Pacemaker is an open source cluster resource manager (CRM), a system that coordinates resources and services that are managed and made highly available by a cluster. In essence, Corosync enables servers to communicate as a cluster, while Pacemaker provides the ability to control how the cluster behaves.
What is Corosync pacemaker in Linux?
Corosync is an open source Cluster Engine. It is actually a Communication System that enables two or more Linux Cluster nodes to transfer information between them. Corosync Communication System enables all of the nodes to know the exact state of each other at all time. Beside above, how is a pacemaker set up?
How does the Corosync software work?
The software is composed of an executive binary which uses a client-server communication model between libraries and service engines. Loadable modules, called service engines, are loaded into the Corosync Cluster Engine and use the services provided by the Corosync Service Engine internal API.
What is Corosync Cluster Engine?
The Corosync Cluster Engine is an open source implementation of the Totem Single Ring Ordering and Membership protocol. It was originally derived from the OpenAIS project and licensed under the new BSD License. The mission of the Corosync effort is to develop, release, and support a community-defined, open source cluster .
What is Corosync used for?
Corosync is an open source program that provides cluster membership and messaging capabilities, often referred to as the messaging layer, to client servers.
What is the pacemaker and Corosync administration tool?
Pacemaker features two configuration tools for cluster deployment, monitoring, and management. pcs can control all aspects of Pacemaker and the Corosync heartbeat daemon. A command-line based program, pcs can perform the following cluster management tasks: Create and configure a Pacemaker/Corosync cluster.
What is pacemaker in Db2?
Pacemaker is an open-source, high availability cluster manager software integrated with Db2® Advanced Edition and Db2 Standard Edition on Linux®. It provides high availability and disaster recovery capabilities for on-premises deployments and non-container cloud environments, such as Amazon Web Service (AWS).
What is pacemaker in Linux?
Pacemaker is an open source high-availability cluster resource manager software that runs on a set of nodes.
What is Pacemaker in SAP?
How Pacemaker Cluster works with SAP HANA System Replication. SUSE developed in collaboration with SAP the SAPHanaSR solution and released it as part of SLES for SAP Applications. This solution is based on Pacemaker Cluster that is automating failovers between two SAP HANA databases that are mirroring each other.
What is Pacemaker in server?
Pacemaker is a high-availability cluster resource manager. It achieves maximum availability for your cluster services (a.k.a. resources) by detecting and recovering from node- and resource-level failures by making use of the messaging and membership capabilities provided by Corosync.
What is pacemaker database?
The database stores medically useful information about the patients and their pacemaker test results in order to highlight serial changes, which determine whether the pacemaker is still functioning normally, or whether the patient requires further intervention.
What is Corosync in Redhat Cluster?
Corosync: Corosync is an opensource cluster engine which communicates with multiple cluster nodes and updates the cluster information database (cib. xml) frequently . In previous redhat cluster release, “cman” was responsible for cluster interconnect, messaging and membership capabilities.
What is pacemaker AWS?
Pacemaker is a Cluster Resource Manager (CRM) that help running a service in a high availability mode.
What is pacemaker in cloud?
Pacemaker is a high availability Cluster Resource Manager (CRM) that can be used to manage resources, and ensure that they remain available in the event of a node failure.
What is pacemaker in CentOS?
We will create the Active-Passive Cluster or Failover-cluster Nginx web server using Pacemaker on a CentOS 7 system. Pacemaker is an open source cluster manager software that achieves maximum high availability of your services. It's an advanced and scalable HA cluster manager distributed by ClusterLabs.
What is heartbeat in Linux cluster?
Heartbeat is an open source program that provides cluster infrastructure capabilities—cluster membership and messaging—to client servers, which is a critical component in a high availability (HA) server infrastructure.
What is Corosync conf?
The corosync.conf instructs the corosync executive about various parameters needed to control the corosync executive. Empty lines and lines starting with # character are ignored. The configuration file consists of bracketed top level directives.
What is Totem Corosync?
Corosync, more specifically its Totem protocol implementation, defines a maximum number of cluster messages that can be sent during one token rotation. By default, that number is 50, but you may modify this value by setting the window_size parameter in your corosync. conf configuration file.
How do you enable Stonith in a Pacemaker?
Enable STONITH for your HA topology.Enable the cluster STONITH property by using the following command. $ pcs property set stonith-enabled=true.Update the environment for your deployment to set the ibm-openstack. ha. pacemaker. properties. stonith-enabled. value property to true .
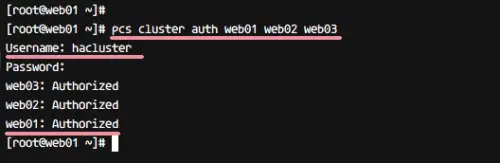
How do you activate a Pacemaker?
The broad steps for the cluster configuration include:Install Pacemaker packages on both nodes of the cluster. ... Create the HACLUSTER user ID with. ... Enable and start the pcs services. ... Authenticate pcs with hacluster user. ... Create the cluster. ... Start the cluster. ... Enable the cluster to auto-start after reboot.
Terms and abbreviations
Corosync allows any number of servers to be part of the cluster using any number of fault-tolerant configurations (active/passive, active/active, N+1, etc.)
Cluster configuration
On OpenSUSE servers OCF resource definitions can be found in /usr/lib/ocf/resource.d/.
Features
The Corosync Cluster Engine is a group communication system with additional features for implementing high availability within applications.
Architecture
The software is composed of an executive binary which uses a client-server communication model between libraries and service engines. Loadable modules, called service engines, are loaded into the Corosync Cluster Engine and use the services provided by the Corosync Service Engine internal API.
History
The project was formally announced in July 2008 via a conference paper at the Ottawa Linux Symposium. The source code of OpenAIS was refactored such that the core infrastructure components were placed into Corosync and the SA Forum APIs were kept in OpenAIS.
Can IPMI be applied to any fencing device?
This Parameter can be applied to any Fencing Device. IPMI above is only an example.
Does one fencing device delay?
this will make it more likely, that one fencing device will have a delay. It is at that moment irrelevant which node fences which node, as there is no way for a Cluster without Quorum to determine the right node to be fenced.
Overview
- Corosyncallows any number of servers to be part of the cluster using any number of fault-tolerant configurations (active/passive, active/active, N+1, etc.) Corosyncprovides messaging between servers within the same cluster. Pacemakermanages the resources and applications on a node within the cluster. OpenAIS can be thought of as the API between Cor...
Features
Architecture
History
The Corosync Cluster Engine is an open source implementation of the Totem Single Ring Ordering and Membership protocol. It was originally derived from the OpenAIS project and licensed under the new BSD License. The mission of the Corosync effort is to develop, release, and support a community-defined, open source cluster.
See also
The Corosync Cluster Engine is a group communication system with additional features for implementing high availability within applications.
The project provides four C API features:
• A closed process group communication model with virtual synchrony guarantees for creating replicated state machines.
External links
The software is composed of an executive binary which uses a client-server communication model between libraries and service engines. Loadable modules, called service engines, are loaded into the Corosync Cluster Engine and use the services provided by the Corosync Service Engine internal API.
The services provided by the Corosync Service Engine internal API are: