What is voluntary export restraint (VER)?
A voluntary export restraint (VER) is a self-imposed limit on the quantity of a good that an exporting country is allowed to export. VERs are considered non-tariff barriers, which are restrictive trade barriers—such as quotas and embargoes.
What is a world trade restraint?
World trade. A voluntary export restraint (VER) or voluntary export restriction is a government-imposed limit on the quantity of some category of goods that can be exported to a specified country during a specified period of time.
What are voluntary export barriers?
Voluntary export restraints (VERs) fall under the broad category of non-tariff barriers, which are restrictive trade barriers, like quotas, embargoes, sanctions levies, and other restrictions.
What is Voluntary Import Expansion (VIE)?
Related to voluntary export restraint (VER) is a voluntary import expansion (VIE), which is a change in a country's economic and trade policy to allow for more imports by lowering tariffs or dropping quotas. Often VIEs are part of trade agreements with another country or the result of international pressure.
What is a voluntary export restraint quizlet?
a voluntary export restraint occurs when an exporting country or companies in an exporting country agree to limit how many of a product that they will export to another country.
What is a voluntary export restraint in business?
Definition: Voluntary export restraints (VER) are arrangements between exporting and importing countries in which the exporting country agrees to limit the quantity of specific exports below a certain level in order to avoid imposition of mandatory restrictions by the importing country.
What is voluntary restraint?
Bilateral arrangement whereby an exporting country (government or industry) agrees to reduce or restrict exports without the importing country having to make use of quotas, tariffs or other import controls.
What are the effects of voluntary export restraints?
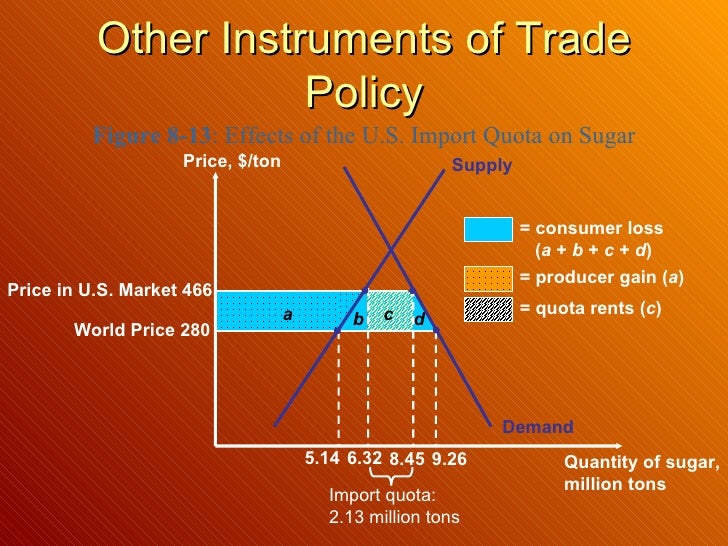
A VER raises consumer surplus in the export market and lowers it in the import country market. A VER lowers producer surplus in the export market and raises it in the import country market. National welfare may rise or fall when a large exporting country implements a VER.
Why would a country impose a voluntary export restraint on products?
Why would a country impose a voluntary export restraint on products? To reduce the chances that the importing country will set up trade barriers.
How do voluntary export restraints affect the prices of goods?
VERs always raise the domestic price of an imported good. VERs always raise the domestic price of an imported good. When imports are limited to a low percentage of the market by a quota or VER, the price is bid up for that limited foreign supply.
What is the main difference between a quota and a voluntary export restraint?
Chapter 15 Outlinea. One difference is the fact that a tariff generates revenue for the federal government; a quota does not.b. Another difference is the fact that a quota may result in a higher price than a tariff because imports cannot respond to an increase in demand.C. Voluntary Export Restraints10 more rows
How are voluntary export restraints and import quotas different?
An import quota is a limit on the amount of a good that can be imported. A voluntary export restraint (VER) is a self-imposed limitation on the quantity of products a country ships to another country.
When the United States imposed a VER voluntary export restraint on cars from Japan?
On March 1 1985, President Reagan announced that the United States was no longer requesting Japanese VERs on automobiles.
Why do nations sometimes agree to voluntary export restrictions?
One of the reasons given for the imposition of a protectionist policy such as a tariff is to: protect domestic workers from foreign competition. Exporting nations often agree to voluntary export restraints in an attempt to: avoid more-restrictive trade policies.
How do the effects of voluntary restraint agreements differ from the effects of a tariff?
(d) Voluntary restraint agreements result in higher prices, which increase revenue for foreign firms, while the revenue raised from tariffs goes to the domestic government.
What is an example of a protective tariff?
For example, if similar cloth for sale in America cost $4 in for a version imported from Britain (including additional shipping, etc.) and $4 for a version originating in the United States, the American government may wish to impose a protective tariff to make the price of British cloth higher for Americans.
What is voluntary export restraint?
A voluntary export restraint (VER) is a self-imposed trade restriction where the government of a country limits the amount of a certain good or category of goods that are allowed to be exported to a different country. The restraint could be a preset limit, a reduction in the exported amount, or a complete restriction. ...
When were export restraints used?
Voluntary export restraints have been historically used on a wide variety of traded products and have been used since the 1930s. The popularity of this particular trade restraint increased in the 1980s since it abided by the terms agreed to under the GATT (General Agreement on Trades and Tariffs).
Why do exporting countries use a VER?
The exporting country establishes a VER to avoid facing trade restrictions from the importing country. Through the use of a voluntary export restraint, the exporting country is able to exercise some degree of control over the restriction, which would otherwise be lost if it faced trade restrictions from the importing country.
What is voluntary export?
Typically, a country imposes a voluntary export. Exports Exports are goods and services made by a country and sold to another. They are crucial to many economies, as they provide goods and services. restraint at the request of an importing country that seeks protection for its domestic producers. The exporting country establishes a VER ...
What is a tariff in international trade?
Tariff A tariff is a form of tax imposed on imported goods or services. Tariffs are a common element in international trading. The primary goals of imposing. .
What is voluntary import expansion?
A voluntary import expansion occurs when a country agrees to increase the number of imports into its country. It is implemented by reducing restrictions such as import tariffs. A voluntary import expansion, much like a VER, is enacted voluntarily at the request of another country and negatively affects the trade balance#N#Balance of Trade (BOT) The balance of trade (BOT), also known as the trade balance, refers to the difference between the monetary value of a country’s imports and#N#of the country that volunteers to set up the arrangement.
What is the balance of trade?
Balance of Trade (BOT) The balance of trade (BOT), also known as the trade balance, refers to the difference between the monetary value of a country’s imports and. of the country that volunteers to set up the arrangement.
What is a voluntary export restriction?
A voluntary export restraint ( VER) or voluntary export restriction is a government-imposed limit on the quantity of some category of goods that can be exported to a specified country during a specified period of time. They are sometimes referred to as 'Export Visas'.
Why are export restrictions voluntary?
Voluntary export restrictions are usually due to pressure from importing countries. Therefore, one can consider export restrictions to be "voluntary" simply because exporting countries may find such restrictions more desirable than alternative trade barriers that importing countries may establish.
What is manifestation in export?
Manifestation. 1. Unilateral automatic export restrictions. Unilateral automatic export restriction means that the exporting country unilaterally sets export quotas on its own to restrict the export of commodities. Some of these quotas are stipulated and announced by the government of the exporting country.
How many cars did Japan export to the US?
When the automobile industry in the United States was threatened by the popularity of cheaper, more fuel efficient Japanese cars, a 1981 voluntary restraint agreement limited the Japanese to exporting 1.68 million cars to the U.S. annually as stipulated by U.S Government. This quota was originally intended to expire after three years, in April 1984. However, with a growing deficit in trade with Japan, and under pressure from domestic manufacturers, the US government extended the quotas for an additional year. The cap was raised to 1.85 million cars for this additional year, then to 2.3 million for 1985. The voluntary restraint was removed in 1994.
What is the General Agreement on Tariffs and Trade Regulations?
The - General Agreement on Tariffs and Trade regulations on government's influence on trade prohibit export restrictions under normal circumstances ; if export restrictions are approved, these restrictions must be non-discriminatory and can only be implemented through tariffs, taxes and fees.
When were VERs used?
VERs are typically implemented on exports from one specific country to another. VERs have been used since the 1930s at least, and have been applied to products ranging from textiles and footwear to steel, machine tools and automobiles.
Do exporters have to apply for quotas?
Exporters must apply for quotas from relevant agencies and obtain an export license before exporting. Some are stipulated by exporters or trade associations of the exporting country according to the government's policy intentions. 2. Agreement automatic export restrictions.
Motivations Behind Voluntary Export Restraints
History of Vers
- Voluntary export restraints have been historically used on a wide variety of traded products and have been used since the 1930s. The popularity of this particular trade restraint increased in the 1980s since it abided by the terms agreed to under the GATT (General Agreement on Trades and Tariffs). However, members of the WTO in 1994 agreed not to impose any new voluntary export …
Effectiveness of Vers
- Studies conducted on the effectiveness of VERs suggest that they are not effective over a longer term. An example is the voluntary export restraint imposed by Japan on the export of Japanese manufactured cars into the U.S. The US government wanted to protect its automobile manufacturers since the domestic industry was threatened by the cheaper and ...
Vers on Textiles
- US-based producers of textiles faced increasing competition from Southeast Asian countries in the 1950s and the 1960s. The US government requested VERs to be established by many of the Southeast Asian countries and was successful in doing so. Textile producers in Europe faced similarly stiff competition as their US counterparts, and as a result, negotiated voluntary export r…
Voluntary Export Restraints vs. Voluntary Import Expansion
- A voluntary import expansion occurs when a country agrees to increase the number of imports into its country. It is implemented by reducing restrictions such as import tariffs. A voluntary import expansion, much like a VER, is enacted voluntarily at the request of another country and negatively affects the trade balanceof the country that volunteers to set up the arrangement.
More Resources
- CFI is the official provider of the global Commercial Banking & Credit Analyst (CBCA)™certification program, designed to help anyone become a world-class financial analyst. To keep advancing your career, the additional resources below will be useful: 1. International Trade 2. Export Trading Company (ETC) 3. Trade Barriers 4. World Trade Organization (WTO)
Summary
A voluntary export restraint (VER) or voluntary export restriction is a measure by which the government or an industry in the importing country arranges with the government or the competing industry in the exporting country for a restriction on the volume of the latter's exports of one or more products.
By this definition, the term VER is a generic reference for all bilaterally agreed …
Overview
Voluntary export restrictions are usually due to pressure from importing countries. Therefore, one can consider export restrictions to be "voluntary" simply because exporting countries may find such restrictions more desirable than alternative trade barriers that importing countries may establish. In addition, in non-competitive, especially oligopolistic industries, export companies may find that negotiating voluntary export restrictions is beneficial to them, and then export restrictio…
Characteristics
VERs are typically implemented on exports from one specific country to another. VERs have been used since the 1930s at least, and have been applied to products ranging from textiles and footwear to steel, machine tools and automobiles. They became a popular form of protection during the 1980s ; they did not violate countries' agreements under the General Agreement on Tariffs and Trade (GATT) in force. As a result of the Uruguay round of the GATT, completed in 1994, World Tr…
Manifestation
1. Unilateral automatic export restrictions
Unilateral automatic export restriction means that the exporting country unilaterally sets export quotas on its own to restrict the export of commodities. Some of these quotas are stipulated and announced by the government of the exporting country. Exporters must apply for quotas from relevant agencies and obtain an export license before exporting. Some are stipulated by exporte…
Reasons for introduction
In general, restrictive trade measures are usually taken for two purposes: to protect or improve the balance of payments situation, and to provide relief for industries adversely affected by foreign competition, thus allowing them to undertake the adjustments necessary to regain competitiveness.
VERs were usually implemented for the second reason and compared to the other protectionist …
Limitations
There are ways in which a company can avoid a VER. For example, the exporting country's company can build a manufacturing plant in the country to which its exports would be directed, so that it no longer needs to export its goods to this country, and therefore would not be bound by the country's VER. This suggests that VERs were usually not effective in the long run.
This strategy was used by the Japanese car manufacturers in the attempt to avoid a US imposed …
Advantages and disadvantages
With functioning VERs, producers in the importing country experience an increase in well-being as there is decreased competition, which should result in higher prices, profits, and employment. VERs are also noted for having a less-damaging effect on the political relations between countries and they are also relatively easy to remove.
Such benefits to producers and the labor market, however, come with some notable trade-offs. …
1950s-1960s VERs on textiles in America and Europe
In the 1950s and the 1960s American manufacturers of textiles faced increasing competition from Southeast Asian countries. Therefore, the US government requested VERs be established by many of these Asian countries and was successful in doing so. Textile producers in Europe faced in the 1950s and the 1960s similar problems to their US counterparts, and as a result negotiated voluntary export restraints as well. Eventually, an agreement was reached between the exportin…