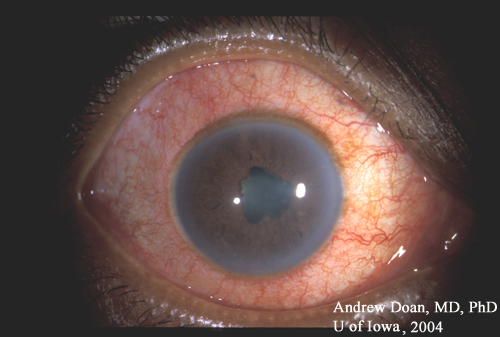
Ciliary flush. Ciliary flush is usually present in eyes with corneal inflammation, iridocyclitis or acute glaucoma, though not simple conjunctivitis. A ciliary flush is a ring of red or violet spreading out from around the cornea of the eye.
What is ciliary flush in eye?
Ciliary flush is usually present in eyes with corneal inflammation, iridocyclitis or acute glaucoma, though not simple conjunctivitis. A ciliary flush is a ring of red or violet spreading out from around the cornea of the eye. Click to see full answer.
What is the file size for ciliary flush?
Ciliary flush File Size: 90 KB Related: red eye, ciliary flush Cornea/External Disease View Full Image Image License and Citation Guidelines Add to My Bookmarks View Mark Complete Remove Comments Ciliary flush.
What is anterior uveitis with ciliary flush?
* Anterior uveitis/iritis causes sensitivity to light in both the affected and unaffected eyes, as well as ciliary flush (a red ring around the iris). Symptoms associated with anterior uveitis, such as unilateral red eye, ciliary flush, and irregular pupil, were reported by 13 (9.4%) patients.
What is the function of the ciliary body?
ciliary body the thickened part of the vascular tunic of the eye, connecting choroid and iris, made up of the ciliary muscle and the ciliary processes. These processes radiate from the ciliary muscle and give attachment to ligaments supporting the lens of the eye.
What is ciliary injection?
Ciliary injection involves branches of the anterior ciliary arteries and indicates inflammation of the cornea, iris, or ciliary body. Conjunctival injection mainly affects the posterior conjunctival blood vessels.Feb 25, 2022
What is ciliary injection limbal flush?
Slightly decreased visual acuity may be present as well. What does anterior uveitis look like on exam? The eye exam will show conjunctival injection, worse around the limbus, which is the area of the conjunctiva adjacent to the iris. This is called perilimbal injection or ciliary flush.Aug 22, 2017
How can you tell the difference between keratitis and conjunctivitis?
Keratitis is inflammation of the cornea, the clear dome that covers the iris and the pupil. Conjunctivitis is inflammation of the conjunctiva. That's the thin membrane over the white part of the eye and the inner surface of the eyelid. Conjunctivitis is also known as pink eye.Nov 22, 2019
What does injection of the cornea mean?
The inside of the eye is filled with a jelly-like fluid (vitreous). During this procedure, your health care provider injects medicine into the vitreous, near the retina at the back of the eye. The medicine can treat certain eye problems and help protect your vision.Dec 14, 2020
Where is the ciliary body?
The ciliary body is found behind the iris and includes the ring-shaped muscle that changes the shape of the lens when the eye focuses. It also makes the clear fluid that fills the space between the cornea and the iris.
What is the difference between scleritis and Episcleritis?
Episcleritis is inflammation of the superficial, episcleral layer of the eye. It is relatively common, benign and self-limiting. Scleritis is inflammation involving the sclera. It is a severe ocular inflammation, often with ocular complications, which nearly always requires systemic treatment [1, 2].Oct 22, 2021
What does keratitis look like?
The result of that inflammation is that the normally white part of the eye looks pink – or red. Similarly, keratitis – the inflammation of the cornea, the transparent part of the eye in front of the pupil and iris – gives the eye a comparably reddened, irritated look. "They both look like red eye or pink eye.Feb 20, 2020
Does keratitis go away on its own?
If your keratitis is caused by an injury, it usually clears up on its own as your eye heals. You may get an antibiotic ointment to help with symptoms and prevent infection. Infections are treated with prescription eye drops and sometimes antibiotics or antiviral medicine.
What antibiotics treat keratitis?
The traditional therapy for bacterial keratitis is fortified antibiotics, tobramycin (14 mg/mL) 1 drop every hour alternating with fortified cefazolin (50 mg/mL) or vancomycin (50mg/mL) 1 drop every hour. In cases of severe ulcers, this is still the recommended initial therapy.Dec 9, 2019
How long do eye injections last?
These are injected into the eye every four weeks for around one year. After one year, the frequency at which you require injections may be decided by your eye doctor. These injections have shown to halt the ongoing vision loss and, in some cases, even improve the vision.Sep 25, 2020
Is eye injection painful?
Pain in the hours following an eye injection The eye can develop significant discomfort or severe pain about one hour or more after the injection. This may be due to corneal abrasion: a scratch on the cornea (the clear glassy part of the eye). The injection can also cause the eye to become very dry.
How long do floaters last after eye injection?
Moving circular black spots in your vision (floaters) may be noticeable immediately following the injection and can last up to 24 hours. A small red area or hemorrhage at the site of injection is also commonly seen in the first few days after injection.
Ciliary Flush
Ciliary flush, Ciliary injection, Ciliary body congestion, ciliary flush, ciliary injection, Ciliary flush (disorder)
Ciliary injection ( C0271108 )
Ciliary flush, Ciliary injection, Ciliary body congestion, ciliary flush, ciliary injection, Ciliary flush (disorder)
Symptoms and Signs of Conjunctivitis
Any source of inflammation can cause lacrimation or discharge and diffuse conjunctival vascular dilation. Discharge may cause the eyes to crust overnight. Thick discharge may blur vision, but once discharge is cleared, visual acuity should be unaffected.
Diagnosis of Conjunctivitis
Usually, diagnosis of conjunctivitis is made by history and examination (see table Differentiating Features in Acute Conjunctivitis Differentiating Features in Acute Conjunctivitis Conjunctival inflammation typically results from infection, allergy, or irritation.
Treatment of Conjunctivitis
Most infectious conjunctivitis is highly contagious and spreads by droplets, fomites, and hand-to-eye inoculation. To avoid transmitting infection, physicians must
Key Points
Conjunctivitis typically results from infection, allergy, or irritation.
Drugs Mentioned In This Article
Pediatric orbital tumors most commonly include dermoid tumors, capillary hemangiomas, and lymphangiomas. When a pediatric patient has a capillary hemangioma on the upper eyelid that is affecting vision, which of the following is the most appropriate treatment?
Merck and the Merck Manuals
Merck & Co., Inc., Kenilworth, NJ, USA is a global healthcare leader working to help the world be well. From developing new therapies that treat and prevent disease to helping people in need, we are committed to improving health and well-being around the world. The Merck Manual was first published in 1899 as a service to the community.
Visual acuity
A reduction in visual acuity in a 'red eye' is indicative of serious ocular disease, such as keratitis, iridocyclitis, and glaucoma, and never occurs in simple conjunctivitis without accompanying corneal involvement.
Ciliary flush
Ciliary flush is usually present in eyes with corneal inflammation, iridocyclitis or acute glaucoma, though not simple conjunctivitis. A ciliary flush is a ring of red or violet spreading out from around the cornea of the eye.
Corneal abnormalities
The cornea is required to be transparent to transmit light to the retina. Because of injury, infection or inflammation, an area of opacity may develop which can be seen with a penlight or slit lamp. In rare instances, this opacity is congenital. In some, there is a family history of corneal growth disorders which may be progressive with age.
Pupillary abnormalities
In an eye with iridocyclitis, (inflammation of both the iris and ciliary body), the involved pupil will be smaller than the uninvolved, due to reflex muscle spasm of the sphincter muscle of the iris . Generally, conjunctivitis does not affect the pupils.
Abnormal intraocular pressure
Intraocular pressure should be measured as part of the routine eye examination . It is usually only elevated by iridocyclitis or acute-closure glaucoma, but not by relatively benign conditions. In iritis and traumatic perforating ocular injuries, the intraocular pressure is usually low.
Severe pain
Those with conjunctivitis may report mild irritation or scratchiness, but never extreme pain, which is an indicator of more serious disease such as keratitis, corneal ulceration, iridocyclitis, or acute glaucoma .
Differential diagnosis
Of the many causes, conjunctivitis is the most common. Others include: Usually nonurgent