What is normal cerebral perfusion pressure?
Cerebral perfusion pressure is expressed by the following equation: Cerebral perfusion pressure = mean arterial pressure (MAP) – intracranial pressure (ICP) Normal cerebral perfusion pressure is 55 mm Hg to 60 mm Hg. An increase in intracranial pressure (ICP) can decrease the cerebral perfusion pressure (CPP)
What happens if CSF is not drained properly?
What should you avoid with a VP shunt?
- Martial arts. Any activity that involves being grabbed around the neck is not advised, as the shunt tubing in the neck can crack.
- Rugby.
- Gymnastics and dance.
- Water sports.
- Golf.
- Other activities.
What is the normal spinal fluid pressure?
The upper limit of normal CSF pressure in adults is 25 cmH 2 O, although this probably falls slightly after the age of 50. This upper limit has been emphasized in the most recent definition of IIH . CSF-OP probably does increase with increasing BMI, but the correlation is poor, and most authors now suggest that this effect is not clinically relevant.
What is the normal opening pressure for Spinal Tap?
What is a Normal Opening Pressure? The normal range for CSF is reported differently in various sources, with most reporting a normal range of 7-18 cmH2O in adults, 1 though some consider the normal range 5-25 cmH 2 O. 2 However, a pressure >25 cmH 2 O or <5 cmH 2 O should certainly prompt you to look for a source.
What is considered high CSF pressure?
The diagnosis is also confirmed by detecting a high spinal CSF pressure reading, usually greater than 250 mmH2O or 25 cmH2O (200-250 mmH2O or 20-25 cmH2O is considered borderline high) and normal laboratory and imaging studies including CT scans and MRIs.
What is CSF opening and closing pressure?
o Initial opening pressure is 44. o Closing pressure is 21. o CSF is negative for blood.
What is a low CSF opening pressure?
By very definition, the opening CSF pressure is low, below 60 mm H(2)O, and often a "dry" tap is encountered. However, the pressure may be normal, especially with intermittent leaks and may vary tap to tap. Fluid analysis is normal.
What is normal CSF closing pressure?
Low-volume cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) removal to a "high-normal" closing pressure (CP), approximately 18-20 cm H2O, may result in relief of IIH-associated headache with a lowered frequency of post-LP headache.
How is CSF opening pressure measured?
Abstract. It is often difficult to measure cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) pressure in children. CSF flow through a spinal needle is described by the equation: Flow = pressure/(needle constant x relative viscosity). Thus, CSF flow rate during lumbar puncture can be used to estimate CSF pressure.
What are normal CSF values?
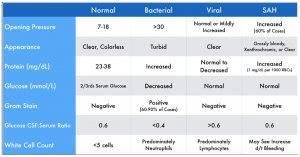
Normal values typically range as follows:Pressure: 70 to 180 mm H2O.Appearance: clear, colorless.CSF total protein: 15 to 60 mg/100 mL.Gamma globulin: 3% to 12% of the total protein.CSF glucose: 50 to 80 mg/100 mL (or greater than two thirds of blood sugar level)More items...•Apr 5, 2021
What is high opening pressure?
Elevated opening pressure correlates with increased risk of morbidity and mortality in bacterial and fungal meningitis. In bacterial meningitis, elevated opening pressure (reference range, 80-200 mm H2 O) suggests increased intracranial pressure (ICP) from cerebral edema.
How is opening pressure measured?
Opening Pressure at Lumbar Puncture is a surrogate measurement of Intracranial Pressure. An accurate Opening Pressure requires the needle entry point to be on the same level as the midline of the spine (Figure 4), which should also be at the same level as the patient's head.
What is the CSF-OP of a child?
CSF-OP in children is addressed in an accompanying article, which suggests that normal children may have a CSF-OP as high as 28 cmH 2 O ( 33 ). A recent study of 40 healthy older subjects aged between 60 and 82 years found a median CSF-OP of 15.8 cmH 2 O (95% CI, 10.6–19.4 cmH 2 O) ( 34 ), and the authors concluded that these results were similar to those found in young and middle-aged patients. However, their numbers were small. According to a very large retrospective chart review of over 12,000 patients, mean CSF-OP declines steadily after the age of 50 years. This study found the mean CSF-OP in patients aged 90–95 years to be only 11.4 ± 3.2 cmH 2 O, about 27% lower than the normal range quoted above ( 19) (as discussed previously, however, all patients with CSF-OP above 25 cmH 2 O were excluded from this study, so the absolute value of CSF-OP may have been somewhat underestimated; this would be unlikely to influence the finding of an age-related effect of lowering ICP).
Why do you have to extend your legs before measuring CSF-OP?
It is widely recommended that patients be asked to extend their legs and neck before measuring CSF-OP because that hip flexion may increase CSF-OP by increasing intra-abdominal pressure ( 16,41 ). Two earlier studies found that a tightly flexed position elevates CSF-OP by, on average, 6–8 cmH 2 O ( 42,43 ), whereas more recent studies have found differences of only 1–2 cmH 2 O ( 44,45 ). Occasional subjects paradoxically demonstrate increased CSF-OP with leg extension ( 42,44,46 ), so the practice of extending legs may not be that important. This is particularly relevant to performing LPs in children when it can be difficult to get the patient into an extended position ( 45,47 ).
What is the normal range of ICP?
The normal range of ICP measured by LP in adults in a typical clinical setting should now be regarded as 6 to 25 cmH 2 O (95% confidence intervals), with a population mean of about 18 cmH 2 O . There is, however, considerable variability: some normal individuals have pressures of 30 cmH 2 O (or, occasionally, even higher) meaning that pressure measurements must be interpreted in the clinical context.
What are the factors that affect ICP?
A century of investigation has shown that normal ICP is influenced by a number of factors, both internal (e.g ., arterial pressure, respiration, temperature, pCO 2, and sleep) and external ( e.g., gravity and position).
Can ICP be used to confirm a diagnosis?
OTHER WAYS OF MEASURING CEREBROSPINAL FLUID PRESSURE. A single measurement of ICP may not, by itself, confirm or refute a diagnosis. All measurements need to be interpreted in clinical context, and it may be necessary to undertake repeated measurements to clarify the diagnosis.
What happens to the red blood cells in the CSF?
Within several hours, the red blood cells in the cerebrospinal fluid are destroyed, releasing their oxygen-carrying molecule heme , which is metabolized by enzymes to bilirubin, a yellow pigment.
Is CSF PCR useful for meningitis?
The CSF findings are more suggestive of viral meningitis given the clear appearance of the CSF, the mildly raised WCC (consisting mainly of lymphocytes), raised protein level and normal glucose. Further investigations including CSF PCR would be useful in identifying the specific causative virus.