What is a homologous chromosome pair called?
In metaphase I of meiosis I, the pairs of homologous chromosomes, also known as bivalents or tetrads, line up in a random order along the metaphase plate.
Which is a homologous chromosome pair quizlet?
Homologous chromosomes are chromosome pairs, one from each parent, that are similar in length, gene position and centromere location. Homologous chromosomes are two sister chromatids stuck together with cohesions forming a tetrad.
What is a homologous pair biology?
1. A pair of chromosomes made up of two homologs. Homologous chromosomes have corresponding DNA sequences and come from separate parents; one homolog comes from the mother and the other comes from the father. Homologous chromosomes line up and synapse during meiosis.
What is a homologous pair easy definition?
Homologous-pair definition Two chromosomes that are identical, with the same genes. noun.
What are homologous chromosomes in biology quizlet?
Homologous Chromosomes. Chromosome pairs (one from each parent) that are similar in length, gene position-banding, and centromere location. Homologous chromosomes are similar but not identical. Each carries the same genes in the same order, but the alleles for each trait may not be the same.
Which of the following best describes homologous chromosomes?
Which of the following statements best describes homologous chromosomes? Chromosomes that have the same genes in the same position and are the same size and shape.
What is a homologous pair in meiosis?
Homologous chromosomes are matched pairs containing the same genes in identical locations along their length. Diploid organisms inherit one copy of each homologous chromosome from each parent; all together, they are considered a full set of chromosomes.
Why do chromosomes occur in homologous pairs?
The two chromosomes in a homologous pair are very similar to one another and have the same size and shape. Most importantly, they carry the same type of genetic information: that is, they have the same genes in the same locations. However, they don't necessarily have the same versions of genes.
What is the function of homologous chromosomes?
Homologous Chromosome Function Having two copies of each chromosome, called homologous chromosomes, helps increase both the variety and stability of a species. While each homologous chromosome carries the same genes, they can carry different versions of the gene.
What is the best definition of a homologous gene?
Homologous genes are those that can be traced from two separate creatures to a single common ancestor. Learn about homologous and analogous traits, as well as orthologous and paralogous genes.
What is meant by a pair of chromosomes?
Each pair contains two chromosomes, one coming from each parent, which means that children inherit half of their chromosomes from their mother and half from their father. Chromosomes can be seen through a microscope when the nucleus dissolves during cell division.
What is a homologous chromosome?
Homologues, or homologous chromosomes, are pairs of chromosomes that come from each parent. In terms of structure, they have the same length and amount of genes, banding pattern, location of genes, as well as the location of centromeres.
Where are homologous chromosomes located?
While they are known to be located in the nucleus, chromosomes are only visible when ...
What happens to homologous chromosomes during the fusion stage?
During this stage, the homologous chromosomes become duplicated and start to fuse as sister chromatids. These sister chromatids are simply replicated chromosomes that are attached together in a region called centromere.
What happens if a chromosome is not disjuncted in meiosis I?
If nondisjunction happens in meiosis I, the homologous chromosomes will fail to separate whereas if during meiosis II, it is the sister chromosomes that will fail to do so. In both cases, the mutation can be passed on to the next generation.
What is the behavior of sister chromatids during meiosis?
The behavior of sister chromatids is slightly different during meiosis. In this phase, the homologous chromosomes form the sister chromatids that pair into tetrads. Also during this stage, the homologous chromosomes exchange some of their genetic material in a process called recombination. This genetic recombination is what produces ...
What is the term for the error that occurs when chromosomes try to separate during anaphase?
Nondisjuntion refers to the error that occurs when chromosomes try to separate during anaphase (be it mitosis or meiosis). The fertilization of the cells that contain the defective chromosomes may result to either not enough number or too many chromosomes.
Do diploids have homologous chromosomes?
Basically, diploid organisms, like humans, have two pairs of homologous chromosomes that are inherited from the mother and father.
What is a homologous chromosome?
Homologous chromosomes are made up of chromosome pairs of approximately the same length, centromere position, and staining pattern, for genes with the same corresponding loci. One homologous chromosome is inherited from the organism's mother; the other is inherited from the organism's father. Click to see full answer.
Where do the chromosomes in a homologous pair come from?
One member of each pair comes from the female parent (mother) and the other from the male parent. The maternal and paternal chromosomes in a homologous pair have the same genes at the same loci, but possibly different alleles.
What is a homologous pair?
A homologous pair consists of one paternal and one maternal chromosome. The pairing up of homologous chromosomes during meiosis is important to promote genetic variation.
Is a homologous chromosome identical to a maternal chromosome?
Similarly, are homologous chromosomes identical? One chromosome of each homologous pair comes from the mother (called a maternal chromosome) and one comes from the father (paternal chromsosome). Homologous chromosomes are similiar but not identical. Each carries the same genes in the same order, but the alleles for each trait may not be the same.
Hiding on Chromosomes
Have you ever heard that certain features skip generations? For example someone with blue eyes may have two parents with brown eyes but a grandparent with blue eyes. Or two black colored cats may produce white kittens. How and why does this occur?
Studying Life
Of the various courses I teach, my current favorite is called Accelerated Biology. It's essentially like any introductory biology course, but due to its accelerated nature, we're able to move quickly and cover more detail on certain topics. One such topic is genetics. We'll study genetics from a multitude of angles.
Genetic Differences
Chromosome number varies between species. For example, turkeys have 80 chromosomes; dogs have 78, mosquitoes only 6, and the black mulberry plant has a whopping 308! Humans on the other hand contain 46 chromosomes (23 pair). Below is an illustration for your reference.
Making Copies
When cells prepare to divide, they must replicate their chromosomes. This ensures that each new cell contains the same genetic information as the original cell. Following replication, your chromosomes take on a slightly altered appearance. Below is an image to assist in understanding.
What is a couple of homologous chromosomes?
A couple of homologous chromosomes, or homologs, are a set of one maternal and one paternal chromosome that pair up with each other inside a cell during fertilization.
Why are homologous chromosomes important?
Homologous chromosomes are important in the processes of meiosis and mitosis. They allow for the recombination and random segregation of genetic material from the mother and father into new cells.
What is the difference between prophase I and prophase I?
Prophase I. In prophase I of meiosis I, each chromosome is aligned with its homologous partner and pairs completely. In prophase I, the DNA has already undergone replication so each chromosome consists of two identical chromatids connected by a common centromere.
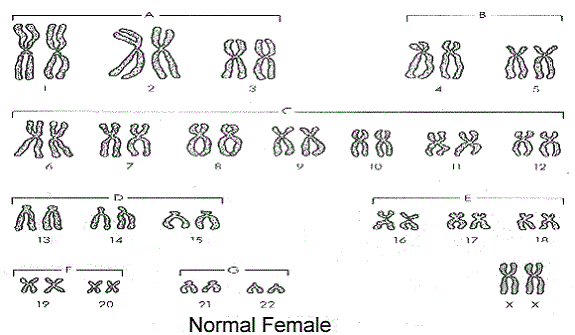
How many chromosomes are in a diploid cell?
As this karyotype displays, a diploid human cell contains 22 pairs of homologous chromosomes and 2 sex chromosomes. The cell has two sets of each chromosome; one of the pair is derived from the mother and the other from the father.
How many homologous chromosomes are in diploid (2n)?
In diploid (2n) organisms, the genome is composed of one set of each homologous chromosome pair, as compared to tetraploid organisms which may have two sets of each homologous chromosome pair. The alleles on the homologous chromosomes may be different, resulting in different phenotypes of the same genes.
What is the order of the chromosomes in metaphase I?
In metaphase I of meiosis I, the pairs of homologous chromosomes, also known as bivalents or tetrads, line up in a random order along the metaphase plate. The random orientation is another way for cells to introduce genetic variation.
What is the chromatin complex?
Overview. Chromosomes are linear arrangements of condensed deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) and histone proteins, which form a complex called chromatin. Homologous chromosomes are made up of chromosome pairs of approximately the same length, centromere position, and staining pattern, for genes with the same corresponding loci.
Homologous Chromosomes Definition
Homologous Chromosome Function
- Two Versions of Each Gene
Diploid organisms, like humans, carry two copies of the genome in each one of their cells. Having two copies of each chromosome, called homologous chromosomes, helps increase both the variety and stability of a species. While each homologous chromosome carries the same genes, … - Homologous Recombination
Lastly, homologous chromosomes take part in a process known as homologous recombination during the formation of gametes. This process is also known as “crossing over”, because parts of the homologous chromosomes are exchanged when they come into close contact. The chromo…
Homologous Chromosome Examples
- In a Simple Organism
The image below shows a simple organism. This organism is diploid, but only has a 1 pair of chromosomes. These are homologous chromosomes, because they carry the same genes. However, they can carry different alleles of each gene, shown by their internal pattern. This orga… - In Humans
As with the simple hypothetical organism above, humans also have homologous chromosomes. One half of each pair comes from our mother, while the other comes from our father. These chromosomes are carried in the haploid gamete cells, sperm and eggs. When a sperm meets a…