Difference Between Additive Identity and Multiplicative Identity
| Additive Identity | Multiplicative Identity |
| Additive identity for any real number is ... | Multiplicative identity for any real num ... |
| It is denoted by a + 0 = a, where a is a ... | It is denoted by a x 1 = a, where a is a ... |
| It is used in addition | It is used in the multiplication operati ... |
| Example: 7 + 0 = 7 | Example: 7 x 0 = 7 |
How do I prove the uniqueness of additive identity?
- For all , .
- For all , .
- For all , .
What number do you add when using the additive identity?
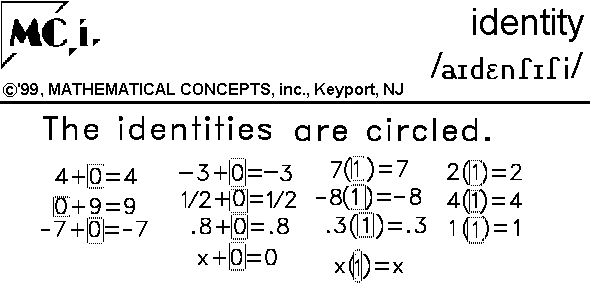
Additive identity is the value when added to a number, results in the original number. When we add 0 to any real number, we get the same real number. For example, 5 + 0 = 5. Therefore, 0 is the additive identity of any real number.
What is the formal definition of additive identity?
In review, the additive identity definition is the property that states any number plus 0 will be itself. It is also referred to as the identity property of addition and the identity property of zero. The additive identity works for all number types: real numbers, imaginary numbers, complex numbers, and sets.
What does additive identity mean?
Additive identity of numbers, as the name suggests, is a property of numbers that are applied when carrying out addition operations. The property states that when a number is added to zero it will give the same number.
What is additive identity give example?
Additive identity is a number, which when added to any number, gives the sum as the number itself. It means that additive identity is “0” as adding 0 to any number, gives the sum as the number itself. Example: 2 + 0 = 2.
What is called additive identity?
Definition of additive identity : an identity element (such as 0 in the group of whole numbers under the operation of addition) that in a given mathematical system leaves unchanged any element to which it is added.
What is an additive identity Class 7?
Additive Identity Property: If a is any integer, then a + 0 = a = 0 + a. The number 'zero' has a special role in addition. When we add zero to any integer the result is the same integer again.
What is the additive identity Class 8?
Additive identity is the number which when added to another number gives the same number. Only 0 is used as an additive identity because if we add o with any number the result we get as the same number.
What is the additive identity of 2?
Additive identity for any real number is 0.
What is the additive identity of 3?
The additive identity of whole numbers is zero. This means if zero is added to any whole number like 0, 3, or 12, the result is the number itself.
What is the additive identity of 8 Class 7?
1 is the additive identity of integers.
What is the additive identity element of 76?
The number zero is known as the identity element, or the additive identity.Aug 9, 2020
What is the additive inverse of 1 class 7?
Additive inverse is the element, by adding the inverse to that element we will get the additive identity. For example, for integers 0 is the additive identity. Now for any integer a, -1 is the additive inverse of a.
What is the additive inverse of 2 3?
-2/3In mathematics, the additive inverse of a number 'a' is the number that, when added to 'a', yields zero. Therefore, the additive inverse of 2/3 is -2/3.
What is additive identity and additive inverse?
The opposite of a number is its additive inverse. A number and its opposite add to 0 , which is the additive identity.Mar 11, 2020
What is additive and multiplicative?
Two numbers are called additive inverses if their sum is 0. Another one is two numbers are called multiplicative inverses if their products is 1, if their product is 1.
Additive Identity Property Formula
The formula of additive identity is written as a + 0 = a. This explains that when any number is added to zero, the sum is the number itself. For example, if we add 5 to 0 we get 5 as the sum. 5 + 0 = 5.
Additive Identity of Whole Numbers
The additive identity of whole numbers is zero. This means when a whole number is added to zero, it results in the number itself. So if "s" is a whole number that is added to zero then the result will be the whole number. For each and every whole number s, s + 0 = 0 + s = s. Zero is the additive identity element in the set of W.
Additive Identity and Multiplicative Identity
The following points show the difference between the additive identity and the multiplicative identity of numbers.
FAQs on Additive Identity Property
According to the additive identity property, when a number is added to zero, it results in the number itself. For example, if 7 is added to 0, the sum is the number itself. 7 + 0 = 7. Here, zero is known as the identity element which keeps the identity of the number.
What is Additive Identity?
Every number in math has an identity. The number one, for example, has the identity of being number one with just one meaning. One means there is exactly one of something, not two, not three, not zero. One means one. So what is additive identity in math?
Additive Identity
The additive identity is useful when doing math problems and the identity element presents itself.
Formal definition
Let N be a group that is closed under the operation of addition, denoted +. An additive identity for N, denoted e, is an element in N such that for any element n in N ,
The additive identity annihilates ring elements
In a system with a multiplication operation that distributes over addition, the additive identity is a multiplicative absorbing element, meaning that for any s in S, s · 0 = 0. This follows because:
The additive and multiplicative identities are different in a non-trivial ring
Let R be a ring and suppose that the additive identity 0 and the multiplicative identity 1 are equal, i.e. 0 = 1. Let r be any element of R. Then
What is the additive identity of numbers?
Additive identity of numbers, as the name suggests, is a property of numbers which is applied when carrying out addition operations. The property states that when a number is added to zero it will give the same number.
Is -1 a multiplicative identity?
Is -1 also a multiplicative identity? -1 is not a multiplicative identity, because if we multiply -1 to any real number, the sign of that number gets changed. Examples are: 4 x -1 = -4. -4 x -1 = 4.
Additive Identity
The additive identity of numbers is a property of numbers that is applied to addition operations. When a number is added to zero, it will result in the same number. This is called "additive identity." Zero is known as the identity element or additive identity. Zero is added to any number, such that the result is the same number.
Multiplicative Identity
The multiplicative identity of numbers is a property of numbers that is applied to multiplication operations. When a number is multiplied by 1, it will result in the same number. This is called "multiplicative identity." One is known as the identity element or multiplicative identity.
Difference Between Additive And Multiplicative Identity
Check out the differences between the additive and multiplicative identity in the table given below:
Things to remember
There are two types of identity for numbers: additive and multiplicative identity.
Sample Questions
Ques. Is additive identity applicable to negative integers? ( 2 Marks)