What are the four basic sampling methods?
Random Sampling Techniques
- Simple Random Sampling. Simple random sampling requires using randomly generated numbers to choose a sample. ...
- Stratified Random Sampling. Stratified random sampling starts off by dividing a population into groups with similar attributes. ...
- Cluster Random Sampling. ...
- Systematic Random Sampling
What are the principle steps in a sampling survey?
- Population OR Universe: The entire aggregation of items from which samples can be drawn is known as a population. ...
- Census: A complete study of all the elements present in the population is known as a census. ...
- Precision: Precision is a measure of how close an estimate is expected to be, to the true value of a parameter. ...
What is the difference between sampling plan and inspection?
“Use of a sampling plan with an acceptance criterion that is tighter than that for the corresponding plan for normal inspection.” Reduced inspection (or level-I inspection): fewer samples are inspected. This inspection level is appropriate when the client is confident that the quality of the products is acceptable.
What does a sampling plan provides?
- What should be the Sampling unit i.e. choosing the category of the population to be surveyed is the first and the foremost decision in a sampling plan that initiates the ...
- The second decision in sampling plan is determining the size of the sample i.e. ...
- The final decision that completes the sampling plan is selecting the sampling procedure i.e. ...
What is the purpose of sampling plan?
A sampling plan allows an auditor or a researcher to study a group (e.g. a batch of products, a segment of the population) by observing only a part of that group, and to reach conclusions with a pre-defined level of certainty.
How do you describe a sampling plan?
Definition: A sampling plan is a term widely used in research studies that provide an outline on the basis of which research is conducted. It tells which category is to be surveyed, what should be the sample size and how the respondents should be chosen out of the population.
What are the 4 types of sampling plans?
There are four main types of probability sample.Simple random sampling. In a simple random sample, every member of the population has an equal chance of being selected. ... Systematic sampling. ... Stratified sampling. ... Cluster sampling.
What are the main components of a sampling plan?
Elements of Sampling PlansSampling strategy.Sampling design.Size of the sample.Method for determining the size.Recruitment plan.
What are the different types of a sampling plan?
The types are: 1. Single Sampling Plan 2. Double Sampling Plan 3. Sequential Sampling Plan.
What are the things you should consider before you select a sampling plan?
Such considerations include understanding of:the reasons for and objectives of sampling.the relationship between accuracy and precision.the reliability of estimates with varying sample size.the determination of safe sample sizes for surveys.the variability of data.More items...
What are the 5 basic sampling methods?
Five Basic Sampling MethodsSimple Random.Convenience.Systematic.Cluster.Stratified.
What are the 5 types of samples?
There are five types of sampling: Random, Systematic, Convenience, Cluster, and Stratified.
What is the best sampling method?
Random samples are the best method of selecting your sample from the population of interest.The advantages are that your sample should represent the target population and eliminate sampling bias.The disadvantage is that it is very difficult to achieve (i.e. time, effort and money).
What is AQL in sampling plan?
Acceptable Quality Limit (AQL) AQL (Acceptable Quality Limit) Sampling is a method widely used to define a production order sample to find whether or not the entire product order has met the client's specifications. Based on the sampling data, the customer can make an informed decision to accept or reject the lot.
Why do we have to set the sampling plan and collect samples?
To ensure that the estimated value obtained from the laboratory sample is a good representation of the true value of the population it is necessary to develop a sampling plan .
What is a sampling plan in nursing research?
A sampling plan defines the process of making the sample selections; sample denotes the selected group of people or elements included in a study. Sampling decisions have a major impact on the meaning and generalizability of the findings.
Parameters Affecting Sampling Plans
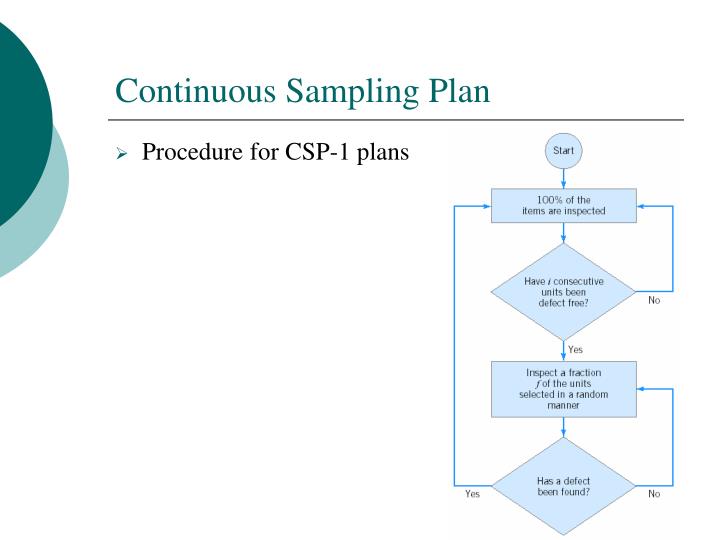
Sampling plans are of two general types: lot-by-lot inspection plans, and continuous process plans. These two are the most often used types, but there are other plans which can be used for special inspection problems.
Classifying Sampling Plans according to AQL, LTPD, and AOQL
Sampling plans are classified according to three quality indexes: AQL, LTPD, and AOQL.
Types of Sampling Plans
Sampling plans are either attribute plans or variables plans. An attribute plan is one in which each sample is inspected and classified as defective or nondefective. The lot is accepted or rejected based on the number of defects found compared with the acceptance number from the plan.
Single, Double, and Multiple Sampling
Many sampling plans offer a choice of single, double, or multiple sampling. In single sampling plans, a random sample of n items is drawn from the lot. If the number of defectives is less than or equal to the acceptance number, c, the lot is accepted. If not, it’s rejected.
Characteristics of Effective Sampling Plans
Good acceptance sampling plans have several characteristics. They are listed below and elaborated in following subsections (Juran/Gryna, 1970, p.418).
Sampling Bias
When sample selection is left to human choice, human biases can inadvertently intrude. Here are some examples:
Sampling Plans Based on Prior Quality Data
Conventional sampling plans assume that the frequency distribution of sampling lots follows classical probabilities of occurrence. In short, they ignore any previous knowledge gained on the past quality sampling. If this knowledge could be rationally applied to future sampling processes, it should reduce sample sizes and, thus, inspection costs.
What is sample unit?
More commonly known as the Sample unit, it comprises of the type of customers / people that you want to contact for your market research study. To determine the sample population, first you need to decide what the ideal customer for the firm looks like.
Why do you need to determine the type of analysis you are going to carry out?
The type of analysis you are going to carry out (probability or non probability) has to be determined in the sampling plan because you need to contact the customers accordingly. Do note, that this has to be incorporated in your market research study so you need to decide your population accordingly as well.
What is a sampling plan?
The sampling plan is a procedure for an appropriate examination, which should be carried out on the product, using the required number of samples and using a specific method. This can precede under two different plans, a two-class plan or a three-class plan.
Why are sampling plans important?
Sampling plans are useful components within food safety management and quality control, however results should be interpreted with care, because results do not give an absolute indication of the quality of the batch under study . The cases as defined by the ICMSF give useful guidelines for selecting the characteristics of sampling plans, taking into account the degree of concern of the hazard and the conditions of storage and use of the product. By determining the performance of sampling plans or the OC-curves, a quantitative indication of the performance of sampling plans can be obtained.
Why use sampling tables?
The use of sampling tables provides a quicker way of selecting a sampling plan instead of developing a sampling plan using complex statistics. The standard provides instructions as to how it is supposed to be applied; however, this is often misinterpreted.
Why is it important to have a sampling system?
Sampling systems and sampling plans can both improve the efficiency of product inspection and reduce the inspector’s workload whilst at the same time providing a rigorous statistical basis for the sampling and inspection process.
How to prioritize water sampling methods?
One method to prioritize water sampling methods or elements is to first evaluate those questions that are time-sensitive. Petroleum products, when spilled into the open environment, undergo rapid physical and chemical alterations when exposed to wind, sunlight, waves, and other natural forces.
What is attribute sampling?
Attribute sampling plans are often used to inspect the effectiveness of the product/process and to determine the rate of compliance with established criteria. It is a common pharmaceutical industry practice to employ American National Standards Institute (ANSI)/American Society for Quality (ASQ) Z1.4-2008: Sampling Procedures and Tables for Inspection by Attributes for inspection of product/process defects. ANSI/ASQ Z1.4-2008: Sampling Procedures and Tables for Inspection by Attributes is an acceptance sampling system that provides tightened, normal and reduced plans to be applied to attributes for inspection for the percentage of nonconformities per 100 units. The use of sampling tables provides a quicker way of selecting a sampling plan instead of developing a sampling plan using complex statistics. The standard provides instructions as to how it is supposed to be applied; however, this is often misinterpreted. The common mistakes include, but not are limited to, the selection of incorrect sampling size, selection of incorrect acceptance criteria, or an attribute plan used for variable data, etc. Therefore, it is very important to properly interpret the standard and apply the inspection rules as they are prescribed. Incorrect application can result in regulatory observations (Fig. 12.13 ).
Why are water column samples important?
Discrete water column samples are important for every oil spill, whether the source is known or not, and analyses of these samples provide key information on the chemical and physical properties of the oil, its potential toxicity to organisms, its projected persistence in the environment, and other details to aid in spill response decision making. There are several elements that must be considered when designing a sampling plan, whatever the purpose of the samples (Brown, 1999 ). First, there must always be collection of clean reference samples for comparison. When possible, samples should be collected in triplicate and stored frozen in solvent-washed glass jars.
What is sampling plan?
A sampling plan allows an auditor or a researcher to study a group (e.g. a batch of products, a segment of the population) by observing only a part of that group, and to reach conclusions with a pre-defined level of certainty.
What is double stage sampling?
A “ double-stage sampling plan” is a bit more efficient. The inspector would start by taking a smaller number of sample (n1). If the finding is not clear (not very good, not very bad), more samples are picked. There are also multiple and sequential plans.
What is the most popular inspection plan?
The most popular plan was developed by the US Department of Defense, and was formalized in standards MIL-STD 105E, 2859-1, and ANSI Z1.4. Many people call it an “AQL inspection”.
Why did the authors write each plan?
The main reason that the authors wrote each plan was to determine the sample size, accept and reject criteria. After finding this you are done with the standards until the next inspection.
What does AQL stand for in a process?
AQL stands for “Acceptable Quality Level”. AQL is the poorest level of quality for the process that you would consider acceptable. You establish the AQL % depending on the feature that under inspection. If the feature has high importance, you will select a lower AQL.
What is an AQL inspection?
Inspectors depend on AQL plans to determine the amount of parts to inspect. AQL stands for “Acceptable Quality Level”. AQL is the poorest level of quality for the process that you would consider acceptable.
Do some plans allow for defects?
Some plans allow for reduction of inspection when defect levels decrease, some don’t. Some plans allow for defects (or inspection mistakes), some don’t. Because of the complexity, there are college level courses that cover sampling theory. These courses detail the major plans and elaborate on the AQL tables.
What is AQL in a product inspection?
AQL stands for ‘Acceptance Quality Limit, ’ and it’s an essential sampling method used in quality control. It’s defined in ISO 2859-1 as “The quality level that is the worst tolerable” over the course of many inspections. When an inspector goes to your manufacturer to conduct a product quality inspection, they use AQL sampling to answer two crucial ...
What is an AQL chart?
AQL or Acceptable Quality Limits are an important tool to help you and your inspection services provider determine how to conduct inspections. You can use the standard AQL chart to determine the sample size to inspect and the number of rejected units that are acceptable.
What is AQL based on?
AQL is based on the quality levels you deem to be most appropriate for your product. In essence, it is not designed to ensure zero defects. And it is generally unreasonable to expect zero defects outside of high-risk industries like aerospace or pharmaceuticals.
Is AQL a statistical model?
AQL is a proven statistical model that has been used successfully for decades. It has broad adoption across the quality control industry for a reason — it works. However, it’s important to remember that conducting an AQL inspection will not guarantee a defect-free inspection, as this is not its purpose. For more information, see Should You Conduct ...
Parameters Affecting Sampling Plans
Types of Sampling Plans
Single, Double, and Multiple Sampling
Characteristics of Effective Sampling Plans
Sampling Bias
Sampling Plans Based on Prior Quality Data
- Conventional sampling plans assume that the frequency distribution of sampling lots follows classical probabilities of occurrence. In short, they ignore any previous knowledge gained on the past quality sampling. If this knowledge could be rationally applied to future sampling processes, it should reduce sample sizes and, thus, inspection costs. Th...