What is an organic family in chemistry?
What is an organic family in chemistry? The term, organic compounds, is applied to materials that contain carbon and are associated with living organisms. Carbon atoms form strong covalent bonds to other carbon atoms and to hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen, and sulfur.
What are some examples of organic chemistry?
These common products make use of organic chemistry:
- Shampoo
- Gasoline
- Perfume
- Lotion
- Drugs
- Food and food additives
- Plastics
- Paper
- Insect repellent
- Synthetic fabrics (nylon, polyester, rayon)
What are the families of organic compounds?
Oxygen-containing organic compounds, a third family, may be divided into two main types: those that contain at least one C–O bond, which include alcohols, phenols (derivatives of benzene), and ethers, and those that contain a carbonyl group (C=O), which include aldehydes, ketones, and carboxylic acids.
What are the principles of organic chemistry?
Table of contents
- Structure of Organic Compounds
- Properties of Organic Compounds
- Alkanes and Cycloalkanes
- Alkenes and Alkynes
- Aromatic Compounds
- Stereochemistry
- Nucleophilic Substitution and Elimination Reactions
- Alcohols and Phenols
- Ethers and Epoxides
- Aldehydes and Ketones
What are organic families in chemistry?
Major Organic Families and the Functional Groups They ContainFamilyFunctional GroupAlcoholhydroxyl group: C-OHEthercarbon-oxygen-carbon bonding: C-O-CAldehyde and ketonecarboxyl (C=O) group: C-C=OCarboxylic acidcarboxylic (C=O) group:5 more rows
What does organic family mean?
1 of, relating to, derived from, or characteristic of living plants and animals. 2 of or relating to animal or plant constituents or products having a carbon basis.
How do you identify an organic family?
14:3724:21It's in the Family! Recognition and Examples of Organic Chemistry ...YouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipExcept instead of having an hydrogen on one side. It's got another R group on the other side of thatMoreExcept instead of having an hydrogen on one side. It's got another R group on the other side of that carbon. And so aldehydes and ketones are very similar except notice on the aldehyde.
What does organic mean in chemistry?
Organic chemistry is the study of the structure, properties, composition, reactions, and preparation of carbon-containing compounds. Most organic compounds contain carbon and hydrogen, but they may also include any number of other elements (e.g., nitrogen, oxygen, halogens, phosphorus, silicon, sulfur).
What is the difference between an organic and inorganic molecule?
Organic compounds and inorganic compounds form the basis of chemistry. The primary difference between organic vs. inorganic compounds is that organic compounds always contain carbon while most inorganic compounds do not contain carbon. Also, nearly all organic compounds contain carbon-hydrogen or C-H bonds.
What does organic actually mean?
In a nutshell, organic produce and other ingredients are grown without the use of synthetic pesticides, sewage sludge, synthetic fertilizers, genetically modified organisms, bioengineering, or ionizing radiation.
What are the four main organic families?
4 Families of Organic Compounds with Important Biological...Carbohydrates. These molecules consist of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen in a ratio of roughly 1:2:1. ... Lipids. Commonly known as fats, these molecules contain carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen, and sometimes nitrogen and phosphorous. ... Proteins. ... Nucleic acids.
How do you identify organic molecules?
A molecule is organic if it contains carbon and hydrogen. Some exceptions to the rule are compounds like H2CO3 and HCN , which are usually considered to be inorganic molecules.
How do you identify organic functional groups?
Identification and extraction of functional groupsmark all heteroatoms in a molecule, including halogens.mark also the following carbon atoms: atoms connected by non-aromatic double or triple bond to any heteroatom. atoms in nonaromatic carbon–carbon double or triple bonds. ... merge all connected marked atoms to a single FG.
What is organic and inorganic?
1. Organic compounds are characterized by the presence of carbon atoms in them. Most inorganic compounds do not have carbon atoms in them (some exceptions do exist) 2. Organic compounds consisting of hydrogen, oxygen, carbon, and their other derivatives.
Why is it called organic chemistry?
specialized field of chemistry called organic chemistry, which derives its name from the fact that in the 19th century most of the then-known carbon compounds were considered to have originated in living organisms.
What molecules are organic?
Organic molecules are molecules that are made of carbon and hydrogen, and can include other elements. Organic molecules must contain carbon atoms covalently bonded to hydrogen atoms (C-H bonds). They usually involve oxygen and can also contain nitrogen, sulfur, phosphorous, and others.
What is organic chemistry?
e. Organic chemistry is a branch of chemistry that studies the structure, properties and reactions of organic compounds, which contain carbon in covalent bonding. Study of structure determines their chemical composition and formula. Study of properties includes physical and chemical properties, and evaluation of chemical reactivity ...
What are the elements that are found in organic chemistry?
The range of chemicals studied in organic chemistry includes hydrocarbons (compounds containing only carbon and hydrogen) as well as compounds based on carbon, but also containing other elements, especially oxygen, nitrogen, sulfur, phosphorus (included in many biochemicals) and the halogens. Organometallic chemistry is the study ...
What is the multiple step synthesis of complex organic compounds called?
The multiple-step synthesis of complex organic compounds is called total synthesis. Total synthes is of complex natural compounds increased in complexity to glucose and terpineol. For example, cholesterol -related compounds have opened ways to synthesize complex human hormones and their modified derivatives.
What is the study of organic reactions?
The study of organic reactions includes the chemical synthesis of natural products, drugs, and polymers, and study of individual organic molecules in the laboratory and via theoretical ( in silico) study.
When was the first systematic study of organic compounds?
During the first half of the nineteenth century, some of the first systematic studies of organic compounds were reported. Around 1816 Michel Chevreul started a study of soaps made from various fats and alkalis. He separated the acids that, in combination with the alkali, produced the soap.
Which compounds are not normally grouped together?
Organic compounds containing bonds of carbon to nitrogen, oxygen and the halogens are not normally grouped separately. Others are sometimes put into major groups within organic chemistry and discussed under titles such as organosulfur chemistry, organometallic chemistry, organophosphorus chemistry and organosilicon chemistry .
Is organic compound a systematic or nonsystematic name?
The names of organic compounds are either systematic, following logically from a set of rules, or nonsystematic, following various traditions. Systematic nomenclature is stipulated by specifications from IUPAC. Systematic nomenclature starts with the name for a parent structure within the molecule of interest.
What is organic chemistry?
Organic chemistry is a highly creative science that allows chemists to create and explore molecules and compounds. Organic chemists spend much of their time developing new compounds and finding better ways of synthesizing existing ones.
What are organic compounds?
Organic compounds are all around us. Many modern materials are at least partially composed of organic compounds. They’re central to economic growth, and are foundational to the fields of biochemistry, biotechnology, and medicine.
What are the elements that make up organic compounds?
Most organic compounds contain carbon and hydrogen, but they may also include any number of other elements (e.g., nitrogen, oxygen, halogens, phosphorus, silicon, sulfur). Originally limited to the study of compounds produced by living organisms, organic chemistry has been broadened to include human-made substances (e.g., plastics).
Who hires organic chemists?
Federal offices (e.g., Food and Drug Administration, Patent and Trademark Office) as well as state and local governments hire organic chemists in the fields of specialization noted above.
What are the major industries in organic chemistry?
Major organic industrial chemistry sectors include: Rubber and plastic products. Textiles and apparel. Petroleum refining.
What is functional group?
Functional groups measure the chemical reactivity of the given molecule. Functional groups can be a single atom or a group of atoms, like Br or CHO. Functional groups characterize the prior families of organic compounds.
What are alkyl halides?
Alkyl halides and aryl halides are halogen substituted alkyl or aryl groups. An alkyl group can be an alkane, alkene or alkyne. Oxygen containing functional groups can be various types. These are alcohol, aldehyde, ketone, carboxylic acid, ester and ether.
What is organic chemistry?
Organic chemistry is the study of carbon and the study of the chemistry of life. Since not all carbon reactions are organic, another way to look at organic chemistry would be to consider it the study of molecules containing the carbon-hydrogen (C-H) bond and their reactions.
Why is organic chemistry important?
Organic chemistry is important because it is the study of life and all of the chemical reactions related to life. Several careers apply an understanding of organic chemistry, such as doctors, veterinarians, dentists, pharmacologists, chemical engineers, and chemists. Organic chemistry plays a part in the development of common household chemicals, ...
What projects would use organic chemists?
Projects that would use organic chemists would include the development of a better painkilling drug, formulating a shampoo that would result in silkier hair, making a stain resistant carpet, or finding a non-toxic insect repellent. Cite this Article. Format. mla apa chicago. Your Citation.
What degree do you need to become an organic chemist?
Typically this would be a doctorate or master's degree in organic chemistry, though a bachelor's degree in chemistry may be sufficient for some entry-level positions. Organic chemists usually conduct research and development in a laboratory setting.
Is benzene an organic molecule?
Benzene is an example of an organic molecule. Dr. Helmenstine holds a Ph.D. in biomedical sciences and is a science writer, educator, and consultant. She has taught science courses at the high school, college, and graduate levels.
What are organic compounds?
Organic compounds are a type chemical compounds where one or more than one carbon covalently bonded with each other and with other atom like nitrogen, oxygen, halogen etc. Such as, methane (CH 4 ), ethane (C 2 H 6 ), benzene (C 6 H 6) etc. Image source: wikimedia commons by An elite.
What are the properties of organic compounds?
Properties. Organic compounds have unique chemical and physical properties what can differ them from inorganic compounds. Such as, Low boiling point . Low melting point. Low solubility in water. High solubility in organic solvent. Non conductor of electricity. Isomerism possible.
What type of bond does carbon have?
Carbon can share more than one electrons with same element to form double or triple bond . Such as: Image source: wikimedia commons by Jake V.
Can organic compounds be made synthetically?
Organic compounds can also be made synthetically in different industries. These compounds some time exist naturally and some time they can only make synthetically. These molecules can be small or large polymer like plastics, rubber etc.
What is organic chemistry?
THE CHEMICAL DEFINITION OF ORGANIC. In chemistry, the definition is based solely on chemical structure. With very few exceptions a chemical is classified as organic if it contains at least one carbon atom, regardless of its source. This is why organic chemistry is called “the chemistry of carbon.”. Generally that carbon atom is bonded to ...
What is organic food?
The agricultural use of the term ‘organic’ is entirely different from the chemical use and is focused on product labeling. For a food or feed product to be labeled ‘organic’ there are agronomic and animal husbandry practices that have to be followed. According to the United States Department of Agriculture (USDA): “Organic meat, poultry, eggs, and dairy products come from animals that are given no antibiotics or growth hormones. Organic food is produced without using most conventional pesticides; fertilizers made with synthetic ingredients or sewage sludge; bioengineering; or ionizing radiation.” Food produced in this way can be labeled with the USDA symbol and sold as ‘organic.’
Is organic food safe?
It’s important to note that labeling a food ‘organic’ does not mean that the product is nutritious, healthy, or safe; the labeling standards are based solely on agricultural field or farm practices.
What are some examples of compounds containing halogens?
Compounds containing halogens. Example 1: Write the structural formula for 1,1,1-trichloroethane. This is a two carbon chain (eth) with no double bonds (an). There are three chlorine atoms all on the first carbon atom. Example 2: Write the structural formula for 2-bromo-2-methylpropane.
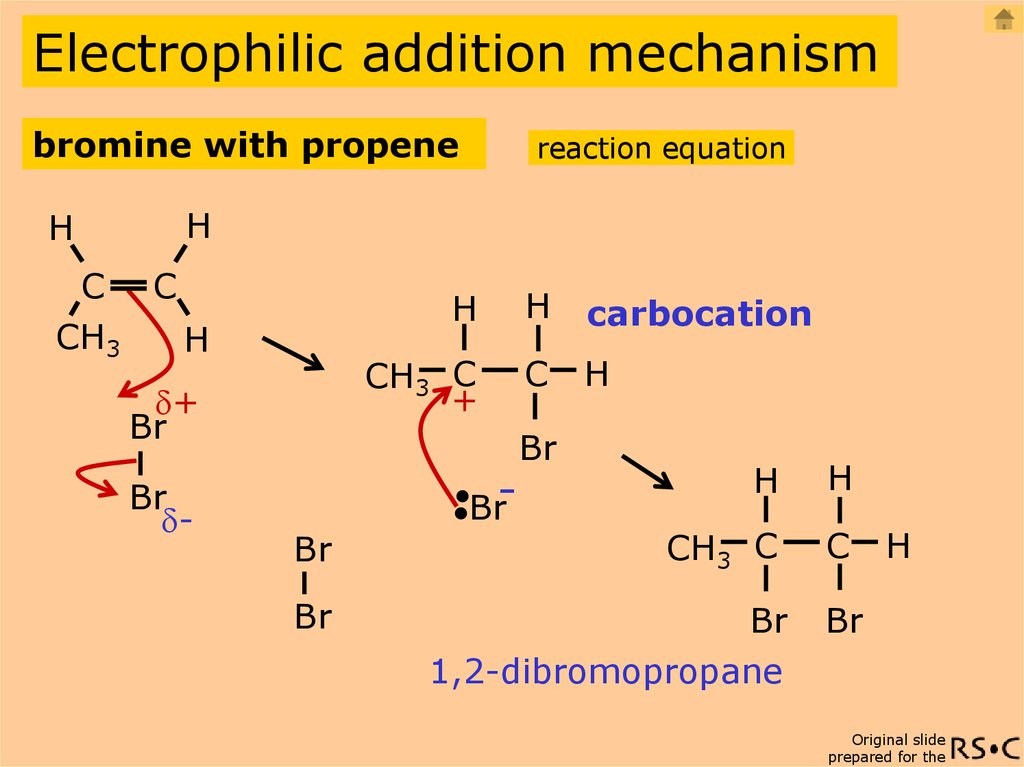
Which compound contains a carbon-carbon double bond?
Propenemeans three carbons in a chain with a double bond between two of the carbons. Alkyl groups. Compounds like methane, CH4, and ethane, CH3CH3 , are members of a family of compounds called alkanes.
How many carbons are in the longest chain?
Start with the carbon backbone. There are 4 carbons in the longest chain (but) with no carbon-carbon double bonds (an). This time there are two methyl groups (di) on the number 2 and number 3 carbon atoms. Completing the formula by filling in the hydrogen atoms gives:
Where is the carbon-oxygen double bond?
The carbon-oxygen double bond has to be in the middle of the chain and so must be on the number 2 carbon. Ketones are often written in this way to emphasise the carbon-oxygen double bond. Example 2: Write the structural formula for pentan-3-one.
Why is no number necessary in the propene example above?
No number was necessary in the propene example above because the double bond has to start on one of the end carbon atoms. In the case of butene, though, the double bond could either be at the end of the chain or in the middle - and so the name has to code for the its position. The carbon skeleton is:
What determines the structure, properties, and chemical reactions of organic and biochemicals?
The structures, properties, and chemical reactions of organic and biochemicals are determined by the functional groups present. Functional groups are defined as specific groupings of atoms or bonds which are part of a larger hydrocarbon chain.
What is the name of the part with the single bond oxygen?
The part with the single bond oxygen is named first with the root plus "-yl" ending . Example: methyl. The part with the carbon double bond oxygen is named second with the root plus "-oate" ending.
What Are Organic compounds?
Table of Contents
Organic Compounds Classification
- Moving on to their classification in detail: Organic compounds are seen in a number of formats, including Lewis structures, space filled models and structural formulas. It is not uncommon to view the hydrogens as lines or to leave them all together in a structural formula of an organic molecule. They are understood to be present in order to complete the 4-bonds provided by the c…
Organic Compounds
- Organic chemistry was once thought to be confined to the study of substances produced as part of the natural processes of living organisms, but as Friedrich Wohler discovered in the early 1800s, organic compounds can be synthesized from minerals and other non-organic materials in the laboratory. Indeed, modern chemistry and materials sciences have ...
Acyclic Or Open Chain Compounds
- These compounds are also known as aliphatic compounds, they have branched or straight chains. Following are the examples in this category.
Alicyclic Or Closed Chain Or Ring Compounds
- These are cyclic compounds which contain carbon atoms connected to each other in a ring (homocyclic). When atoms other than carbon are also present then it is called heterocyclic. Examples of this type are as follows: They exhibit some properties similar to aliphatic compounds.
Aromatic Compounds
- They are a special type of compound which contains benzeneand other ring related compounds. Similar to alicyclic, they can also have heteroatoms in the ring. Such compounds are called heterocyclic aromatic compounds. Some examples are as follows:
Heterocyclic Aromatic Compounds
- Organic compounds can also be classified on the basis of functional groupsinto families or homologous series.
Overview
Organic chemistry is a branch of chemistry that studies the structure, properties and reactions of organic compounds, which contain carbon-carbon covalent bonds. Study of structure determines their structural formula. Study of properties includes physical and chemical properties, and evaluation of chemical reactivity to understand their behavior. The study of organic reactions includes t…
Classification of organic compounds
The concept of functional groups is central in organic chemistry, both as a means to classify structures and for predicting properties. A functional group is a molecular module, and the reactivity of that functional group is assumed, within limits, to be the same in a variety of molecules. Functional groups can have a decisive influence on the chemical and physical properties of organic c…
History
Before the 18th century, chemists generally believed that compounds obtained from living organisms were endowed with a vital force that distinguished them from inorganic compounds. According to the concept of vitalism (vital force theory), organic matter was endowed with a "vital force". During the first half of the nineteenth century, some of the first systematic studies of organic compo…
Characterization
Since organic compounds often exist as mixtures, a variety of techniques have also been developed to assess purity; chromatography techniques are especially important for this application, and include HPLC and gas chromatography. Traditional methods of separation include distillation, crystallization, evaporation, magnetic separation and solvent extraction.
Organic compounds were traditionally characterized by a variety of chemical tests, called "wet m…
Properties
The physical properties of organic compounds typically of interest include both quantitative and qualitative features. Quantitative information includes a melting point, boiling point, and index of refraction. Qualitative properties include odor, consistency, solubility, and color.
Organic compounds typically melt and many boil. In contrast, while inorganic materials generally can be melted, many do not boil, and instead tend to degrade. In earlier times, the melting point (…
Nomenclature
The names of organic compounds are either systematic, following logically from a set of rules, or nonsystematic, following various traditions. Systematic nomenclature is stipulated by specifications from IUPAC. Systematic nomenclature starts with the name for a parent structure within the molecule of interest. This parent name is then modified by prefixes, suffixes, and numbers …
Organic reactions
Organic reactions are chemical reactions involving organic compounds. Many of these reactions are associated with functional groups. The general theory of these reactions involves careful analysis of such properties as the electron affinity of key atoms, bond strengths and steric hindrance. These factors can determine the relative stability of short-lived reactive intermediates, which usually directly determine the path of the reaction.
Organic synthesis
Synthetic organic chemistry is an applied science as it borders engineering, the "design, analysis, and/or construction of works for practical purposes". Organic synthesis of a novel compound is a problem-solving task, where a synthesis is designed for a target molecule by selecting optimal reactions from optimal starting materials. Complex compounds can have tens of reaction steps that s…