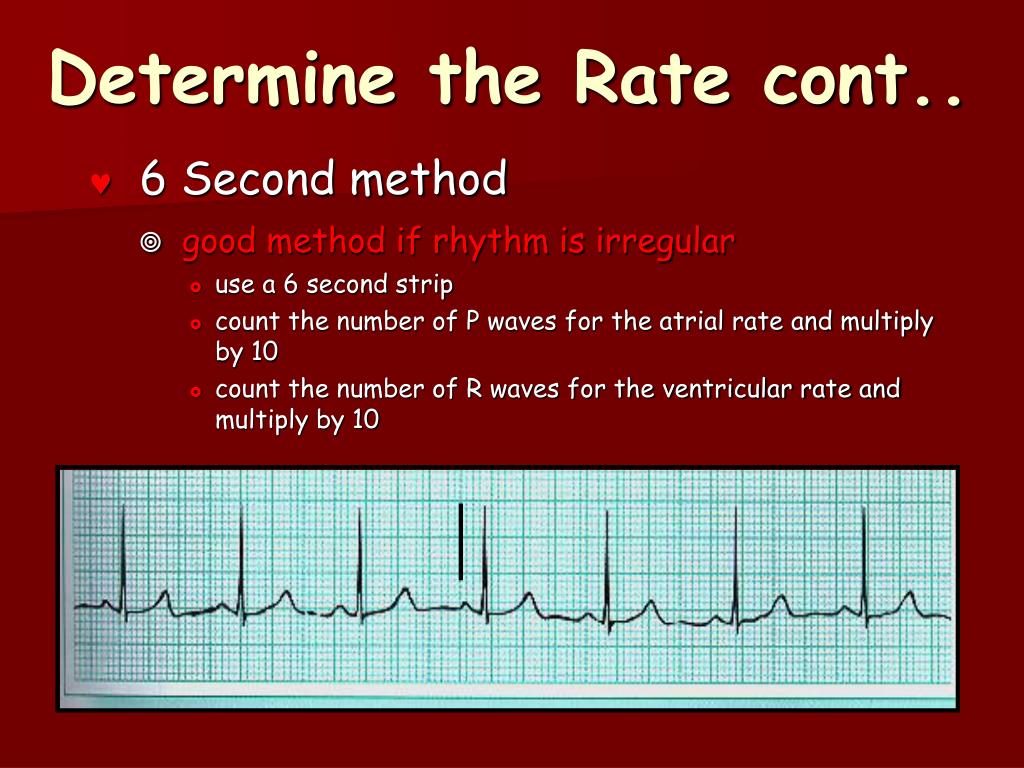
Attain a 6 second EKG strip (30 large boxes) and multiply the number of p-waves in the six second strip by 10 to determine the number of atrial beats in one minute. To determine the number of ventricular contraction multiply the number of r-waves in the 6 second EKG strip by 10.
What is a 6 second EKG strip?
An EKG or ECG stands for Electrocardiography, which is the electrical activity of the heart traced on paper (or a monitor). A rhythm strip is at least a 6-second tracing printed out on graph paper which shows activity from one or two leads. Leads are “views” of the heart.
How to read an EKG strip?
When assessing a QRS complex, you need to pay attention to the following characteristics:
- Width
- Height
- Morphology
How do you read an EKG?
- Ekg Interpretation, And For Further Reading, The Dubin Textbook Is The Introductory Book Of Choice.
- The Use Of Words Such As “Unstable” Or “Unusual” When Describing Vfas Can Further Complicate The Diagnosis.
- If Playback Doesn't Begin Shortly, Try Restarting Your Device.
- How Do You Read An Ekg Strip?
- How Many Seconds Is An Ekg Strip?
What is an EKG rhythm strip?
The ECG Rhythm Strip Interpretation
- Is the rhythm regular? Is every R-R interval equal?
- What’s the rate? This is usually printed for you
- P wave: Are there P waves before every QRS?
- PR interval: Is it wide >200ms?
- QRS: Is the QRS narrow or wide (>100-120ms)?
- T waves: Are the T waves upright and normal-appearing?
How can you tell if its a 6 second strip?
34 second clip suggested5:29How to Count the Heart Rate on EKG strip 6 (six) Second Rule - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipSo 30 large squares equals six seconds because five small squares equals zero point two zero secondsMoreSo 30 large squares equals six seconds because five small squares equals zero point two zero seconds. So when you add up all these large squares thirty of them you get your six seconds.
How do you do 6 second method on ECG?
ECG RateThe Cardiac Ruler or Sequence Method: Count the number of big boxes between R waves and count using the following numbers: 300-150-100-75-60-50. ... The Six Second Method: Get 6 seconds of ECG tracing (i.e. 30 big boxes) and count the number of R waves that appear within that 6 second period and multiply by 10.More items...
How many big boxes are in a 6 second ECG strip?
These QRS complexes are exactly three large boxes apart; therefore, the ventricular heart rate is 100 bpm. Now, multiply the number of QRS complexes on this strip by six.
How many seconds are in a cardiac strip?
First, the standard 12-lead ECG is a 10-second strip. The bottom one or two lines will be a full “rhythm strip” of a specific lead, spanning the whole 10 seconds of the ECG. Other leads will span only about 2.5 seconds. Each ECG is divided by large boxes and small boxes to help measure times and distances.
What is the heart rate in sinus tachycardia?
Normal sinus rhythm typically results in a heart rate of 60 to 100 beats per minute. Sometimes, these electrical impulses are sent out faster than normal, causing sinus tachycardia, which often results in a heart rate of over 100 beats per minute.
How many seconds is each box on ECG?
The ECG paper speed is ordinarily 25 mm/sec. As a result, each 1 mm (small) horizontal box corresponds to 0.04 sec (40 ms), with heavier lines forming larger boxes that include five small boxes and hence represent 0.20 sec (200 ms) intervals.21-Oct-2021
What is the 6 second method?
The second method can be used with an irregular rhythm to estimate the rate. Count the number of R waves in a 6 second strip and multiply by 10. For example, if there are 7 R waves in a 6 second strip, the heart rate is 70 (7x10=70).
What is a normal ECG reading?
The normal range of the ECG differed between men and women: heart rate 49 to 100 bpm vs. 55 to 108 bpm, P wave duration 81 to 130 ms vs. 84 to 130 ms, PR interval 119 to 210 ms vs. 120 to 202 ms, QRS duration 74 to 110 ms vs.
What causes AFib RVR?
Rapid ventricular rate or response (RVR) AFib is caused by abnormal electrical impulses in the atria, which are the upper chambers of the heart. These chambers fibrillate, or quiver, rapidly. The result is a rapid and irregular pumping of blood through the heart.
How are ECG strips measured?
60 second clip suggested4:43How to Measure a PR Interval on EKG Strip | How to Interpret EKGsYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipSo when you measure the PR interval you're going to start at the beginning of the P way which isMoreSo when you measure the PR interval you're going to start at the beginning of the P way which is represented by this line here. And you're going to stop at the beginning of where the QRS.
How do you read an ECG strip?
58 second clip suggested12:24EKG/ECG Interpretation (Basic) : Easy and Simple! - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipFirst up we have to identify an exam with the p-waves measure. The PR interval measure. That you areMoreFirst up we have to identify an exam with the p-waves measure. The PR interval measure. That you are as complex identify the rhythm determine. The heart rate. And interpret your strip.
What is ECG strip?
This test records the electrical activity of the heart. Changes can indicate such things as heart damage, decreased blood flow, and irritability of the heart muscle. For this test you will be lying on your back while electrodes are applied to your chest, arms and legs.
How many leads are in a rhythm strip?
A rhythm strip is at least a 6-second tracing printed out on graph paper which shows activity from one or two leads. Leads are “views” of the heart. There are 12 leads that are traditionally obtained with a 12-lead EKG, but most portable and bedside monitors only monitor 3-5 leads at a time. Luckily – interpreting a single rhythm strip is much ...
What is a 12-lead EKG?
A 12-lead EKG also looks at the rate and rhythm, but additionally gives nearly a complete 360° view of the heart.
What does QRS mean in lead?
In lead II, usually all three waves are present. This includes an initial downward deflection (Q wave), an upward deflection (R wave), followed by a downward deflection (S wave). The presence of a QRS complex indicates that the ventricles are receiving the electrical signal.
What is a heart block?
Heart blocks are when there is significant delay or blockage in transmitting the signal from the atria to the ventricles. This is usually associated with a junctional or ventricular escape rhythm.
How many waves are in the QRS complex?
In a healthy heart – this should correlate with the pulse. The QRS complex is actually made up of 1-3 waves, the Q wave, the R wave, and the S wave. Depending on which lead you look at and the specific heart, any combination of these waves may be present. In lead II, usually all three waves are present.
What is an inverted P wave?
An inverted P wave means there is anterograde conduction to the atria (backwards direction). This means the electrical impulse originates from near, at, or below the AV node. Examples of this include Junctional rhythm, certain PACs, and PJCs.
How fast is SVT?
SVT can be as “slow” as 140bpm to as fast as 220bpm. The faster the heart rate, the more symptomatic the patient usually is. In SVT, P waves are usually not present, there is usually ST depression, and the rhythm is regular with narrow QRS complexes.