What is defect rate?
More ... A defect rate is the percentage of output that fails to meet a quality target. Defect rates can be used to evaluate and control programs, projects, production, services and processes. A defect rate is calculated by testing output for non-compliances to a quality target.
What is the acceptable percentage of defects in a product?
0% for critical defects (totally unacceptable: a user might get harmed, or regulations are not respected). 2.5% for major defects (these products would usually not be considered acceptable by the end user). 4.0% for minor defects (there is some departure from specifications, but most users would not mind it).
How many defects should you have?
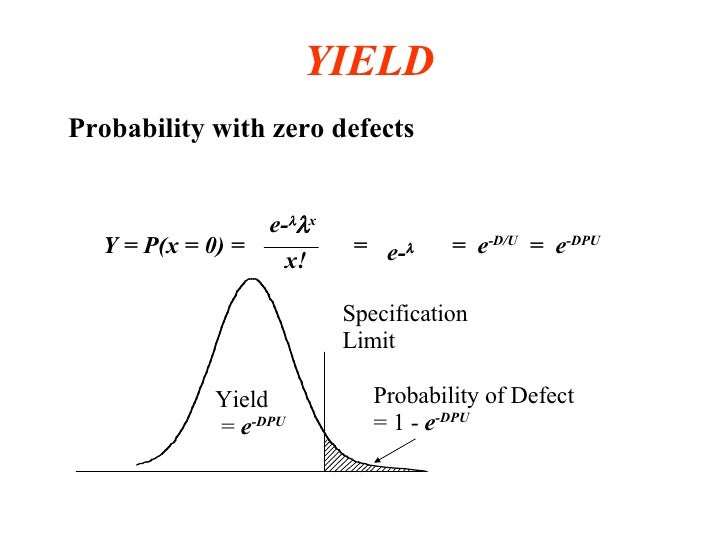
If your yield is 90 percent, you naturally must have 10 percent defects. When a process or characteristic doesn’t perform within its specifications, it is considered defective; in other words, it produces a noncompliant condition called a defect. Automatically defining a defect as a noncompliance with specifications may seem overly simplified.
How do you calculate defect rate from test output?
A defect rate is calculated by testing output for non-compliances to a quality target. Quality is typically specified by functional and non-functional requirements. The following formula can be used to calculate defect rate.defect rate = (defects / output tested) x 100 Defects is the number of items that failed quality tests.
What is a good defect rate?
“In fact, modern quality goals require new standards of measure. Six Sigma quality, which translates into a defect rate of 3.4 parts per million and was originally established by Motorola Inc. as an internal stretch goal, is the de facto standard at many of the best plants.”
What is the defect rate?
The term defect rate designates the portion of defective elements in relation to all items produced. The rate is deduced by dividing the number of defective elements by the number of non-defective elements. This number is a measure of quality of the production.
What is minimum acceptable quality?
The Acceptable Quality Level (AQL) is a quality control concept. It is the minimum level of faults acceptable in a sample of a manufactured product for the entire batch of the product to be accepted. If the number of faults is higher than the AQL, then the entire batch is rejected.
What is a good PPM rate?
According to Rapidtables, PPM means one (defect or event) in a million or 1/1,000,000. There was a time when suppliers with a defect rate less than 10,000 PPM or 1% were considered as quality suppliers. However, nowadays, the expectation is that the supplier defect rate should be less than 25 PPM or 0.0025 %.
Why Six Sigma means 3.4 defects?
The term implies high-quality performance because a process performing at a Six Sigma level allows only 3.4 defects per one million opportunities. The higher the sigma level the better the quality of the product or service and the fewer the defects.
How do you measure defects?
To measure defect density, you need to have the data on the number of defective units of a single product, as well as the total number of units produced. To find the density, divide the number of defective units by the total number of units produced.
How do you calculate acceptable quality level?
To calculate sample size using AQL, you need to know:Lot or Batch Size of incoming or outgoing product.Acceptable Quality Level (AQL) Input value of 1 means 1% or 1 defect per 100 units.Inspection Level (I, II, III - usually level II)
What does an AQL of 0.65 mean?
AQL means the poorest level of quality that is considered acceptable in a particular population or in a pre-defined sample size. For example: “AQL is 0.65%” means “I want no more than 0.65% defective items in the whole order quantity, on average over several production runs with that supplier”.
What does an AQL of 0.4 mean?
For most general consumer products, the standard AQL levels are 2.5% for major defects, 4.0% for minor defects, and 0% for critical defects. That's why we've underlined '2.5' and '4.0' above. Going by this standard, we can see that your inspector will accept a maximum of: 7 major defects, and. 10 minor defects.
What is an acceptable defect rate in manufacturing?
The AQL for major defects is 2.5%. Minor defects: Defects not likely to reduce materially the usability of the product for its intended purpose but that differ from specified standards; some end users will still buy such products. The AQL for minor defects is 4%. 1
What is supplier defect rate?
Supplier defect rate is the percentage of materials from suppliers that don't meet quality specifications. The quality of materials from suppliers can have a huge impact on quality costs.
What is ppm defective?
PPM defectives is one of the simplest metrics in Six Sigma to understand. It refers to the expected number of parts out of one million that you can expect to be defective. It is a measurement used today by many customers to measure the quality performance of their suppliers.
Calculation
A defect rate is calculated by testing output for non-compliances to a quality target. Quality is typically specified by functional and non-functional requirements. The following formula can be used to calculate defect rate.defect rate = (defects / output tested) x 100 Defects is the number of items that failed quality tests.
Production
A bicycle production line tests every unit for defects. In a week, 4000 bicycles are produced and 3 fail quality tests.defect rate = (3 / 4000) × 100 = 0.075%Product lines may calculate multiple defect rates based on different levels of testing.
Code
Software testing tests 500,000 lines of code and discovers 33 defects.defect rate = (33/500000) × 100 = 0.0066%Code defects are also commonly measured as defects per thousand lines of code.
Use Cases
Software testing tests 33 use cases and discovers 4 defects.defect rate = (4/33) × 100 = 12.12% It is common to calculate defect rate according to the number of user stories, use cases, requirements or function points that are tested.
Services
Services may be tested for quality control with sampling of service interactions. For example, a call center evaluates 400 calls in a week for customer service quality and finds that 4 calls fail to meet quality standards.defect rate = (4/400) × 100 = 1%Automated services can also be tested for quality control purposes.
What is acceptable quality level?
The Acceptable Quality Level is a statistical tool to inspect a particular sample size for a given lot and set maximum number of acceptable defects. In order words, it is the worst tolerable process average when a continuing series of lots is submitted for acceptance sampling.
What is the AQL for major defects?
Major Defects: Defects usually not acceptable by the end users, as it is likely to result in failure. The AQL for major defect is 2.5%. Minor Defects: Defects, which are not likely to reduce materially the usability of the product for its intended purpose but slightly differs from specified standards. Some end users still go ahead and buy such ...
Thursday, March 5, 2015
What is an acceptable defect rate target? Has the mortgage industry set a maximum defect rate target that lenders need to adhere to?
Quality Control: Defect Rate
What is an acceptable defect rate target? Has the mortgage industry set a maximum defect rate target that lenders need to adhere to?
What are the classes of defects?
What the classes of defects should be. In most inspections, defective units can be classified as “critical”, “major”, or “minor”, and each company can define what is in what class. Some companies add extra classes: incidental, catastrophic, etc.
What are the limits on consumer goods?
For most consumer goods, the limits are: 0% for critical defects (totally unacceptable: a user might get harmed, or regulations are not respected). 2.5% for major defects (these products would usually not be considered acceptable by the end user).
What is the lot size of a batch?
(The quantity of each product is the lot size). If you ordered only one product, the lot size is the total batch quantity.
Does a supplier have to deliver defect free goods?
Therefore, in many supplier/buyer relationships (particularly when the application does not result in life or death outcomes), the supplier is not expected to deliver defect-free goods. The buyer needs to control the quality of purchased goods since he does not want too many defects.
Is visual inspection 100% reliable?
It is often true even after the manufacturer has checked each individual product and has repaired the defective ones since the visual inspection is not 100% reliable.