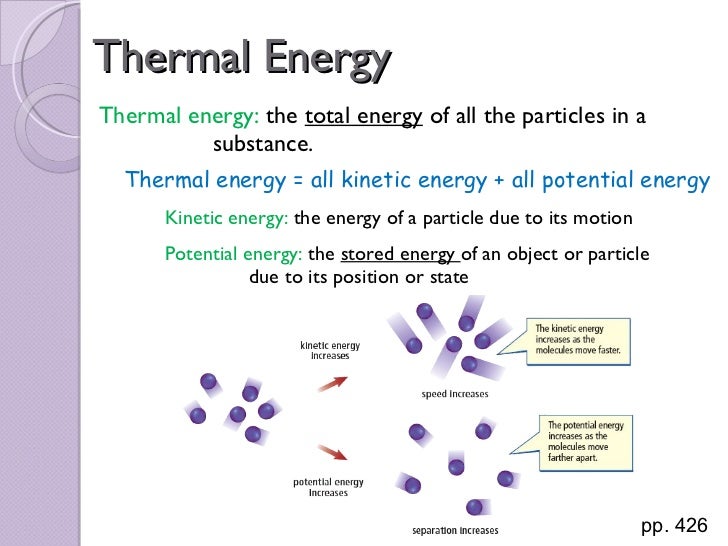
What is a measure of the total energy in a substance?
Heat is a measurement of the total energy in a substance. Also, is a measure of the total kinetic energy of the atoms and molecules in a substance? Anything that is moving has kinetic energy, including the atoms and molecules vibrating in a substance.
Is temperature a measure of the total kinetic energy in a substance?
If temperature is measured in Kelvin degrees, then this number is directly proportional to the average kinetic energy of the molecules. Heat is a measurement of the total energy in a substance. Also, is a measure of the total kinetic energy of the atoms and molecules in a substance?
What is kinetic energy of a particle?
It is the kinetic energy of a typical particle. in a substance. It is the kinetic energy of a typical particle. While the earlier answer is correct, I’ll just elaborate on this a little: The particles of any substance are, assuming equilibrium, all at temperature T, which by definition represents the energy of each.
What is the average energy of the particles in a sample?
Temperature is the average amount of energy of motion of each particle of a substance. That is, temperature is a measure of how hot or cold a substance is. In contrast, the total energy of motion in the particles of a substance is called thermal energy. Additionally, what happens to the average kinetic energy of the particles in a sample?
What is the measure of kinetic energy?
What is a measure of the total energy of the particles in an object?
What energy is the total energy of an object?
What type of energy is the total energy in all the particles of an object?
What is kinetic energy?
Kinetic energy is the energy that an object has because of its motion. This energy can be converted into other kinds, such as gravitational or electric potential , which is the energy that an object has because of its position in a gravitational or electric field.
What is the energy of each particle?
While the earlier answer is correct, I’ll just elaborate on this a little: The particles of any substance are, assuming equilibrium, all at temperature T, which by definition represents the energy of each. Because T is in units of degrees, the multiplier k (Boltzmann’s constant) converts degrees (Kelvin) to energy (ergs), so kT is the total energy of each particle by virtue of it being at temperature T. By the equipartition theorem, this energy is divided equally between kinetic (energy of motion) and potential (energy of position), but this is per degree of freedom, which means, in this case,