Key Takeaways: Base Definition
- A base is a substance that reacts with an acid in an acid-base reaction.
- The mechanism through which a base works has been argued throughout history. ...
- Examples of bases include hydroxides and soap.
What can one do with a BS in biology?
Your Job Options with a Biology Degree
- Higher Education Lecturer. Biology lectures at a university can find the opportunity to establish a long-term and successful academic career that involves teaching, conducting research and leading research groups.
- Microbiologist. ...
- Nature Conservative Officer. ...
- Pharmacologist. ...
- Physician Associate. ...
- Secondary School Teacher. ...
- Research Scientist. ...
- Soil Scientist. ...
What are acids and bases in biology?
Svante Arrhenius Acids and Bases
- acids produce H + ions in aqueous solutions
- bases produce OH - ions in aqueous solutions
- water required, so only allows for aqueous solutions
- only protic acids are allowed; required to produce hydrogen ions
- only hydroxide bases are allowed
What is the basis of biology?
“If you imagine a cell, you probably picture the colorful diagram in your cell biology textbook, with mitochondria ... Eventually, we might be able to better understand the molecular basis of many diseases by comparing what’s different between healthy ...
Which is the best field in biology?
- Actinobiology: It is a relatively new branch of biology dealing with the effects of the radiation on organisms. ...
- Anthology: It is the branch dealing with the study of flowers. ...
- Pharmacognosy: The branch of science concerned with medicinal plants and leveraging its effect for the benefit of humans. ...
What is a simple definition of a base?
A base is a substance that can neutralize the acid by reacting with hydrogen ions. Most bases are minerals that react with acids to form water and salts. Bases include the oxides, hydroxides and carbonates of metals.
What is a base in biology examples?
Examples of bases are the hydroxides of the alkali and alkaline earth metals (sodium, calcium, etc.) and the water solutions of ammonia or its organic derivatives (amines). Such substances produce hydroxide ions (OH-) in water solutions (see Arrhenius theory).
What is a base in biology pH?
If a solution has a lower concentration of hydronium ions than pure water, it has a pH higher than 7. A solution with a pH higher than 7 is called a base .
What is a base in biology DNA?
Bases are the part of DNA that stores information and gives DNA the ability to encode phenotype, a person's visible traits. Adenine and guanine are purine bases. These are structures composed of a 5-sided and 6-sided ring.
What is base or acid?
An acid is any hydrogen-containing substance that is capable of donating a proton (hydrogen ion) to another substance. A base is a molecule or ion able to accept a hydrogen ion from an acid.
What are 5 examples of bases?
14.3: Bases: Properties and ExamplesBases.Sodium Hydroxide.Potassium Hydroxide.Magnesium Hydroxide.Calcium Hydroxide.Ammonia.Contributions & Attributions.
What is a base in biology quizlet?
base. a compound that produces hydroxide ions (OH-) in solution and measures more than 7 on the pH scale.
What is pH base and acid?
pH is a measure of how acidic/basic water is. The range goes from 0 - 14, with 7 being neutral. pHs of less than 7 indicate acidity, whereas a pH of greater than 7 indicates a base. pH is really a measure of the relative amount of free hydrogen and hydroxyl ions in the water.
Is water a base?
Pure water is neither acidic or basic; it is neutral.
What are acids and bases in biology?
Acids are substances that provide hydrogen ions (H+) and lower pH, whereas bases provide hydroxide ions (OH–) and raise pH. The stronger the acid, the more readily it donates H+. For example, hydrochloric acid and lemon juice are very acidic and readily give up H+ when added to water.
What are bases in RNA?
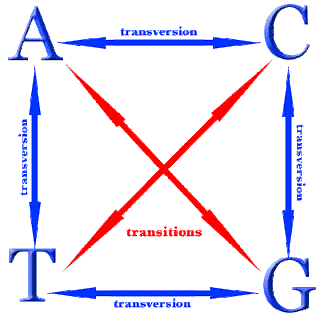
An RNA molecule has a backbone made of alternating phosphate groups and the sugar ribose, rather than the deoxyribose found in DNA. Attached to each sugar is one of four bases: adenine (A), uracil (U), cytosine (C) or guanine (G).
Why are nucleotides called bases?
A nucleotide is the basic building block of nucleic acids (RNA and DNA). A nucleotide consists of a sugar molecule (either ribose in RNA or deoxyribose in DNA) attached to a phosphate group and a nitrogen-containing base. The bases used in DNA are adenine (A), cytosine (C), guanine (G) and thymine (T).
What is the importance of base pairs?
Another important facet of base pairs is that the resultant dimers are of the exact same dimension and occupy the same amount of three-dimensional space. This allows DNA to assume a “steric fit” that ascertains a uniform helical structure throughout.
What is base pair?
Base Pair Definition. Base pairs refer to the sets of hydrogen-linked nucleobases that make up nucleic acids DNA and RNA. They were first described by Dr. Francis Crick and Dr. James Watson who are best known for discovering the helical, “twist around,” structure of DNA (1953). At this time, DNA was also identified as the source ...
What is the bond between thymine and adenine?
Adenine and Thymine form two hydrogen bonds. This is a so called “double bond” that affords a strong link between the pair that is harder to break than a single bond. Again, thymine is only found in DNA. 4.
What are the two groups of the DNA helix?
The sugar and phosphate groups form the hydrophilic outer “backbone” of the DNA helix, while the nitrogenous bases point toward the nonpolar, hydrophobic core. Adenine and guanine belong to a class called “purines,” while cytosine and thymine belong to the “ pyrimidine ” group. These bases adhere together following a set ...
What is the source of material that takes place during cell division?
At this time, DNA was also identified as the source of transferring material that takes place during cell division. In their model, Watson and Crick predicted that the two strands of DNA are able to intertwine with the help of rule-abiding hydrogen bonds.
Why is nitrogenous base important?
This, of course, has the benefit of making DNA a sturdy structure which is so important as it contains our entire genetic code that we need to protect and preserve.
What are the four types of nucleobases?
Taking a step back, our DNA is composed of four types of nucleobases: adenine, thymine, guanine, and cytosine. Nucleotides can be thought of as the biological “building blocks” that create and sustain life. Each contains a nitrogenous base, a sugar ( deoxyribose in DNA), and a phosphate group. The sugar and phosphate groups form ...
What is a base in chemistry?
Updated May 06, 2019. In chemistry, a base is a chemical species that donates electrons, accepts protons, or releases hydroxide (OH-) ions in aqueous solution. Bases display certain characteristic properties that can be used to help identify them.
How does a base work?
Generally, a base either accepts a proton, releases a hydroxide anion when dissolved in water, or donates an electron. Examples of bases include hydroxides and soap.
Why can't superbases remain in aqueous solution?
A superbase cannot remain in aqueous solution because it is a stronger base than the hydroxide ion. An example of a superbase in sodium hydride (NaH).
What color does a base react with?
They react vigorously with acids and organic matter. Bases react in predictable ways with pH indicators. A base turns litmus paper blue, methyl orange yellow, and phenolphthalein pink. Bromothymol blue remains blue in the presence of a base.
What is a strong base?
A strong base completely dissociates into its ions in water or is a compound that can remove a proton (H +) from a very weak acid. Examples of strong bases include sodium hydroxide (NaOH) and potassium hydroxide (KOH). A weak base incompletely dissociates in water.
How do acid and base react?
An acid and a base react with each other in a neutralization reaction. In neutralization, an aqueous acid and aqueous base produce an aqueous solution of salt and water. If the salt is saturated or insoluble, then it may precipitate out of the solution.
What is a neutral base?
A neutral base is one which forms a bond with a neutral acid such that the acid and base share an electron pair from the base. A solid base is active in solid form. Examples include silicon dioxide (SiO 2) and NaOH mounted on alumina. Solid bases may be used in anion exchange resins or for reactions with gaseous acids.
What is the meaning of the term "base"?
What is the meaning of the term ‘Base’? In the field of chemistry, a ‘base’ can be defined as a substance that releases hydroxide ions when dissolved in aqueous media. Typically, basic substances have a bitter taste (especially alkalis) and are slippery to the touch.
What is the pH of a base?
Bases typically have bitter tastes and soapy textures. The pH values of basic solutions are always above 7. Bases react with acids to form salts. Such a chemical reaction is called an acid-base neutralization reaction.
What is a monoacidic base?
A monoacidic base is a base that produces one hydroxide ion when one of its molecules undergoes complete ionization. Examples of such bases include potassium hydroxide and sodium hydroxide. A diacidic base is a base that produces two hydroxide ions when one of its molecules undergoes complete ionization. Examples of such bases include magnesium ...
How do bases reduce hydrogen ion activity in water?
When dissolved in water, bases reduce the hydrogen ion activity in the water by changing the autoionization equilibrium of water ( in which an equilibrium is established between water molecules, positively charged hydronium/hydrogen ions, and negatively charged hydroxide ions).
What are the effects of powerful bases?
Powerful bases are also known to have caustic effects on organic matter. Great care must be taken while handling such substances since accidental spillage on the skin can result in severe burns and permanent damage to the tissue. All basic substances have similar effects on certain chemical indicators.
What is the pH of a solution?
Under standard conditions, the pH value of a basic solution is always greater than 7. Concentrated solutions of relatively strong bases (such as concentrated sodium hydroxide) are known to react with acidic substances in a violent manner. Such substances must, therefore, be stored with caution.
Do bases increase hydroxide?
Bases are known to increase the hydroxide ion activity or reduce the hydronium ion activity when they are dissolved in aqueous media. It is important to note that strong bases can react quite violently with acidic substances and can also cause damage to organic tissues.
What is a Base in Chemistry
In chemistry, a "base" is defined as a molecule in an aqueous solution that can accept protons or donate electrons. They often taste bitter and are slippery to the touch. They are classified using the pH scale, a scale that measures the extent to which a solution is acid, basic, or neutral.
Properties of Bases
Bases have several distinct properties that separate them from acids and solutions with a neutral pH. The following list includes a few examples:
Base Testing
During this lab activity, students will be testing the pH of various substances to determine if they are an acid or a base. To do this lab, you'll need several small cups for samples of the liquids and a pH paper indicator, such as litmus paper. This is available from many scientific or educational suppliers and is relatively inexpensive.
What is the Lewis definition of base?
Lewis definition of base in chemistry defines base as a molecule with a high-energy pair of electrons that can donate a pair of nonbonding electrons to the acids that accept it and form an adduct.
What is a strong base?
A strong base can be defined as a chemical compound that has the capacity to remove a proton from a molecule of even a very weak acid in an acid-base reaction. A strong base is that which has the ability to completely dissociate in an aqueous solution to yield one or more hydroxide ions per molecule of the base. A strong base reacts with strong acid to form stable compounds.
What is the Arrhenius base?
Arrhenius base definition, chemistry defines base as a substance that gets dissociated in an aqueous solution to form hydroxide ions OH ̄. These hydroxide ions react with hydrogen ions to form water in an acid-base solution.
What are the three bases?
The word base has three different definitions in chemistry, and they are Arrhenius base, Bronsted base, and Lewis base. All the base definitions agree to the fact that bases react with acids.
What is a bronsted base?
Bronsted base definition, chemistry defines base as a substance that can accept the hydrogen cations or protons. According to Bronsted, these substances that accept cations do not contain hydroxide ions, but they still react with water in order to increase the number of hydroxide ions.
What is a weak base?
A weak base can be defined as a chemical compound that does not fully dissociate in an aqueous solution , or it can be said that the protonation in a weak base is always incomplete. When a weak base is added to an aqueous solution, it does not ionise entirely as a result of which the aqueous solution still contains a large number of undissociated molecules of the base. Now below, we will list some weak base examples.
What is the basic work of alkalis?
All alkalis are bases, but all bases are not alkalis, only the bases that dissolve in water are known as alkalis. The main work of a base is to neutralize an acid, but an alkali not only neutralizes the acids, but it also produces hydroxide ions. Alkalis are usually called the subset of bases. Bases never completely dissolve in water, but alkalis completely dissociate in water to produce hydroxide ions OH⁻.