How do you document caput and moulding?
You can document the degree of caput either on the back of the partograph, or on the mother's health record (if you have it). Hereof, what is caput and Moulding?
How do you grade a caput?
Like moulding, you grade the degree of caput as 0, +1, +2 or +3. Because of its subjective nature, grading the caput as +1 or +3 simply indicates a 'small' and a 'large' caput respectively.
What is the difference between a +1 and +3 caput?
Because of its subjective nature, grading the caput as +1 or +3 simply indicates a 'small' and a 'large' caput respectively. You can document the degree of caput either on the back of the partograph, or on the mother's health record (if you have it).
What is caput in fetal anatomy?
It may extend over the midline (as opposed to cephalhaematoma) and is associated with moulding of the head. Caput can make it difficult to define the position of the fetal head.
What does caput and Moulding mean?
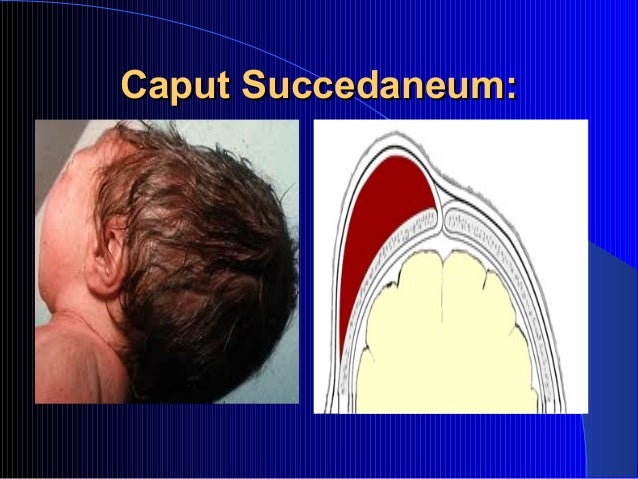
Images from Radswiki Caput succedaneum is a diffuse swelling of the scalp caused by the pressure of the scalp against the dilating cervix during labour. It may extend over the midline (as opposed to cephalhaematoma) and is associated with moulding of the head.
What is Moulding in labour?
The extent of overlapping of fetal skull bones is called moulding, and it can produce a pointed or flattened shape to the baby's head when it is born (Figure 4.5). Figure 4.5 Normal variations in moulding of the newborn skull, which usually disappears within 1–3 days after the birth.
What is Moulding in anatomy?
This is the term applied to the change in shape of the fetal head which takes place as it passes through the birth canal. It is brought about by pressure between the fetal skull and the maternal pelvis. It results in compression of the movable bones and elongation of those which are not compressed.
What is caput formation?
“Caput succedaneum” refers to swelling, or edema, of an infant's scalp that appears as a lump or bump on their head shortly after delivery. This condition is harmless and is due to pressure put on the infant's head during delivery. It doesn't indicate damage to the brain or the bones of the cranium.
Is Caput Succedaneum the same as molding?
Abstract. Caput succedaneum is defined as a diffuse swelling of the fetal scalp caused by the pressure of the scalp against the dilating cervix during labor. Caput is often associated with molding and may extend across the midline (as opposed to cephalohematoma, which does not cross the suture lines).
What causes fetal moulding?
When a baby is born in a head-first position, pressure on the head in the birth canal may mold the head into an oblong shape. These spaces between the bones allow the baby's head to change shape. Depending on the amount and length of pressure, the skull bones may even overlap.
What is the difference between molding and moulding?
While the spelling “molding” is still used in some regions of the United States, the spelling “moulding” is the preferred spelling used by those in the industry. In fact, the official industry association, the Moulding & Millwork Producers Association, uses this spelling exclusively.
What are the types of moulding?
4 Types of Molding Processes: Applications and Advantages1) Compression Molding. The compression molding process is used to make rubber and plastic parts. ... 2) Melt Molding. When applied to thermoplastic materials, compression molding is referred to as melt molding. ... 3) Transfer Molding. ... 4) Injection Molding.
What is the normal moulding?
What is normal? Up to 2+ occipito-parietal moulding may be normal in the later stages of labour. No moulding – parietal bones (sagital suture) are not apposed. +1 moulding – parietal bones are touching but not overlapping.
What is Moulding of the fetal skull?
Overview. During a head first birth, pressure on the head caused by the tight birth canal may "mold" the head into an oblong rather than round shape. This is a common occurrence that usually disappears after a few days.
How do you assess Moulding?
The degree of moulding is assessed according to the following scale: 0 = Normal separation of the bones with open sutures. 1+ = Bones touching each other. 2+ = Bones overlapping, but can be separated with gentle digital pressure.
What is a caput in medical?
Medical Definition of caput 1 : a knoblike protuberance (as of a bone or muscle) 2 : caput succedaneum.
What is a caput?
Caput. Caput succedaneum is a diffuse swelling of the scalp caused by the pressure of the scalp against the dilating cervix during labour. It may extend over the midline (as opposed to cephalhaematoma) and is associated with moulding of the head. Caput can make it difficult to define the position of the fetal head.
Is caput a first line instrument?
It is graded subjectively from 0 (none) to +3 (marked). The vacuum cup may not maintain its suction if there is marked caput – forceps should be considered as a first-line instrument.
Why do the bones of the fetal head move closer together?
The bones of the fetal head can move closer together or overlap to help the head fit through the pelvis.
Is parieto-parietal moulding normal?
Severe parieto–parieto moulding is never normal and should be interpreted as a sign of relative or absolute cephalopevic disproportion. Irreducible parieto-parietal moulding may indicate cephalopelvic disproportion. Consider if caesarean delivery is more appropriate.
What is a newborn head molding?
Newborn head molding is an abnormal head shape that results from pressure on the baby's head during childbirth.
What are the spaces between the bony plates of the skull called?
The spaces between the bony plates of the skull are called cranial sutures. The front ( anterior) and back (posterior) fontanelles are 2 gaps that are particularly large. These are the soft spots you can feel when you touch the top of your baby's head. When a baby is born in a head-first position, pressure on the head in ...