the area.
What is the population density of a country?
The population density of a country is the number of people in that country divided by the area in square kilometers or miles. The country of Singapore is one of the most densely populated countries in the world. It has a population of 4,839,400 and an area of 687 square kilometers (265 square miles), so its density is 7,044 people per square ...
What type of rock has a low density?
Many igneous rocks, or rocks formed from volcanic eruptions, have a low density. They are full of pockets of air. One type of igneous rock, pumice, has such a low density that it can actually float on water. The water is more dense than the rock. Densely packed in the "Pink City.".
Why do densely populated cities have poor air quality?
Densely populated cities often have poor air quality because of the air pollution density. Density is used to measure the salinity of seawater. Water densely packed with salt has a high salinity. Water that has few salt molecules has low salinity. Rocks and minerals are also measured for density.
What is the definition of a pollutant?
pollutant. Noun. chemical or other substance that harms a natural resource. population density. Noun. the number of people living in a set area, such as a square mile. predator. Noun. animal that hunts other animals for food.