What is a Baro-VNAV system?
A Baro-VNAV is an RNAV system which uses the aircraft altimeter to compute and display a vertical guidance path. The path is either geometric between two waypoints, or based on an angle from a single waypoint. Baro-VNAV procedures include a minimum and maximum temperature limitation.
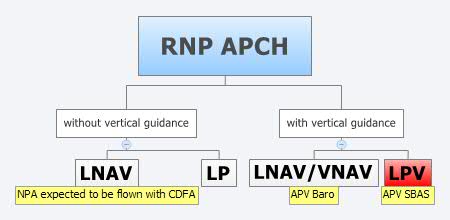
What is the difference between an LNAV and a VNAV approach?
LNAV/VNAV approaches provide both horizontal and approved vertical approach guidance. Vertical Navigation (VNAV) utilizes an internally generated glideslope based on WAAS or baro-VNAV systems. Minimums are published as a DA.
What is baro-aided GPS?
Baro-aided GPS allowed the aircraft to receive vertical guidance from a non-satellite navigation source like the pitot-static system. They will have slightly higher minimums, but they still use a DA. Now the CDI sensitivity for this approach – it remains the same for each segment depending on what mode you’re in.
How is the VNAV path of an aircraft computed?
The VNAV path is computed using aircraft performance, approach constraints, weather data, and aircraft weight. The approach path is computed from the top of descent point to the end of descent waypoint, which is typically the runway or missed approach point.
What is RNP approach with Baro-VNAV?
RNP APCH to LNAV/VNAV is a vertically guided approach that can be flown by modern aircraft with VNAV functionality using barometric inputs. Most Boeing and Airbus aircraft have this capability meaning that a large part of the commercial air transport (CAT) fleet is equipped.
What is the purpose of Baro aiding?
Barometric Aiding (Baro-Aiding) Barometric aiding is an integrity augmentation that allows a GPS system to use a non-satellite input source (e.g. the aircraft pitot-static system) to provide vertical reference and reduces the number of required satellites from five to four.
In what circumstances would a Baro-VNAV approach not be authorized?
In what circumstances would a baro-VNAV approach not be authorized? In areas of hazardous terrain or when a remote altimeter setting is required.
What is APV Baro-VNAV?
1 APV/baro-VNAV procedures are to be used by aircraft equipped with flight management systems (FMS) or other RNAV or RNP systems capable of calculating barometric VNAV paths and, based on these, display deviations on the instrument visual indicator.
Can you fly LNAV VNAV without WAAS?
Pilots may use a WAAS-enabled GPS for LNAV, but WAAS is not mandatory. Vertical guidance is not provided.
Does Cirrus have Baro-VNAV?
Bookmark this question. Show activity on this post. On Cirrus' 2015 aircraft page, they advertise Baro-VNAV capability in the new model.
Are ILS approaches going away?
The FAA will likely cut 200-plus ILS approaches over the next five years. After more than 80 years of robust service, it's the beginning of the end for ILS.
What is the difference between IAF and if?
IF is the Initial Fix leg that starts the approach (or transition). IAF is the Initial Approach Fix. This is a waypoint or navaid.
Can you fly a VOR approach with GPS?
The AIM prohibits you from using GPS (even if it's IFR approach approved) as the sole source of navigation on a VOR approach - one that doesn't say "or GPS" in the title. But, it does allow you to use GPS for navigation, as long as you tune and monitor your position for final course alignment using VOR indications.
Do airline pilots use VNAV?
Pilots generally use the VNAV function during the climb and cruise phases of flight. In a survey of 203 pilots at a major U.S. airline, McCrobie et al., (1997) found that 73% of pilots used VNAV in climb phase, while only 20% used the function in descent and 5% use the function in approach.
What does APV mean in aviation?
APV – Approach Procedure with Vertical guidance. This term is used for RNP APCH operations that include vertical. guidance. That is, those flown to LNAV/VNAV or LPV minima.
What is a RNAV GNSS approach?
Non-precision GNSS (RNAV Approaches) Non-precision GNSS approaches are those that rely upon satellite navigation to provide the required accuracy for approaches without vertical guidance. In effect there are 2 types of approaches defined by ICAO's PBN Concept that conform to this.
What is Baro VNAV?
A Baro-VNAV is an RNAV system which uses the aircraft altimeter to compute and display a vertical guidance path. The path is either geometric between two waypoints, or based on an angle from a single waypoint. Baro-VNAV procedures include a minimum and maximum temperature limitation. Otherwise, temperature compensations must be used.
What aircraft are approved for LNAV?
Aircraft approved for LNAV/VNAV minimums include the Boeing 737NG, 767, 777, the Airbus A300 and some ATRs.
What is baro VNAV?
Baro-VNAV is an RNAV system which uses barometric altitude information from the aircraft’s altimeter to compute vertical guidance for the pilot . The specified vertical path is typically computed between two waypoints or an angle from a single way point. When using baro-VNAV guidance, the pilots should check for any temperature limitations which may result in approach restrictions. See AIM 5-4-5.. . .It is the pilot’s responsibility to use the barometric altimeter to ensure compliance with altitude restrictions for all approach operations.
What is LPV approach?
LPV approaches take advantage of the refined accuracy of WAAS lateral and vertical guidance to provide an approach very similar to a Category I ILS. Like an ILS, an LPV has vertical guidance and is flown to a Decision Altitude (DA). The design of an LPV approach incorporates angular guidance with increasing sensitivity as an aircraft gets closer to the runway (or point in space (PinS) type approaches for helicopters). Sensitivities are nearly identical to those of the ILS at similar distances. This is intentional to aid pilots in transferring their ILS flying skills to LPV approaches.
What is Baro Aided GPS?
Baro-aided GPS allowed the aircraft to receive vertical guidance from a non-satellite navigation source like the pitot-static system. They will have slightly higher minimums, but they still use a DA. Now the CDI sensitivity for this approach – it remains the same for each segment depending on what mode you’re in.
What is LPV in WAAS?
This is only available for WAAS aircraft. The LPV is the most precise because that CDI needle becomes more sensitive the closer you get to the runway. LPV will allow the lowest minimums – it’s close to 200 feet – and it also comes with a DA not an MDA.
How to know if you are in GPS approach mode?
When flying a GPS approach, make sure your approach mode is armed and sequencing. You will see in the center of your HSI the words ‘en route’, ‘terminal’ or ‘approach’. Once you’re in approach mode you will see the type of approach that is available to you, such as LPV or LNAV/VNAV or LNAV.