Halogen Properties
- They are highly reactive nonmetals.
- Atoms of belonging to the halogen group have 7 electrons in their outermost (valence) shell. ...
- The usual oxidation state of a halogen atom is -1.
- Halogens are highly electronegative, with high electron affinities.
What is meant by halogen atom?
The halogens are non-metallic elements found in group 17 of the periodic table. The word Halogens is derived from the Greek word 'hals' meaning "salt" or "sea", and 'gen' from the Greek word 'gígnomai meaning "come to be" for an element that produces a salt when it forms a compound with a metal.
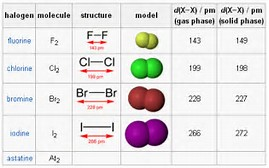
Which halogen has the smallest atomic radii?
Note trends for ionic radii:
- ionic radius of a cation is less than atomic radius of the atom
- ionic radius of an anion is greater than atomic radius of the atom
- ionic radii of group 1 cations increases down the group
- ionic radii of group 17 anions increases down the group
What are two characteristics of the halogens?
Halogens
- They all form acids when combined with hydrogen.
- They are all fairly toxic.
- They readily combine with metals to form salts.
- They have seven valence electrons in their outer shell.
- They are highly reactive and electronegative.
- They all exist as diatomic molecules (two atoms) when in their pure form.
What do the elements in halogens have in common?
What do the halogens all have in common? As you can see in the periodic table below, the halogens include the elements fluorine (F), chlorine (Cl), bromine (Br), iodine (I), and astatine (At). All of them are relatively common on Earth except for astatine .Therefore, halogens have seven valence electrons.
What are halogen elements?
The halogen elements are the six elements in Group 17 of the periodic table. Group 17 occupies the second column from the right in the periodic tab...
What are the major properties of the halogen elements?
Halogen elements are very reactive. With sodium, they produce salts, of which table salt (sodium chloride, NaCl) is the most well known. Each halog...
What are some uses of halogen elements?
Chlorine is used to purify water. In addition, chlorine is part of table salt, sodium chloride, which is one of the most widely used chemical compo...
Why are these elements called halogens?
When these elements react with sodium, they produce salts. The most well known of these is sodium chloride, or common table salt (also called halit...
What is halogen in the periodic table?
Halogen, any of the six nonmetallic elements that constitute Group 17 (Group VIIa) of the periodic table. The halogen elements are fluorine (F), chlorine (Cl), bromine (Br), iodine (I), astatine (At), and tennessine (Ts). They were given the name halogen, from the Greek roots hal - (“salt”) and - gen (“to produce”), ...
How many valence electrons does a halogen have?
They produce salts with sodium, of which table salt (sodium chloride, NaCl) is the most well-known. The halogen elements have seven valence electrons in their outermost electron shell. Therefore, when these elements can receive an electron from another atom, they form very stable compounds since their outermost shell is full.
What are the elements in Group 17?
Group 17 is the second column from the right in the periodic table and contains six elements: fluorine (F), chlorine (Cl), bromine (Br), iodine (I), astatine (As), and tennessine (Ts). Astatine and tennessine are radioactive elements with very short half-lives ...
What is the difference between chlorine and fluorine?
Chlorine is used to purify water. Chlorine also is part of salt, sodium chloride, which is one of the most widely used chemical compounds. Fluorine is used in fluorides, which are added to water supplies to prevent tooth decay. Iodine is used as an antiseptic.
Which element is the most reactive?
Fluorine is the most reactive of the halogens and, in fact, of all elements, and it has certain other properties that set it apart from the other halogens. Chlorine is the best known of the halogen elements. The free element is widely used as a water-purification agent, and it is employed in a number of chemical processes.
What is the oxidation number of a halogen?
In oxidizing another element, a halogen is itself reduced; i.e., the oxidation number 0 of the free element is reduced to −1. The halogens can combine with other elements to form compounds known as halides —namely, fluorides, chlorides, bromides, iodides, and astatides.
Which element is more stable, fluoride or bromide?
Fluorides are usually more stable than the corresponding chlorides, bromides, or iodides. (Often astatine is omitted from general discussions of the halogens because less is known about it than about the other elements.) ionic bond: sodium chloride, or table salt. Ionic bonding in sodium chloride.
What is the halogen family?
The halogen family comprises a collection of non metallic elements. This series of elements fall under Group 17 of the periodic table of chemical elements. The members that are a part of the halogen family include chlorine, fluorine, iodine, bromine, and astatine.
Why do halogens form compounds?
This is because halogen elements tend to create salt when they come in contact with the metals and combine with them to form compounds. As mentioned previously, halogens are the only elemental group in the entire periodic table, which is composed of elements that belong to all three classical states of matter (solid, liquid, and gas).
What are halogen lamps used for?
Uses of halogens include utilizing them as key components for manufacturing disinfectants, refrigerants, insecticides, food colorings, dyes, petroleum products, flame proofing agents, etc. Halogen lamps are manufactured by filling inert gas, containing a small amount of either iodine or bromine, inside a bulb that has a tungsten filament.
Why do halogens react with other matter?
Halogens get their high tendency to react with other matter due to high levels of electronegativity of their atoms, which is a result of the high effective nuclear charge of all halogen atoms.
Is bromine a solid or a gas?
This is proved by the fact that when kept under room temperature and normal pressure, astatine and iodine take the form of solids, bromine appears as a liquid, and chlorine and fluorine occur as gases. All halogen elements form hydrogen halides, which are very strong acids, when they combine with hydrogen, and form binary compounds.
Can halogens be pure?
Due to this tendency towards high reactivity, the halogens cannot exist in the environment as pure elements. They are usually found occurring as compounds or as ions. Most halogen ions and atoms can be found in combination with other compounds present in the sea or mineral water.
Is halogen a colorless substance?
No halogen is completely colorless. Typical to non-metals, halogens have very low melting and boiling points. In their solid forms, all halogens have a brittle texture. Halogens are poor conductors of heat and electricity, irrespective of their physical state.
Physical properties of halogens
Regarding color, halogens can range from pale yellow to purple or black.
Chemical properties of halogens
Halogens are highly reactive , so they are never found in their monatomic form, but rather as part of other compounds . At most they can be found by forming diatomic molecules of the same element. For example: F 2 , Cl 2 , Br 2, and I 2 .
Halogen abundance
Of all halogens, fluorine and chlorine are the most abundant in nature (corresponding to 0.065% and 0.055% respectively). Due to their great reactivity, they are always part of other compounds.
Tenese (element 117)
Tenese or ununseptium, represented by the symbol Ts or Uus (provisional name) , is a heavy synthetic element with atomic number 117. It was discovered in 2010 at the Central Institute for Nuclear Research in Dubná, Russia.
Examples of everyday substances with halogens
CFC is a halogen-containing substance that used to be used in aerosols.
How many electrons are in a halogen atom?
They are highly reactive nonmetals. Atoms of belonging to the halogen group have 7 electrons in their outermost (valence) shell.
Why do halogens need more electrons?
These atoms need one more electron in order to have a stable octet. Halogens are highly electronegative, with high electron affinities. The melting and boiling points of the halogens increase as you increase atomic number (as you move down the periodic table).
Where are halogens found in the periodic table?
The halogen elements are located in group VIIA of the periodic table, which is the second-to-last column of the chart. This is a list of elements that belong to the halogen group and the properties that they share in common:
Is chlorine a halogen?
Fluorine, chlorine, bromine, iodine, and astatine definitely are halogens. Element 117, which has the placeholder name of ununseptium, might have some properties in common with the other elements. Even though it is in the same column or group of the periodic table with the other halogens, most scientists believe element 117 will behave more like ...
What are the elements in the halogen group?
There are either five or six halogen elements, depending on how strictly you define the group. The halogen elements are: 1 Fluorine (F) 2 Chlorine (Cl) 3 Bromine (Br) 4 Iodine (I) 5 Astatine (At) 6 Element 117 (ununseptium, Uus), to a certain extent
What is the halogen group?
Updated November 07, 2019. The halogens are a group of elements on the periodic table. It is the only element group that includes elements capable of existing in three of the four main states of matter at room temperature: solid, liquid, and gas. The word halogen means "salt-producing," because halogens react with metals to produce many important ...
What are halogens used for?
Fluorine, in the form of fluoride, is used to help prevent tooth decay. The halogens are also used in lamps and refrigerants. Helmenstine, Anne Marie, Ph.D. "Halogen Elements and Properties.".
Where are halogens located on the periodic table?
Location of the Halogens on the Periodic Table. The halogens are located in Group VIIA of the periodic table , or group 17 using IUPAC nomenclature. The element group is a particular class of nonmetals. They can be found toward the right-hand side of the table, in a vertical line.
Which element has the highest electronegativity?
The chemical properties are more uniform. The halogens have very high electronegativities. Fluorine has the highest electronegativity of all elements.
Is bromine a solid or a gas?
Fluorine and chlorine are gases, while bromine is a liquid and iodine and astatine are solids. It is expected that element 117 will also be a solid under ordinary conditions. The boiling point increases moving down the group because the Van der Waals force is greater with increases size and atomic mass.
Do halogens have free elements?
In fact, halogens are so reactive that they do not occur as free elements in nature. Many, however, are common in combination with other elements Here is a look at the identity of these elements, their location on the periodic table, and their common properties.
Properties of halogens
The halogens are all non-metals. They show many of the properties typical of non-metals.
The elements in the halogens
At the start of this article, we said that the halogen group contains six elements. But it depends on who you ask. The first four members are known as the stable halogens. These are fluorine, chlorine, bromine, and iodine. The fifth member is astatine, an extremely radioactive element.
Reactions of group 7
The halogens take part in multiple different types of reaction, especially fluorine, which is one of the most reactive elements in the periodic table. Remember that reactivity falls as you go down the group.
Uses of halogens
The halogens have myriad different uses in everyday life. We’ve already looked at some above, but further examples include:
Halogens - Key takeaways
The halogens are a group in the periodic table systematically known as group 17. It consists of fluorine, chlorine, bromine, iodine, astatine, and tennessine.
Halogens
Halogens are a group of elements found in group 17 in the periodic table. This group is sometimes known as group 7. They are nonmetals that tend to form anions with a charge of -1. They show many of the properties typical of nonmetals - they have low melting and boiling points, are poor conductors, and are dull and brittle.