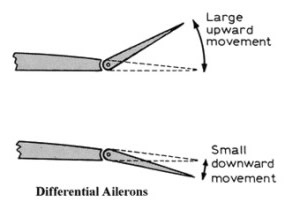
Aileron differential simply means that the ailerons move more in one direction than the other, with the greater deflection being upwards. Ailerons that are set up this way are called differential ailerons. The reason why ailerons are sometimes set up this way is to counteract any adverse yaw when the airplane is in a banked turn.
What is the difference between an aileron and a flap?
What is the difference between flaps and ailerons? Flaps are retractable ‘extensions’ of the wing, that change the angle of the airfoil, allowing for a slower stall speed. Ailerons are wing components controlled directly by the yoke or control stick and lift or lower alternatively to cause the airplane to bank either left or right.
How to setup ailerons?
Videos demonstrating various Flaperon mixes
- Video 1 - Quad Ailerons The first video shows how all four surfaces act as ailerons.
- Video 2 - Flaps This video demonstrates the flaps independently and mixed to the ailerons.
- Video 3 - Quad Flaps This video shows how all four surfaces act as flaps.
- Video 4 - Butterfly Mixing This video demonstrates a Butterfly mix (also called Crow mixing).
What do ailerons do on a plane?
What are the 5 basic parts of an airplane?
- Fuselage. The fuselage is one of the major aircraft components with its long hollow tube that's also known as the body of the airplane, which holds the passengers along with ...
- Wings.
- Empennage.
- Power Plant.
- Landing Gear.
Can variable incidence wings replace ailerons?
Wing tips on opposite wings of an aircraft may be rotated in the same or in opposite directions. The variable incidence wing tip may be raked. The junction between the main wing section and the tip may be non-planar. A morphable structure may be connected between the main wing section and the wing tip.
What is a differential aileron?
Ailerons are a primary flight control surface which control movement about the longitudinal axis of an aircraft. Differential ailerons function in the same manner as symmetrical ailerons except that the upward deflecting aileron is displaced a greater distance than is the downward deflecting aileron.
What is differential aileron control and how does it reduce adverse yaw?
1) Differential Ailerons: One aileron is raised a greater distance than the other aileron is lowered. The extra upward aileron movement produces more drag change than an increase in AOA on the downward aileron. This produces an increase in drag on the descending wing, which reduces adverse yaw.
Does the Cessna 172 have differential ailerons?
In brushing up on general knowledge of the C172, I've seen written many times that the ailerons, whilst described by the AFM as conventional are in fact of both differential and Frise type.
What is the purpose of Frise type aileron?
An arrangement designed to reduce the effect of adverse yaw. The ailerons are so shaped that when the aileron goes down, the complete top surfaces of the main plane and the aileron have a smooth, uninterrupted contour, causing little drag.
What is a Dutch roll in an aircraft?
Description. A Dutch roll is a combination of rolling and yawing oscillations that occurs when the dihedral effects of an aircraft are more powerful than the directional stability. A Dutch roll is usually dynamically stable but it is an objectionable characteristic in an airplane because of its oscillatory nature.
How do you reduce adverse aileron yaw?
1) Differential Ailerons: One aileron is raised a greater distance than the other aileron is lowered. The extra upward aileron movement produces more drag change than an increase in angle of attack (AOA) on the downward aileron. This produces an increase in drag on the descending wing, which reduces adverse yaw.
What type of ailerons are on a Cessna 152?
Flying controls The Cessna 152 is equipped with differential ailerons that move through 20 degrees upwards and 15 degrees downwards. It has single-slotted flaps which are electrically operated and deploy to a maximum of 30 degrees.
How do you pronounce Frise aileron?
0:010:24How to pronounce Frise aileron - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipLuis bourband freese y marrón chris evans louise brown chris evans.MoreLuis bourband freese y marrón chris evans louise brown chris evans.
Which phenomenon is counteracted with differential aileron deflection?
adverse yawDifferential aileron deflection equals the drag of the right and left aileron. Thus differential ailerons counters adverse yaw.
What is Friese aileron?
Definition of Frise aileron : an aileron having a nose portion projecting ahead of the hinge axis and a lower surface in line with the lower surface of the wing.
Did the Wright brothers use ailerons?
The Wright brothers used wing warping instead of ailerons for roll control on their glider in 1902, and about 1904 their Flyer II was the only aircraft of its time able to do a coordinated banked turn.
What is aileron drag?
5) Ailerons Create Induced Drag Just like flaps, when you lower the aileron, you change the chord line of the wing, creating a higher angle of attack (AOA). As AOA and lift increase, induced drag also increases, because the drag created as an aileron is lowered is induced drag.
What is an Aileron differential?
Aileron differential helps keep the model’s tracking straight. YOUR MODEL IS EXPERIENCING ADVERSE YAW IF: The model skids through turns. The tail drops during a turn. The nose swings out of the turn. It’s very difficult to roll your model in a straight line.
Why does the aileron wing panel move up?
The panel with the aileron pointing downward moves up because it creates more lift. The opposite panel goes down (less lift) and causes the model to back toward the up aileron. But here’s the rub! Because of the increased drag caused by the upward motion, that down aileron wing panel also slows down; this causes the model’s nose to yaw in ...
Is aileron differential better than yaw?
Even with high-speed jets and race planes, correcting adverse yaw with aileron differential is much better than relying only on coordinated rudder mixing. If speed is the ultimate goal, then minimizing drag is key. Less rudder deflection equals less drag.
What is differential aileron?
A typical differential aileron operates and functions in a process which is quite identical to that of a symmetrical or traditional aileron except for the part where the aileron which gets deflected upwards is deflected at a greater distance than the one which is deflected in the downward direction.
Which direction does an aileron deflect?
In the meanwhile, the aileron which is deflected in the upwards direction causes an excessive drag as it projects the bottom surface of the aircraft. Therefore, the contour of the aileron surface is itself improved in frise type ailerons.
What is the shape of a Frise ailerons?
The design or the shape of the frise type ailerons is such that when the aileron is bent in the downwards direction, the whole of the upper surface of the main aircraft and the aileron tend to have a no-rough and uninterrupted contour, which ultimately results in having a reduced drag.
What is the purpose of ailerons?
They are typically rectangular in shape with well defined length and made of metal to achieve stability and rigidity. The ailerons function by working in opposite directions, i.e, when one moves in the upward direction the other moves in downward direction. They are generally used to alter the lift on aircraft.
What is the role of ailerons in airplanes?
Ailerons can be used to either increase or decrease the lift, which happens as they are deflected from the center line of the wing. As a result, the ailerons contribute in tilting the aircraft either left or to the right.
Why does an airplane tilt in the upward direction?
The aircraft tilts towards the aileron which is tilted in the upward direction, as a result of the force build up on the wing pointing down. During the flight, the wings' ailerons do not deflect with the same magnitude, the directions are opposite and the displacement of the ailerons also is unequal. This contributes to the fact that the nose of ...
What is an aileron?
An aileron and roll trim tab of a light aircraft. An aileron (French for "little wing" or "fin") is a hinged flight control surface usually forming part of the trailing edge of each wing of a fixed-wing aircraft. Ailerons are used in pairs to control the aircraft in roll (or movement around the aircraft's longitudinal axis ), ...
How do ailerons work?
Pairs of ailerons are typically interconnected so that when one is moved downward, the other is moved upward: the down-going aileron increases the lift on its wing while the up-going aileron reduces the lift on its wing, producing a rolling (also called 'banking') moment about the aircraft's longitudinal axis (which extends from the nose to the tail of an airplane). Ailerons are usually situated near the wing tip, but may sometimes also be situated nearer the wing root. Modern airliners may also have a second pair of ailerons on their wings, with the two positions distinguished by the terms 'outboard aileron' and 'inboard aileron'.
What is the effect of aileron on an aircraft?
An unwanted side effect of aileron operation is adverse yaw —a yawing moment in the opposite direction to the roll. Using the ailerons to roll an aircraft to the right produces a yawing motion to the left. As the aircraft rolls, adverse yaw is caused partly by the change in drag between the left and right wing.
Why did the Frise ailerons have a pivoted shape?
Engineer Leslie George Frise (1897–1979) of the Bristol Aeroplane Company developed an aileron shape that is pivoted at about its 25 to 30% chord line and near its bottom surface [1], in order to decrease stick forces as aircraft became faster during the 1930s.
What is an aileron fence?
Some aileron designs, particularly when fitted on swept wings, include fences like wing fences flush with their inboard plane, in order to suppress some of the spanwise component of the airflow running on the top of the wing, which tends to disrupt the laminar flow above the aileron, when deflected downwards.
Why are ailerons used?
Ailerons are used in pairs to control the aircraft in roll (or movement around the aircraft's longitudinal axis ), which normally results in a change in flight path due to the tilting of the lift vector. Movement around this axis is called 'rolling' or 'banking'. Considerable controversy exists over credit for the invention of the aileron.
What is the meaning of the word "aileron"?
Boulton's 1864 paper, "On Aërial Locomotion" describing several designs including ailerons. The name "aileron", from French, meaning "little wing", also refers to the extremities of a bird's wings used to control their flight.
Plain Aileron
The earliest form of aileron is a simple surface hinged directly to the leading edge of the movable surface. This is called a “plain aileron” and it remains in common use today.
Aerodynamically Balanced Aileron
As airplanes developed, hinge moments became a serious design issue. Airplanes got bigger and faster, and reached the point where stick forces required to control the airplane using simple plain-flap control surfaces directly moved by the pilot’s strength became too high for a single pilot to comfortably handle.
Frise Aileron
The first type of balanced aileron was invented in Britain by Leslie George Frise and is accordingly named after its creator.
Simple Offset Hinge
The second concept is a simple offset hinge aileron. The primary difference between an offset hinge aileron and a Frise aileron is that the hinge of the offset hinge aileron is midway between its upper and lower surface, and the top of the cove is open so that the nose of the aileron can unport on both sides of the wing.