What is unusual P axis?
- Limb lead misplacement (most common cause)
- Dextrocardia
- Ectopic atrial rhythm
- Ventricular to atrial (V-A) conduction - abnormal P wave axis that occurs after the QRS interval
What should a normal ECG look like?
Normal ECG obtained from ECG heart monitor looks like a smooth curve. The distance between each spike is almost constant. Each spike represents one whole heartbeat, the distance between spikes represents your heart rate. If there are irregular gaps and clusters of spikes, there might be a problem with your heart (It might be associated with a ...
What are the normal results for an ECG?
Normal Results. Normal test results most often include: Heart rate: 60 to 100 beats per minute; Heart rhythm: Consistent and even ; What Abnormal Results Mean. Abnormal ECG results may be a sign of: Damage or changes to the heart muscle; Changes in the amount of the electrolytes (such as potassium and calcium) in the blood ...
What does a normal ECG look like?
In a normal healthy heart, an EKG representing one complete heartbeat looks about like this : That first petite little hump, affectionately called the P wave, represents the electrical signal that starts in a group of cells called the Sinoatrial Node. How do you know if your ECG is abnormal?
What is abnormal P axis?
An abnormal P-wave axis (aPWA) obtained in the routine 12‑lead electrocardiogram (ECG) is thought to be a marker of left atrial fibrosis and delayed conduction [14,15]. Consistent with this, aPWA has been linked to the development of atrial fibrillation, stroke and total mortality [[15], [16], [17]].
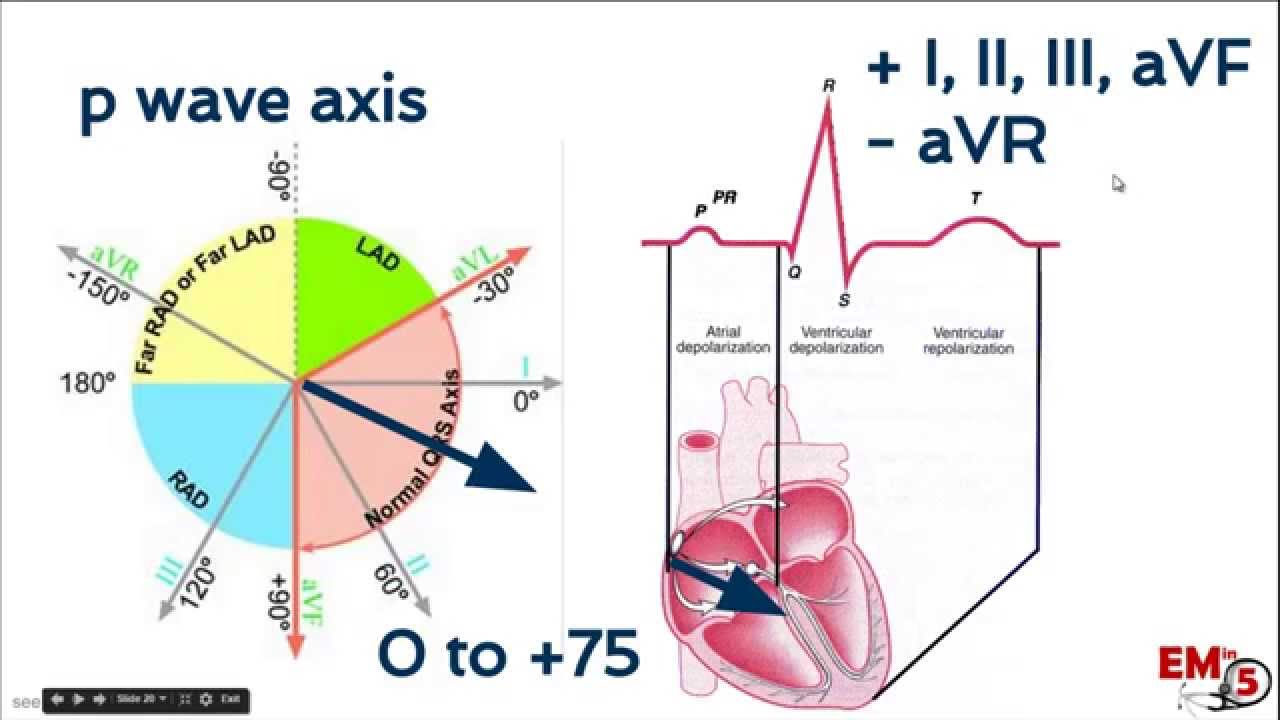
What is normal P QRS axis?
Baseline ECG axes were automatically measured with normal values defined as follows: P-wave axis 0° to 75°, QRS axis -30° to 90°, and T axis 15° to 75°.Feb 1, 2018
What Should P be on ECG?
P-wave duration should be ≤0,12 seconds. P-wave amplitude should be <2,5 mm in the limb leads. P-pulmonale implies that the P-wave has an abnormally high amplitude in lead II (and in other leads in general).
What is a normal frontal axis P?
Frontal plane P wave axis: 0° to +75°
How can you tell if an ECG is abnormal?
Abnormal results can signify several issues. These include: Defects or abnormalities in the heart's shape and size: An abnormal ECG can signal that one or more aspects of the heart's walls are larger than another meaning that the heart is working harder than normal to pump blood.Jan 7, 2021
What does an abnormal P wave look like?
The Abnormal P wave If the p-wave is enlarged, the atria are enlarged. If the P wave is inverted, it is most likely an ectopic atrial rhythm not originating from the sinus node. Altered P wave morphology is seen in left or right atrial enlargement.Jan 12, 2011
What does a small P wave mean?
A short P‐wave duration is a marker of a higher rate of atrial fibrillation recurrences after pulmonary vein isolation procedure.Jan 7, 2021
What is ECG interpretation?
ECG interpretation includes an assessment of the morphology (appearance) of the waves and intervals on the ECG curve. Therefore, ECG interpretation requires a structured assessment of the waves and intervals. Before discussing each component in detail, a brief overview of the waves and intervals is given.
Which side of the ventricular septum is depolarized?
The ventricular septum receives Purkinje fibers from the left bundle branch and therefore depolarization proceeds from its left side towards its right side . The vector is directed forward and to the right. The ventricular septum is relatively small, which is why V1 displays a small positive wave (r-wave) and V5 displays a small negative wave (q-wave). Thus, it is the same electrical vector that results in an r-wave in V1 and q-wave in V5.
What is the QT interval?
QT duration reflects the total duration of ventricular depolarization and repolarization. It is measured from the onset of the QRS complex to the end of the T-wave. The QT duration is inversely related to heart rate; i.e the QT interval increases at slower heart rates and decreases at higher heart rates. Therefore to determine whether the QT interval is within normal limits, it is necessary to adjust for the heart rate. The heart rate-adjusted QT interval is referred to as the corrected QT interval (QTc interval). A long QTc interval increases the risk of ventricular arrhythmias.
Why is the atria small?
It is small because the atria make a relatively small muscle mass. If the rhythm is sinus rhythm (i.e under normal circumstances) the P-wave vector is directed downwards and to the left in the frontal plane and this yields a positive P-wave in lead II ( Figure 2, right-hand side).
Is the QRS complex net positive or negative?
The QRS complex can be classified as net positive or net negative, referring to its net direction. The QRS complex is net positive if the sum of the positive areas (above baseline) exceeds that of the negative areas (below baseline). Refer to Figure 6, panel A. These calculations are approximated simply by eyeballing. Panel B in Figure 6 shows a net negative QRS complex because the negative areas are greater than the positive area.
Where is the T wave vector?
The T-wave vector is directed to the left, downwards and to the back in children and adolescents . This explains why these individuals display T-wave inversions in the chest leads. T-wave inversions may be present in all chest leads. However, these inversions are normalized gradually during puberty. Some individuals may display persisting T-wave inversion in V1–V4, which is called persisting juvenile T-wave pattern. If all T-waves persist inverted into adulthood, the condition is referred to as idiopathic global T-wave inversion.
Is V1 a positive or negative wave?
The ventricular septum is relatively small, which is why V1 displays a small positive wave (r-wa ve) and V5 displays a small negative wave ( q-wave). Thus, it is the same electrical vector that results in an r-wave in V1 and q-wave in V5.
What does the P axis mean on an EKG?
What does P axis mean on an EKG? The P wave is the first positive deflection on the ECG and represents atrial depolarisation. Normal P wave axis is between 0° and +75°.
Where does depolarization occur?
Normally depolarization occurs first in the right atrium and then in the left atrium. Also, what does the P wave represent? The P wave represents the depolarization of the left and right atrium and also corresponds to atrial contraction. Strictly speaking, the atria contract a split second after the P wave begins.
What is the P wave?
It is important to remember that the P wave represents the sequential activation of the right and left atria, and it is common to see notched or biphasic P waves of right and left atrial activation.
What are the two determinates of QRS voltage?
Two determinates of QRS voltages are: Size of the ventricular chambers (i.e., the larger the chamber, the larger the voltage) Proximity of chest electrodes to ventricular chamber (the closer, the larger the voltage) Frontal plane leads:
What is ST segment depression?
ST segment depression is often characterized as "upsloping", "horizontal", or "downsloping". The normal U Wave: (the most neglected of the ECG waveforms) U wave amplitude is usually < 1/3 T wave amplitude in same lead. U wave direction is the same as T wave direction in that lead.
Which direction is the U wave?
U wave direction is the same as T wave direction in that lead. U waves are more prominent at slow heart rates and usually best seen in the right precordial leads. Origin of the U wave is thought to be related to after depolarizations which interrupt or follow repolarization.
Is there a wide range of normal variability in the 12 lead ECG?
It is important to remember that there is a wide range of normal variability in the 12 lead ECG. The following "normal" ECG characteristics, therefore, are not absolute. It takes considerable ECG reading experience to discover all the normal variants. Only by following a structured "Method of ECG Interpretation" ...
Is ST-T a continuous wave?
More often the ST-T wave is a smooth, continuous waveform beginning with the J-point (end of QRS), slowly rising to the peak of the T and followed by a rapid descent to the isoelectric baseline or the onset of the U wave. This gives rise to an asymmetrical T wave.
Is the T wave symmetrical?
In some normal individuals, particularly women, the T wave is symmetrical and a distinct, horizontal ST segment is present. The normal T wave is usually in the same direction as the QRS except in the right precordial leads. In the normal ECG the T wave is always upright in leads I, II, V3-6, and always inverted in lead aVR.
What is the normal axis of the left ventricle?
Since the left ventricle makes up most of the heart muscle under normal circumstances, normal cardiac axis is directed downward and slightly to the left: Normal Axis = QRS axis between -30° and +90°. Abnormal axis deviation, indicating underlying pathology, is demonstrated by:
What is the cardiac axis?
Cardiac axis represents the sum of depolarisation vectors generated by individual cardiac myocytes. Clinically is is reflected by the ventricular axis, and interpretation relies on determining the relationship between the QRS axis and limb leads of the ECG (below diagram)
What is the normal range of the QRS?
The normal adult QRS axis is between -30 degrees and +90 degrees, which is directed downward and to the left. This adult range is sometimes extended from -30 degrees to +100 degrees. Click to see full answer.
What is the R wave in a QRS complex?
The R wave is the first upward deflection after the P wave and part of the QRS complex. If a right bundle branch block is present, there may be two R waves, resulting in the classic “bunny ear” appearance of the QRS complex. In this setting, the second R wave is termed “R'” or “R prime.”. Similar Asks.