Intuitively, the slope of the budget constraint represents how many of the goods on the y-axis the consumer must give up in order to be able to afford one more of the goods on the x-axis. Sometimes, rather than limiting the universe to just two goods, economists write the budget constraint in terms of one good and an "All Other Goods" basket.
What is the slope of the budget constraint?
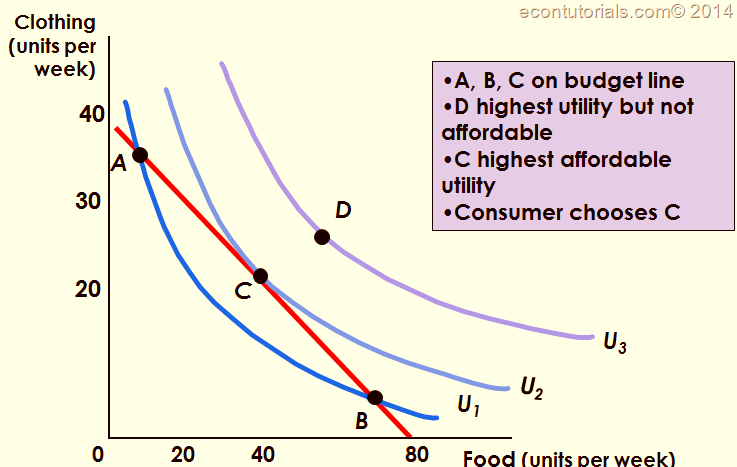
From the graph of the budget constraint in section 3.1, we can see that the budget line slopes downward and has a constant slope along its entire length. This makes intuitive sense: If you buy more of one good, you are going to have to buy less of the other good.
What is beyond the budget constraint line on the graph?
Meanwhile, all the points beyond the budget constraint line on the graph above are the amounts of purchases that the consumer can’t afford. The concept of budget constraint doesn’t account for sunk costs.
What is the slope of the x-axis budget constraint?
It’s saying that the price of the good on the x-axis multiplied by that same good’s quantity, plus the price of the good on the y-axis multiplied by its own quantity, is equal to income. Additionally, the budget constraint’s slope is the negative of the of the x-axis good’s price divided by the y-axis good’s price.
What is the inequality of the budget constraint?
Note the inequality: This equation states that the consumer cannot spend more than his income but can spend less. We can simplify this assumption by restricting the consumer to spending all of his income on the two goods. This will allow us to focus on the frontier of the budget constraint.
What does slope of budget constraint tell us?
Intuitively, the slope of the budget constraint represents how many of the goods on the y-axis the consumer must give up in order to be able to afford one more of the goods on the x-axis.
What does a steeper budget constraint mean?
Price Change The slope of the budget line depends on the relationship between the prices of the two goods. For example, if product X is on the horizontal axis, the line will become steeper when product X becomes cheaper or product Y becomes more expensive.
What is the slope of the budget line and why?
The slope of the budget line is the is the ratio of the prices of good 1 and good 2. This would mean price of good on the x axis divided price of goods on the y axis. The slope of a budget line is always negative as it is downward sloping.
What does the slope of Hillary's budget constraint represent?
The slope of a budget constraint represents: the opportunity cost of one good in terms of another.
What is slope of the budget line?
Slope of budget line shows the rate at which market price allows the consumer to substitute Good-X for Good-Y. It is expressed as Px/Py.
Why is budget line downward sloping?
Budget line is a downward sloping line because given the prices of goods X and Y, and income of the consumer, more of Good-X (on X-axis) can be purchased only when less of Good-Y (on Y-axis) is purchased.
How does the slope of a budget line illustrate opportunity costs and trade offs?
A) Budget lines are always sloped downward. This downward slope shows an inverse relationship between the two goods, meaning that as you increase one, the other must decrease. This decrease is what you are giving up, or opportunity cost, of the good you are getting more of.
What does a budget constraint show?
In a budget constraint, the quantity of one good is measured on the horizontal axis and the quantity of the other good is measured on the vertical axis. The budget constraint shows the various combinations of the two goods that the consumer can afford.
What does the slope of the indifference curve represent?
The slope of the indifference curve is known as the MRS. The MRS is the rate at which the consumer is willing to give up one good for another. If the consumer values apples, for example, the consumer will be slower to give them up for oranges, and the slope will reflect this rate of substitution.
Does the change in income affect the slope of the budget line explain?
In case of budget line, slope = PX/PY As change in income does not disturb the price ratio of the two commodities, the slope will not change and the budget line, after change in income will remain parallel to the original budget line.The Budget Line | Set, Slope and Shift | Microeconomicshttps://www.yourarticlelibrary.com › economics › the-bud...https://www.yourarticlelibrary.com › economics › the-bud...Search for: Does the change in income affect the slope of the budget line explain?
How does the budget constraint affect consumer choices?
The budget constraint framework suggest that when income or price changes, a range of responses are possible. When income rises, households will demand a higher quantity of normal goods, but a lower quantity of inferior goods.6.2 How Changes in Income and Prices Affect Consumption Choiceshttps://opentextbc.ca › principlesofeconomics › chapterhttps://opentextbc.ca › principlesofeconomics › chapterSearch for: How does the budget constraint affect consumer choices?
What is the slope of Marie's budget constraint?
The slope of the budget constraint is -3.Draw Marie's budget constraint with pies on the horizontal axis and ...https://www.numerade.com › ask › question › draw-marie...https://www.numerade.com › ask › question › draw-marie...Search for: What is the slope of Marie's budget constraint?
Why is the budget constraint called a constraint?
The budget constraint is governed by income on the one hand, how much money a consumer has available to spend on consumption, and the prices of the goods the consumer purchases on the other. Exploring the Policy Question.
What is LO1 in economics?
LO1: Define a budget constraint, conceptually, mathematically, and graphically. The budget constraint is the set of all the bundles a consumer can afford given that consumer’s income. We assume that the consumer has a budget – an amount of money available to spend on bundles.
What is budget constraint?
Updated August 02, 2019. The budget constraint is the first piece of the utility maximization framework —or how consumers get the most value out of their money— and it describes all of the combinations of goods and services that the consumer can afford.
What is the point between the budget constraint and the origin?
Therefore, points between the budget constraint and the origin are points where the consumer is not spending all of their income (i.e. is spending less than their income) and points farther from the origin than the budget constraint are unaffordable to the consumer.
Can budget constraints be written in the form above?
In general, budget constraints can be written in the form above unless they have special conditions such as volume discounts, rebates, etc. The above formulation states that the price of the good on the x-axis times the quantity of the good on the x-axis plus the price of the good on the y-axis times the quantity of the good on ...
What is a budget constraint?
Budget Constraint Definition. When consumers’ income limits their consumption behaviors, this is known as a budget constraint. In other words, it’s all of the many combinations of goods/services that consumers are able to purchase in light of their particular income as well as the current prices of these particular goods/services.
Is sunk cost factored into budget constraint?
Sunk costs aren’t Factored into Budget Constraint. The concept of budget constraint doesn’t account for sunk costs. Sunk costs are costs already received in the past that can’t be changed in the present.
What is a budget constraint?
A budget constraint is an economic term referring to the combined amount of items you can afford within the amount of income available to you. For example, if you are a sales professional with a $1,000 budget for promotional items, this sets the upper limit on items you can purchase.
How do budget constraints work?
When calculating budget constraints, you normally have a number of things under consideration for which you are trying to budget. However, it's easier to understand how budget constraints work if you just consider two sets of items. You could spend your entire budget on item one, or you could spend it all on item two.
Budget constraint equation
You can use the following equation to help calculate budget constraint:
What is opportunity cost?
Opportunity cost is the term economists give to the amount of money you've allocated to one item in preference to other items. For example, if you spend $50 on a gift for a friend, that $50 represents the opportunity cost.
What is sunk cost?
Sunk costs refer to costs that you incurred in the past that you can't recover. These costs may be financial or in terms of time or labor. For example, if you buy a ticket to see a two-hour movie and walk out after 10 minutes because you don't like the movie, the money you spent on the movie ticket would be a sunk cost.
Example 1
Jo has a budget of $20 per week with which to buy bread and orange juice. At Jo's local grocery store, a loaf of bread costs $2 and a bottle of orange juice costs $4. If Jo spent $20 only on bread, she could buy 10 loaves. You can express this using the budget constraint equation: