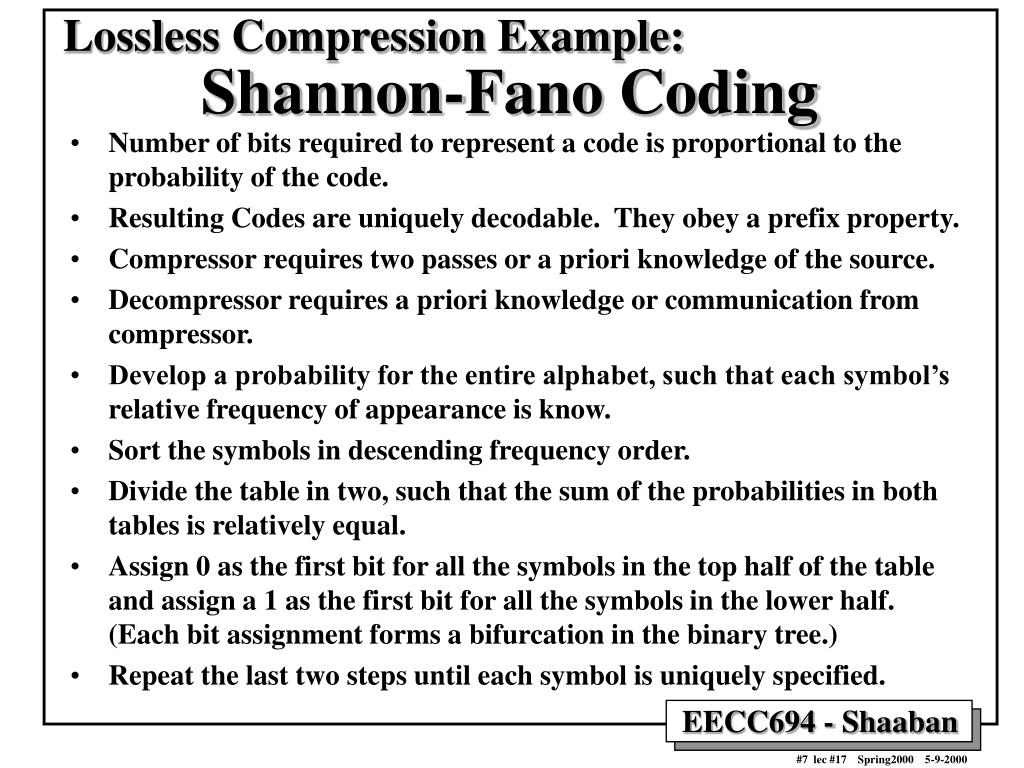
What is A Priori Coding. 1. A process of coding qualitative data whereby the researcher develops the codes ahead of time based on a theoretical framework, the interview question, or pre-existing knowledge.
What is an example of a priori?
This sort of argument is called a priori. The Ontological Argument is a good example of an a priori argument. A priori is a term first used by Immanuel Kant and it means "from the beginning" or "at first". It is a type of argument based on the meaning of terms. It describes things we can know independently of the facts.
How to pronounce priori?
Pronunciation of priori with 1 audio pronunciations 0 rating rating ratings Record the pronunciation of this word in your own voice and play it to listen to how you have pronounced it.
When to use g0127?
Procedure Code G0127 is included in Medicare’s covered foot care when billed with a diagnosis pertaining to dystrophic nails. Refer to the . Diagnosis Code List. Diabetic Sensory Neuropathy with LOPS Coding Criteria Diabetic sensory neuropathy with LOPS is a localized illness of the feet and falls within the regulation's exception to the general
How to use a priori in a sentence?
Use “a priori” in a sentence | “a priori” sentence examples a priori 1. One assumes, a priori, that a parent would be better at dealing with problems. 2. There seems to be no a priori reason why nuclear transfer should work. 3. There is no a priori reason for assuming that these processes will necessarily ” hang together ” functionally. 4.
What is a priori framework?
1. A process of coding qualitative data whereby the researcher develops the codes ahead of time based on a theoretical framework, the interview question, or pre-existing knowledge.
Are priori codes pre determined?
In a priori coding, codes are developed beforehand; they are pre-determined. But in open coding, as the name suggests, a researcher comes up with codes at the time of data analysis. They are not predetermined.
What is emergent coding?
• Emergent coding: The codes used to categorize data emerge from the data; this process is used when your question is broad and exploratory.
What are the different types of qualitative coding?
Read about various types of coding.Thematic Analysis Coding. Find recurring patterns and themes. ... Pattern Coding. ... Focused coding / selective coding. ... Axial coding. ... Theoretical coding. ... Elaborative coding. ... Longitudinal coding. ... Content analysis coding.
Are open coding and inductive coding the same?
Open coding is an inductive, analytical procedure that performs two basic tasks: it makes comparisons and it asks questions. For this reason grounded theory is often referred to as the constant comparative method of analysis (Glaser & Strauss, 1967).
What are priori themes?
In template analysis it is common to identify some themes in advance, usually referred to as 'a priori' themes. Usually this is because a research project has started with the assumption that certain aspects of the phenomena under investigation should be focused on.
What is a priori in qualitative research?
• A priori codes are codes that are developed before examining the current data. • Many qualitative researchers like to develop the codes as they code the data. These codes are called inductive codes.
What is Vivo coding?
In vivo coding is a form of qualitative data analysis that places emphasis on the actual spoken words of the participants.
What is inductive coding?
Inductive coding refers to a data analysis process whereby the researcher reads and interprets raw textual data to develop concepts, themes or a process model through interpretations based on data (Thomas 2006; Boyatzis 1998; Corbin and Strauss 1990).
What are the types of coding?
There are four types of coding:Data compression (or source coding)Error control (or channel coding)Cryptographic coding.Line coding.
Is coding qualitative or quantitative?
All coding involves reading of the text, which is qualitative. Predefined categories used in quantitative research are often derived from preliminary qualitative analysis of the data to make sure that the provided categories can both capture the differences in content and cover its full range.
What is axial coding in qualitative research?
Axial Coding Definition With axial coding in qualitative research, you read over the codes and their underlying data to find how they can be grouped and abstracted into categories. These categories could be created by abstracting out an existing code or developing new concepts that encompass several different codes.
Why is Apriori named Apriori?
Name of the algorithm is Apriori because it uses prior knowledge of frequent itemset properties. We apply an iterative approach or level-wise search where k-frequent itemsets are used to find k+1 itemsets.
What is the Apriori property?
To improve the efficiency of level-wise generation of frequent itemsets, an important property is used called Apriori property which helps by reducing the search space. All non-empty subset of frequent itemset must be frequent. The key concept of Apriori algorithm is its anti-monotonicity of support measure.
Is Apriori algorithm slow?
Apriori Algorithm can be slow. The main limitation is time required to hold a vast number of candidate sets with much frequent itemsets, low minimum support or large itemsets i.e. it is not an efficient approach for large number of datasets.
What is a priori in interview?
The only thing I'd add is that, strictly speaking, the words a priori are Latin for something like "from beforehand". Therefore your a priori "codes" are the ones that you'd have created (quite reasonably in some instances) in establishing your interview guide. To remain with the Latin, any codes that you generated in light ...
Do scholars prefer coding in questionnaires?
This may depend on the choice of researchers. Many scholars prefer the coding from the beginning, in the questionnaire. To me, if it is done in an interview schedule/questionnaire, it helps the researcher during data entry. I prefer coding in a questionnaire.
Is a priori deductive or inductive?
Using a priori codes is frequently referred to as a "deductive" form of analysis, while building the codes during the analysis would be "inductive.". A third option would be a "hybrid" approach, where you begin with a set of a priori codes and then add to them as you examine the data inductively.
What is the difference between inductive and deductive coding?
The main difference between inductive and deductive reasoning is that inductive reasoning aims at developing a theory while deductive reasoning aims at testing an existing theory. Inductive reasoning moves from specific observations to broad generalizations, and deductive reasoning the other way around.
What does open coding mean in qualitative research?
Open coding in grounded theory method is the analytic process by which concepts (codes) to the observed data and phenomenon are attached during qualitative data analysis. Open coding aims at developing substantial codes describing, naming or classifying the phenomenon under consideration.
What is the difference between a code and a theme?
The difference between a code and a theme is relatively unimportant. Codes tend to be shorter, more succinct basic analytic units, whereas themes may be expressed in longer phrases or sentences. After identifying and giving names to the basic meaning units, it is time to put them in categories, or families.
How do you analyze a text theme?
Look for recurring images. Students can easily analyze theme through the repeated images and other motifs throughout the novel.
How do you write a theme description?
That said, there are some agreed upon “rules” of writing theme statements.
What is inductive coding in qualitative research?
Inductive coding refers to a data analysis process whereby the researcher reads and interprets raw textual data to develop concepts, themes or a process model through interpretations based on data (Thomas 2006; Boyatzis 1998; Corbin and Strauss 1990).
Is qualitative data inductive or deductive?
Inductive approaches are generally associated with qualitative research, whilst deductive approaches are more commonly associated with quantitative research. However, there are no set rules and some qualitative studies may have a deductive orientation.
What is the initial stage of coding?
In the initial stage of coding, you could assign the code of “pets” or “animals”. These are just initial, fairly broad codes that you can (and will) develop and refine later. In the initial stage, broad, rough codes are fine – they’re just a starting point which you will build onto in the second stage.
What is code categorisation?
Categorisation is simply the process of reviewing everything you’ve coded and then creating code categories that can be used to guide your future analysis. In other words, it’s about creating categories for your code set. Let’s take a look at a practical example.
What is qualitative data coding?
So, building onto this, qualitative data coding is the process of creating and assigning codes to categorise data extracts.
Why is inductive coding important?
Inductive coding is great when you’re researching something that isn’t yet well understood because the coding derived from the data helps you explore the subject. Therefore, this type of coding is usually used when researchers want to investigate new ideas or concepts, or when they want to create new theories.
What are the different types of coding?
But how exactly do you decide what codes to use when there are many ways to read and interpret any given sentence? Well, there are a few different approaches you can adopt. The main approaches to initial coding include: 1 In vivo coding 2 Process coding 3 Open coding 4 Descriptive coding 5 Structural coding 6 Value coding
What is deductive coding?
With deductive coding, we make use of pre-established codes, which are developed before you interact with the present data. This usually involves drawing up a set of codes based on a research question or previous research. You could also use a code set from the codebook of a previous study.
What is line by line coding?
Line by line coding is pretty much exactly what it sounds like – reviewing your data, line by line, digging deeper and assigning additional codes to each line.
What is a coding frame?
Once you create your codes, you need to put them into a coding frame. A coding frame represents the organizational structure of the themes in your research. There are two types of coding frames: flat and hierarchical.
What is deductive coding?
Deductive coding means you start with a predefined set of codes, then assign those codes to the new qualitative data. These codes might come from previous research, or you might already know what themes you’re interested in analyzing. Deductive coding is also called concept-driven coding.
What is coding in qualitative data?
Coding is the process of labeling and organizing your qualitative data to identify different themes and the relationships between them. When coding customer feedback, you assign labels to words or phrases that represent important (and recurring) themes in each response. These labels can be words, phrases, or numbers;
How do hierarchy frames help you organize codes?
Hierarchical frames help you organize codes based on how they relate to one another. For example, you can organize the codes based on your customers’ feelings on a certain topic:
What happens if you have too many codes?
If you have too many codes, especially in a flat frame, your results can become ambiguous and themes can overlap. Manual coding also requires the coder to remember or be able to find all of the relevant codes; the more codes you have, the harder it is to find the ones you need, no matter how organized your codebook is.