Who do I go to remove an Oral mucocele?
The dentist or doctor:
- Disinfects the area
- Puts a stitch through the mucocele and ties a knot
- Gently presses out saliva
- Removes the stitch after about a week
What are the signs and symptoms of mucoceles?
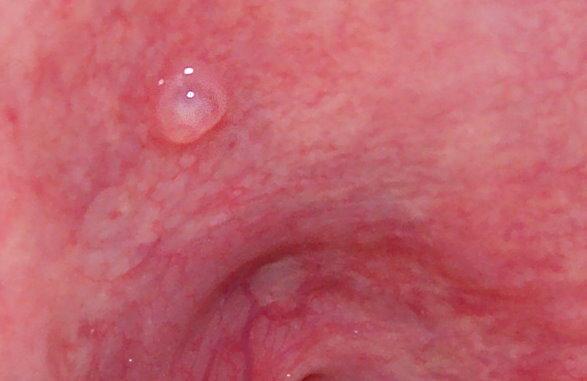
Signs and symptoms. The size of oral mucoceles vary from 1 mm to several centimeters and they usually are slightly transparent with a blue tinge. On palpation, mucoceles may appear fluctuant but can also be firm. Their duration lasts from days to years, and may have recurrent swelling with occasional rupturing of its contents.
What are the causes of mucoceles?
The defining features of a typical mucocele are as follows:
- Mucoceles are benign bumps in the mouth that are typically small and painless but can nevertheless be quite a bother as you are constantly conscious of the lesion.
- Larger the bump, the harder it will be to ignore. ...
- These fluid-filled sacs are characteristically smooth, soft, and shiny in appearance, with the overlying epithelium totally intact.
How to treat mucocele?
- Take an Aloe Vera leaf and peel it to get gel and apply this gel in the affected area. Rinse your mouth with lukewarm water after 20 minutes.
- Repeat it 3-4 times in a day
- You can use Aloe Vera Juice as a mouthwash.
What causes mucoceles in the mouth?
What Causes Oral Mucoceles? Mucoceles usually form at or near a salivary gland opening, also known as a salivary duct. Usually, these cysts result from trauma to the mouth. This trauma causes the duct to rupture and the saliva to spill into the connective tissue, which leads to inflammation and swelling.Mar 28, 2022
How do I get rid of a mucocele in my mouth?
These are the two types of treatment a doctor or dentist most commonly uses: Removing the gland. The dentist or doctor may use a scalpel or laser to remove the salivary gland. Local anesthesia numbs the pain.Jul 9, 2020
Can you pop an oral Mucocele?
Although some mucoceles resolve themselves, most remain large, continue to grow, and cause continuous problems. Unfortunately, simply popping or removing the fluid from the gland does not resolve the problem because the duct will continue to stay blocked.
Do oral Mucocele go away?
Many mucoceles will go away on their own in 3–6 weeks. Mucus-retention cysts often last longer. Avoid the habit of chewing or sucking on the lips or cheek when these lesions are present.
Can mucocele be cancerous?
In most cases, the lumps and bumps we get in our mouths are not cancer. They can be something as benign as a mucocele, but unless we take a biopsy, there's no way to be sure.
What happens if a mucocele is left untreated?
Mucoceles are usually harmless. While mucoceles are not typically dangerous, they can cause scar tissue to form when left untreated. Mucoceles, especially deep mucoceles, can be painful. It is common for a patient with a mucocele on the lower lip to bite the mucocele over and over again.Sep 25, 2013
Are mucoceles common?
Oral mucocele is the most common benign minor (accessory) salivary gland lesion, caused due to mechanical trauma to the excretory duct of the gland.
Does stress cause mucoceles?
The lateral side of lower labial mucosa was the commonest site and the trauma due to teeth or lip biting was the major etiological factor for the occurrence of the mucocele. The article highlights role of psychological stress in occurrence of mucocele.
Will salt help mucocele?
A nonsurgical option that may be effective for a small or newly identified mucocele is to rinse the mouth thoroughly with salt water (one tablespoon of salt per cup) four to six times a day for a few days. This may draw out the fluid trapped underneath the skin without further damaging the surrounding tissue.
How long do mucoceles take to go away?
They are typically painless, but when they can burst, they emit a clear fluid. Most mucoceles are less than 1 cm in diameter but range from 0.1-4 cm in size. The duration of the lesion is usually 3-6 weeks; however, it may vary from a few days to several years in exceptional instances.
What causes mucoceles in the mouth?
Usually, these cysts result from trauma to the mouth. This trauma causes the duct to rupture and the saliva to spill into the connective tissue, which leads to inflammation and swelling.
What is the color of mucoceles?
Oral mucoceles, sometimes known as oral mucous cysts, are painless blisters that occur on the surface of the mouth. These cysts often appear clear or blue in color while smooth and round in shape. They commonly develop on the lower lip's inner surface, inside the cheeks, and the bottom surface of the tongue.
How long does it take for a mucocele to heal?
In most cases, oral mucocele treatment is unnecessary since the cyst ruptures on its own — usually after three to six weeks. If the mucocele is persistent or large in size, your dental professional might use cryotherapy, laser treatment, or surgery to remove the cyst. Do not try to remove or rupture the cyst at home.
What to do if you have bumps in your mouth?
While it might be tempting to take a "wait and see" approach, make an appointment with your dentist right away if you notice any new bumps or lesions in your mouth. Your dental professional can rule out more serious maladies — like oral cancer — and advise on the best course of action.
How many people have mucoceles?
Mucoceles are a common type of oral lesion, affecting 2.4 of every 1000 people, according to the Journal of Oral and Maxillofacial Pathology. Learn what causes oral mucoceles, if you can prevent them, and what treatments are available.
How big is a mucoceles?
Though mucoceles are usually painless, they may get in the way of chewing, speaking, swallowing, and breathing, depending on their size, which ranges from one millimeter to two centimeters.
Can you return to a cyst free mouth?
With a dentist's guidance, you can take the right steps to return to a cyst-free mouth as soon as possible. This article is intended to promote understanding of and knowledge about general oral health topics. It is not intended to be a substitute for professional advice, diagnosis or treatment.
What Is Mucocele in Mouth?
An oral mucocele, also known as an oral mucous cyst, is a bump that usually develops inside the lip, on the floor of the mouth beneath the tongue, on the palate, or the surface of the tongue. They can appear white, transparent, or bluish and are benign.
Pea Sized Lump in Cheek
If you accidentally bite your cheek, you can damage a salivary gland and cause the formation of a mucocele. This can feel like a pea-sized lump in your cheek. Another cause of this can be a blockage of a parotid salivary gland located in front of your ear. A blockage prevents the normal drainage of saliva from the gland into your mouth.
Diagnosing A Mucocele
Because of their very characteristic appearance, your dentist may know from a physical examination if you have a mucocele. However, you may have a swelling that requires other diagnostic methods due to its appearance, location, and health history.
Treatments For A Mucocele
Many mucoceles rupture after swelling and resolve completely without treatment. More extensive or persistent mucoceles, however, may require surgical removal.
Can Mucoceles Recur?
Mucoceles, especially those found on the underside of the tongue, can recur. Recurrence is also more common in younger patients .
Preventing a Mucocele
While you cannot prevent all mucoceles from forming, you can take steps to lower your risk. These include avoiding habits such as biting or sucking on your lip or cheek, maintaining good oral hygiene, and only using a qualified professional for any oral piercings.
Schedule Appointment
Regular oral examinations and professional teeth cleanings can help prevent tooth decay and other oral diseases. Contact us today to schedule an appointment with Trident Dental.
What is an oral mucocele?
When to See a Doctor. Expert Answers (Q&A) Final Word. An oral mucocele refers to a harmless and painless mucous cyst in the oral cavity. It is a non-malignant tumor typically clear in appearance. These fluid-filled lesions usually develop due to damage to the ducts of the minor salivary glands.
Where does a mucocele occur?
A mucocele can develop anywhere inside the oral cavity where a minor salivary gland may be present, but the usual sites of occurrence include: The lower lip, which is the most commonly affected (2) (3) Under the tongue (2) The buccal mucosa or the inside of the cheeks. The gums.
How to treat mucoceles?
The standard choice of treatment for mucoceles includes: The surgical removal of the cyst along with the minor salivary gland with the use of a scalpel blade is perhaps the most commonly used method for the treatment of mucoceles. The incision is then tied together with intermittent sutures. (4)
How big is a cyst in the mouth?
If the damage is deeply rooted, the cyst will naturally take longer to heal. Mucoceles can be of varying sizes but usually figure between 2 and 10 mm in diameter. In fact, approximately 75% of all oral cysts are reported to be less than 1 cm wide.
Why does mucocele take shape?
A mucocele may also take shape if your glandular ducts become plugged or blocked with mucus. Any obstruction in the salivary gland will hamper the secretion of saliva and result in the buildup of mucus within the subepithelial tissue surrounding the affected gland.
How long does it take for mucocele to heal?
Mucoceles may cause difficulty while speaking, chewing, swallowing, and in some cases, breathing. They usually heal within 3–6 weeks.
How to remove mucocele cyst?
Another less invasive way to excise the mucocele and the adjoining salivary gland is with the use of laser therapy . Cryotherapy may be recommended in some cases, which essentially involves the freezing of the affected oral tissue to get rid of the cyst. (5)
Where do mucous cysts occur?
A mucous cyst, also known as a mucocele, is a fluid-filled swelling that occurs on the lip or the mouth. The cyst develops when the mouth’s salivary glands become plugged with mucus. Most cysts are on the lower lip, but they can occur anywhere inside your mouth. They’re usually temporary and painless.
How big is a mucous cyst?
Though most mucous cysts are less than 1 centimeter in diameter, rare cases can result in cysts as large as 3.5 centimeters. Smaller, painless cysts are often not detected until you go to the dentist. This is especially true of mucous cysts that develop inside your mouth.
How long does it take for a mucous cyst to heal?
Mucous cysts can take anywhere from a week to two years after treatment to heal, depending on the type and severity of the cyst.
How to tell if a mucous cyst is cancerous?
By looking at the cells, doctors can determine if the cyst is cancerous or not. Doctors may require a biopsy in cases where: the mucous cyst is larger than 2 centimeters. the cyst’s appearance suggests adenoma (cancer) or lipoma. there is no history of trauma.
What are the complications of mucous cysts?
The greatest complications with mucous cysts are pain and discomfort. If you suspect a mucous cyst in or around your mouth, get it checked out promptly. Last medically reviewed on April 19, 2018.
Can mucous cysts heal on their own?
Treatment is based upon the severity of the mucous cyst. Sometimes cysts may not require treatment and will heal on their own over time. Superficial cysts often resolve on their own. To prevent infection or tissue damage, do not try to open or remove cysts at home.
What is a mucous cyst?
Mucous cyst, often called mucocele, is a fluid-filled swelling that appears in your mouth and inside of your lip. Mucus cyst is caused due to rupture (bursts) of the salivary glands ducts, which causes the salivary fluid (mucin) to leak into the surrounding tissues in your mouth. The damage or trauma is the main cause of these cysts.
Types of mucous cysts
Mucous cysts have the same characteristics and one common cause. The superficial types will rise up from your skin and some of them will be a little deeper in the inner skin of the mouth. Depending on where these cysts begin to form, there may be some small differences.
What causes mucous cyst?
Trauma to your oral soft tissues is the main cause of mucous cysts. You may have accidentally bitten your inner parts of your lip or other soft parts in your mouth. An injury inside oral cavity can cause damages to the interior part of your cheeks, inside of your lower lip, floor of your mouth and where your salivary gland ducts are.
How is mucous cyst diagnosed?
First, your doctor or dentist takes necessary images like X-rays, CT scan or MRI imaging. They may even take biopsy of the tissue if unusual symptoms are present. This is to rule out possibilities of tumors such as salivary gland tumor. Then they are able to plan the best and the most effective treatment required for your mucous cyst removal.
Mucous cyst treatment
It may take a few weeks for most mucous cysts to burst and leave an ulcer that take just some days to heal. You don’t need any treatment for superficial mucous cyst. However, some other mucous cysts are deeper in nature and can persist for longer times, which should be removed. There are no complications and risks in the mucous cyst removal.
A final say
See your dentist or doctor if the bump doesn’t resolve on its own. Do not pick at the cyst at home and avoid trying to empty the fluid yourself. Maybe, your bump is not even a mucous cyst at all. See a specialist especially when the cyst has become annoying and has caused problems with eating, speaking and interferes with your daily life.
What is a lump on the inside of your mouth called?
If you have a smooth, soft lump on the inner surface of your lower lip, on your tongue, or anywhere else inside your mouth, it might be a mucous cyst. Sometimes, mucous cysts can happen on other parts of the body. People also call these cysts “mucoceles.”. Mucous cysts are just what they sound like.
What causes a lump in the mouth?
In those spots, mucus and saliva can leak out into surrounding tissue. That fluid can stay in the tissue in your mouth and form a lump. It’s often not clear what causes a mucous cyst. They can form if you bite your cheek, tongue, or lip or if you had some other trauma. Sometimes they might happen after a tongue or lip piercing.
How long does a mucous cyst last?
How to Get Rid of a Mucous Cyst. Most of the time, mucous cysts go away on their own. They may last for a few days or weeks before they pop. After the cyst ruptures, the spot usually heals. Some people get multiple mucous cysts. You also can have a mucous cyst that goes away and then comes back.
How to get rid of mucous cyst?
The best way for you to get rid of a mucous cyst for good is to remove it with surgery. The doctor will also remove the minor salivary gland that keeps causing the cyst. That way, the problem can’t recur.
Can a mucous cyst hurt?
A strange lump in your mouth might worry you. Or the feeling might bother you. But mucous cysts usually don’t hurt. And, in case you’re wondering, they aren’t cancer.
Can a mucous cyst come back?
You also can have a mucous cyst that goes away and then comes back. You don’t have to do anything about it. But if you have a mucous cyst that is painful or causing you trouble, a doctor can treat it. Possible treatments include: The best way for you to get rid of a mucous cyst for good is to remove it with surgery.