Nutrition in Paramecium
- Feeding apparatus. Feeding apparatus of paramecium is structurally found as an oral groove on one side of the body. ...
- Mechanism of feeding. During feeding, the cilia of the oral groove beat more strongly than other cilia of body. ...
- Formation of food Vacuole. ...
- Digestion and Assimilation. ...
- Respiration and Excretion. ...
What is the function of contractile vacuole in Paramecium?
Apr 11, 2020 · Paramecium contain an oral groove, which is a channel near the mouth of the paramecium that contains cilia, and it helps to direct food to the mouth. Popular Trending
How does Paramecium move around?
The cilia, which stick out from the Paramecium's outer coat of firm protein, known as the pellicle, don't settle for just locomotion in their job descriptions. As they sway like vibrating feathers all along the edge of the organism, the cilia sweep food particles into the paramecium's oral …
What is binary fission in Paramecium?
Similarly, what is the function of oral groove in paramecium? The paramecium uses its cilia to sweep the food along with some water into the cell mouth after it falls into the oral groove. The food goes through the cell mouth into the gullet. When there is enough food in it so that it has …
What are the functions of the Paramecium parts?
Mar 09, 2020 · At the midpoint, there is an oral groove on the ventral side known as the vestibule. Food is drawn inside the cell due to coordinated movement of cilia; The oral groove opens in …
See more
Aug 27, 2009 · What is the function of an oral grove? an oral groove specially the one found in Paramecium serves as their "mouth" its where their to-be-ingested food enters. an oral groove …
What is the function of paramecium Oral Groove?
What does an oral groove do?
How does the Oral Groove help the paramecium survive?
What are the functions of the parts of paramecium?
What is the function of the oral groove in some protozoa quizlet?
Does paramecium have an oral groove?
What is the function of cytoplasm in paramecium?
How do the structures of the paramecium help it survive?
What organelles are visible inside the paramecium and what are their functions?
What is the organelle of movement in paramecium?
What organelles are in paramecium?
Does paramecium have membrane bound organelles?
What is the groove in the paramecium?
Paramecium contain an oral groove, which is a channel near the mouth of the paramecium that contains cilia, and it helps to direct food to the mouth.
How does the paramecium sweep food?
The paramecium uses its cilia to sweep the food along with some water into the cell mouth after it falls into the oral groove. The food goes through the cell mouth into the gullet. When there is enough food in it so that it has reached a certain size it breaks away and forms a food vacuole.
Where does Paramecium live?
Paramecium live in aquatic environments, usually in stagnant, warm water. The species Paramecium bursaria forms symbiotic relationships with green algae. The algae live in its cytoplasm. Algal photosynthesis provides a food source for Paramecium.
How does paramecium reproduce?
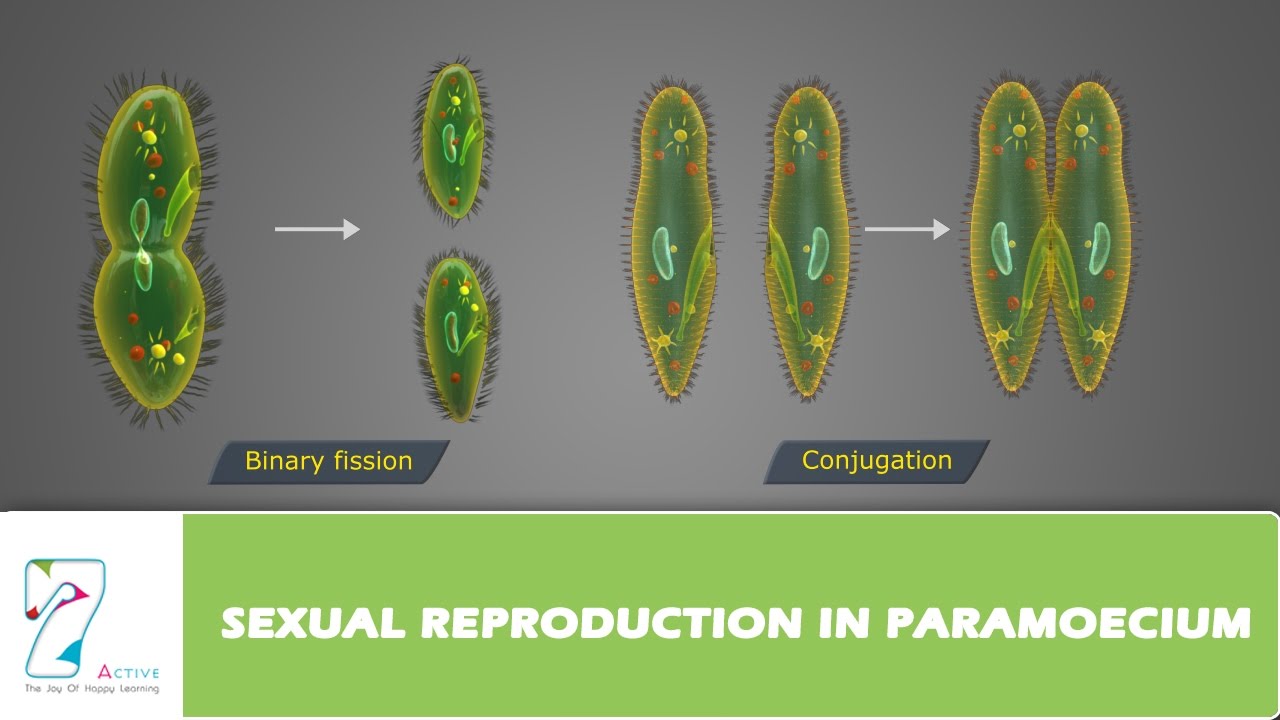
Paramecium Reproduction. Asexual Reproduction in paramecium is by binary fission. The mature cell divides into two cells and each grows rapidly and develops into a new organism. Under favourable conditions, Paramecium multiplies rapidly up to three times a day .
Where is the oral groove located?
The oral groove opens in the mouth known as cytostome and to the gullet or pharynx. There are numerous food vacuoles present for digesting food. There is an anal pore present on the ventral surface in the posterior half of the cell known as cytoproct or cytopyge, which helps in egesting undigested food.
What is the process of conjugation?
In the process of conjugation, the conjugation bridge is formed and united paramecia are known as conjugants. Macronuclei of both the cells disappear. The micronucleus of each conjugant forms 4 haploid nuclei by meiosis. Three of the nuclei degenerate. The haploid nuclei of each conjugant then fuse together to form diploid micronuclei and cross-fertilization takes place. The conjugants separate to form exconjugants. They are identical, but different from the earlier cells. Each exconjugate undergoes further division and forms 4 daughter Paramecia. Micronuclei form a new macronucleus.
How many cycles of fission does a paramecia undergo?
Paramecium rejuvenates and a new macronucleus is formed. A Paramecia undergoes ageing and dies after 100-200 cycles of fission if they do not undergo conjugation. The macronucleus is responsible for clonal ageing.
How many nuclei are in Paramecia?
Paramecia contain at least two nuclei, micronuclei (one or more) and one macronucleus. Micronuclei have diploid chromosomes and take part in the reproduction. Macronuclei regulate all vital metabolic activities and growth. The macronucleus has multiple copies of the genome, i.e. polyploid.
What is the relationship between paramecium and green algae?
Some of the Paramecium species, e.g. Paramecium bursaria, etc. form a symbiotic relationship with green algae. Algae are present as an endosymbiont and provide food to paramecium by photosynthesis, in turn, the algae get a safe and protective habitat.
What kingdom is Paramecium in?
Paramecium Classification. Paramecium is unicellular and eukaryotic, so they are kept in the kingdom Protista. They are ciliated protozoan and come under phylum Ciliophora. The common species of Paramecium include: Paramecium aurelia. Paramecium caudatum. Paramecium woodruffi. Paramecium trichium. Domain.
What is the power of paramecium?
Paramecium is powered by a dual-core CPU – Macronucleus and Micronucleus. The most unusual characteristic of paramecia is their nuclei. They have two types of nuclei, which differ in their shape, content and function. [In this figure] Macronucleus (MA) and Micronucleus (MI) in a P. putrinum cell.
What is the function of the oral groove?
The oral groove serves as the entrance of food materials into the cell. There are oral cilia covering the surface of the oral groove. These oral cilia beat to create an inbound water current and bring the food into the oral groove. [In this figure] The closer view of paramecium’s feeding system.
What happens when a paramecium swims across an obstacle?
Another interesting behavior is paramecium’s way of escape. If a paramecium comes across an obstacle, the beating of the cilia stops and reverses. This causes the paramecium to swim backward to keep away from the obstacle or the predators.
How fast can a paramecium swim?
For a P. caudatum which is 300 micrometers (µm) in length, it can swim at a rate of 1200 µm per second (equal to 0.0027 miles per hour).
What is the skin of Paramecium called?
The anatomy of paramecium. Paramecium wears a soft armor, called pellicle. Paramecium’s skin is covered by many tiny hairs, called cilia. The microscopic view of cilia. The structure of pellicle and cilia. See how cilia do the wave.
Why do scientists study paramecium cilia?
Scientists spent a lot of time and effort studying paramecium cilia. Why?#N#It is because that cilia are not exclusive in microorganisms, like paramecia or ciliates. In fact, we also have cilia on our cells. For example, motile cilia are found on the respiratory epithelium lining the respiratory tract where they clean our lungs by sweeping mucus and dirt out.#N#Advanced microscopy is powerful in these kinds of cell biology research. For example, the scanning electron microscope (SEM) allows us to see the morphology, orientation, and density of paramecium’s cilia. With a transmission electron microscope (TEM), we can see the ultrastructure of cilia in a transverse section. With the help of antibody-based immunofluorescent staining, scientists can even see what kinds of proteins contribute to the structure, motion, and growth of cilia.
What is the pellicle made of?
Pellicle is made up of a thin, gelatinous substance produced by the cell. The layer of the pellicle gives the paramecium a definite shape and good protection of its cell content. The pellicle is also elastic in nature which allows the paramecium to slightly change its shape.